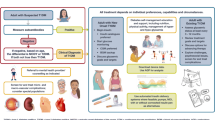
Opinion statement
Patients with chronic pancreatitis should be screening at least annually for diabetes. Lifestyle modifications remain to be an important part of treatment for diabetic control. Unless contraindicated or not tolerated, metformin can be initiated and continued concurrently with other anti-diabetic agents or insulin. All anti-diabetic agents should be used based on their physiology and adverse effect profiles, along with the metabolic status of patients. Insulin therapy should be initiated without delay for any of the following: symptomatic or overt hyperglycemia, catabolic state secondary to uncontrolled diabetes, history of diabetic ketoacidosis, hospitalization or acute exacerbation of pancreatitis, or hyperglycemia that cannot be otherwise controlled. Dose adjustment should be done conservatively as these patients are more likely to be insulin sensitive and have loss of counter regulatory hormones. Insulin pump and continuous glucose monitoring should be considered early during therapy in selected patients. For patients undergoing total pancreatectomy or extensive partial pancreatectomy, evaluations to determine the eligibilities for islet cell autotransplantation should be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- CP:
-
Chronic pancreatitis
- GIP:
-
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide
- GLP:
-
Glucagon-like peptide
- PP:
-
Pancreatic polypeptide
- DKA:
-
Diabetic ketoacidosis
- LKB1-AMPK:
-
Liver kinase B1-adenyl monophosphate protein-activated kinase
- TZD:
-
Thiazolidinedione
- SGLT2:
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2
- TP:
-
Total pancreatectomy
- IAT:
-
Islet cell autotransplantation
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of major importance
Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26 (Suppl 1): S5-20.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2015. Diabetes Care. 2015;38 Suppl 1:S1–93.
Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37 (Suppl 1): S81-90.
Corso G. Secondary forms of diabetes. In: Weir G, Kahn CR, editors. Joslin’s diabetes mellitus. New York: Lea & Febiger; 1994.
Abu-Bakare A et al. Tropical or malnutrition-related diabetes: a real syndrome? Lancet. 1986;1(8490):1135–8.
Barman KK, Premalatha G, Mohan V. Tropical chronic pancreatitis. Postgrad Med J. 2003;79(937):606–15.
Ewald N et al. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012;28(4):338–42.
Rickels MR et al. Detection, evaluation and treatment of diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis: recommendations from PancreasFest 2012. Pancreatology. 2013;13(4):336–42. Official published guideline making recommendations specifically for diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis, including screening, establishing diagnosis, evaluation, treatment and future research directions.
Malka D et al. Risk factors for diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2000;119(5):1324–32.
Wang W et al. Occurrence of and risk factors for diabetes mellitus in Chinese patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2011;40(2):206–12.
Gullo L et al. Diabetic retinopathy in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1990;98(6):1577–81.
Levitt NS et al. The prevalence and severity of microvascular complications in pancreatic diabetes and IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(7):971–4.
Larsen S et al. A comparative study of microvascular complications in patients with secondary and type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 1990;7(9):815–8.
Ziegler O et al. Lower-extremity arterial disease in diabetes mellitus due to chronic pancreatitis. Diabete Metab. 1994;20(6):540–5.
Kornhuber HH et al. The main cause of diabetes (type II): “normal” alcohol drinking]. Versicherungsmedizin. 1990;42(5):132. 134–42.
Choudhuri G, Lakshmi CP, Goel A. Pancreatic diabetes. Trop Gastroenterol. 2009;30(2):71–5.
Schrader H et al. Reduced pancreatic volume and beta-cell area in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(2):513–22.
Cui Y, Andersen DK. Pancreatogenic diabetes: special considerations for management. Pancreatology. 2011;11(3):279–94. Publication with comprehensive discussion about pathophysiology, potential complications and treatment options for chronic pancreatitis-associated diabetes mellitus.
Nealon WH, Townsend Jr CM, Thompson JC. The time course of beta cell dysfunction in chronic ethanol-induced pancreatitis: a prospective analysis. Surgery. 1988;104(6):1074–9.
Sidhu SS, Nundy S, Tandon RK. The effect of the modified puestow procedure on diabetes in patients with tropical chronic pancreatitis—a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(1):107–11.
Kalk WJ et al. Selective loss of beta cell response to glucose in chronic pancreatitis. Horm Metab Res. 1974;6(2):95–8.
Anderson MF et al. Plasma insulin in pancreatic disease. Gut. 1970;11(6):524–31.
Joffe BI et al. Insulin reserve in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Lancet. 1968;2(7574):890–2.
Deckert T et al. Insulin secretion after tolbutamide and after secretin in patients with pancreatic diseases. Acta Med Scand. 1972;192(5):465–70.
Sjoberg RJ, Kidd GS. Pancreatic diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1989;12(10):715–24.
Goldstein JA et al. Reversal of in vitro hepatic insulin resistance in chronic pancreatitis by pancreatic polypeptide in the rat. Surgery. 1989;106(6):1128–32. discussion 1132–3.
Nathan JD et al. Impaired hepatocyte glucose transport protein (GLUT2) internalization in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2001;22(2):172–8.
Bonora E et al. Insulin and C-peptide plasma levels in patients with severe chronic pancreatitis and fasting normoglycemia. Dig Dis Sci. 1988;33(6):732–6.
Nosadini R et al. Insulin sensitivity, binding, and kinetics in pancreatogenic and type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1982;31(4 Pt 1):346–55.
Muggeo M et al. Insulin receptors on circulating blood cells from patients with pancreatogenic diabetes: a comparison with type I diabetes and normal subjects. J Endocrinol Investig. 1987;10(3):311–9.
Cavallini G et al. Diabetes in chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. Role of residual beta cell function and insulin resistance. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38(3):497–501.
Linde J, Nilsson LH, Barany FR. Diabetes and hypoglycemia in chronic pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(3):369–73.
Persson I et al. Pancreatic-glucagon-like immunoreactivity after intravenous insulin in normals and chronic-pancreatitis patients. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1971;67(2):401–4.
Kannan V, Nabarro JD, Cotton PB. Glucagon secretion in chronic pancreatitis. Horm Res. 1979;11(4):203–12.
Aguilar-Parada E, Eisentraut AM, Unger RH. Pancreatic glucagon secretion in normal and diabetic subjects. Am J Med Sci. 1969;257(6):415–9.
Besterman HS et al. Pancreatic and gastrointestinal hormones in chronic pancreatitis. Digestion. 1982;24(3):195–208.
Larsen S et al. The effect of insulin withdrawal on intermediary metabolism in patients with diabetes secondary to chronic pancreatitis. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1991;124(5):510–5.
Larsen S et al. Glucose counterregulation in diabetes secondary to chronic pancreatitis. Metabolism. 1990;39(2):138–43.
Larsen S. Diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis. Dan Med Bull. 1993;40(2):153–62.
Gyr K et al. Circulating somatostatin. Physiological regulator of pancreatic function? J Clin Invest. 1987;79(6):1595–600.
Kloppel G et al. The endocrine pancreas in chronic pancreatitis. Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural studies. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1978;377(2):157–74.
Larsen S et al. Pancreatic hormone secretion in chronic pancreatitis without residual beta-cell function. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1988;118(3):357–64.
Slaff JI, Wolfe MM, Toskes PP. Elevated fasting cholecystokinin levels in pancreatic exocrine impairment: evidence to support feedback regulation. J Lab Clin Med. 1985;105(3):282–5.
Munkgaard S, Kelbaek H, Tronier B. Elevated plasma somatostatin in cirrhosis of the liver. N Engl J Med. 1981;304(23):1429–30.
Hanafusa T et al. Impaired response of human pancreatic polypeptide to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in chronic pancreatitis without diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol Jpn. 1982;29(5):509–15.
Seymour NE et al. Reversal of abnormal glucose production after pancreatic resection by pancreatic polypeptide administration in man. Surgery. 1988;104(2):119–29.
Banerjee A, Onyuksel H. A novel peptide nanomedicine for treatment of pancreatogenic diabetes. Nanomedicine. 2013;9(6):722–8.
Xu G et al. Exendin-4 stimulates both beta-cell replication and neogenesis, resulting in increased beta-cell mass and improved glucose tolerance in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1999;48(12):2270–6.
Gomez-Cerezo J et al. Postprandial glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and insulin responses in patients with chronic pancreatitis with and without secondary diabetes. Regul Pept. 1996;67(3):201–5.
Knop FK et al. Increased postprandial responses of GLP-1 and GIP in patients with chronic pancreatitis and steatorrhea following pancreatic enzyme substitution. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292(1):E324–30.
Hedetoft C et al. Effect of glucagon-like peptide 1(7–36)amide in insulin-treated patients with diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2000;20(1):25–31.
Ewald N et al. Determinants of exocrine pancreatic function as measured by fecal elastase-1 concentrations (FEC) in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur J Med Res. 2009;14(3):118–22.
Vantyghem MC et al. Changes in serum amylase, lipase and leukocyte elastase during diabetic ketoacidosis and poorly controlled diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 1999;36(1–2):39–44.
Ewald N, Hardt PD. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(42):7276–81. Publication proposing a specific criteria and other potential evaluating methods to establish the diagnosis of pancreatogenic diabetes.
Nyboe Andersen B et al. B cell function in patients with chronic pancreatitis and its relation to exocrine pancreatic function. Diabetologia. 1982;23(2):86–9.
Teuscher AU et al. Successful islet autotransplantation in humans: functional insulin secretory reserve as an estimate of surviving islet cell mass. Diabetes. 1998;47(3):324–30.
Bellin MD et al. Total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation: summary of a national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases workshop. Pancreas. 2014;43(8):1163–71.
Bellin MD et al. Total pancreatectomy and islet autotransplantation in chronic pancreatitis: recommendations from PancreasFest. Pancreatology. 2014;14(1):27–35.
Frulloni L et al. Italian consensus guidelines for chronic pancreatitis. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42 Suppl 6:S381–406.
The diabetes control and complications trial (DCCT). Design and methodologic considerations for the feasibility phase. The DCCT research group. Diabetes. 1986; 35(5): 530–45.
Prospective UK. Diabetes study (UKPDS). VIII. Study design, progress and performance. Diabetologia. 1991;34(12):877–90.
Terzin V et al. Improved glycemic control in pancreatic diabetes through intensive conservative insulin therapy. Pancreatology. 2012;12(2):100–3.
Charbonneau A et al. Evidence of hepatic glucagon resistance associated with hepatic steatosis: reversal effect of training. Int J Sports Med. 2005;26(6):432–41.
Lowenfels AB et al. Pancreatitis and the risk of pancreatic cancer. International Pancreatitis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;328(20):1433–7.
Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ et al. Insulin, glucose, insulin resistance, and pancreatic cancer in male smokers. JAMA. 2005;294(22):2872–8.
Maida A et al. Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in mice. Diabetologia. 2011;54(2):339–49.
Zakikhani M et al. Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(21):10269–73.
Shaw RJ. LKB1 and AMP-activated protein kinase control of mTOR signalling and growth. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2009;196(1):65–80.
Kisfalvi K et al. Metformin disrupts crosstalk between G protein-coupled receptor and insulin receptor signaling systems and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Res. 2009;69(16):6539–45.
Schneider MB et al. Prevention of pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters by metformin. Gastroenterology. 2001;120(5):1263–70.
Li D et al. Antidiabetic therapies affect risk of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(2):482–8.
Sadeghi N et al. Metformin use is associated with better survival of diabetic patients with pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(10):2905–12.
Cavaghan MK et al. Treatment with the oral antidiabetic agent troglitazone improves beta cell responses to glucose in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. J Clin Invest. 1997;100(3):530–7.
Dormandy J, Bhattacharya M, van Troostenburg de Bruyn AR. Safety and tolerability of pioglitazone in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes: an overview of data from PROactive. Drug Saf. 2009;32(3):187–202.
Kahn SE et al. Rosiglitazone-associated fractures in type 2 diabetes: an Analysis from a Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial (ADOPT). Diabetes Care. 2008;31(5):845–51.
Meymeh RH, Wooltorton E. Diabetes drug pioglitazone (Actos): risk of fracture. CMAJ. 2007;177(7):723–4.
Matveyenko AV et al. Beneficial endocrine but adverse exocrine effects of sitagliptin in the human islet amyloid polypeptide transgenic rat model of type 2 diabetes: interactions with metformin. Diabetes. 2009;58(7):1604–15.
Singh S et al. Glucagonlike peptide 1-based therapies and risk of hospitalization for acute pancreatitis in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a population-based matched case–control study. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(7):534–9.
Fujita Y, Inagaki N. Renal sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as a novel therapeutic approach to treatment of type 2 diabetes: clinical data and mechanism of action. J Diabetes Investig. 2014;5(3):265–75.
Riser Taylor S, Harris KB. The clinical efficacy and safety of sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacotherapy. 2013;33(9):984–99.
Casneuf VF et al. Expression of SGLT1, Bcl-2 and p53 in primary pancreatic cancer related to survival. Cancer Invest. 2008;26(8):852–9.
Moran A et al. Clinical care guidelines for cystic fibrosis-related diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a clinical practice guideline of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, endorsed by the Pediatric Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(12):2697–708.
Ito T et al. Epidemiological study of pancreatic diabetes in Japan in 2005: a nationwide study. Pancreas. 2010;39(6):829–35.
Russell SJ et al. Outpatient glycemic control with a bionic pancreas in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):313–25.
Trajkovic-Arsic M, Kalideris E, Siveke JT. The role of insulin and IGF system in pancreatic cancer. J Mol Endocrinol. 2013;50(3):R67–74.
Bonelli L et al. Exocrine pancreatic cancer, cigarette smoking, and diabetes mellitus: a case–control study in northern Italy. Pancreas. 2003;27(2):143–9.
Choi EK et al. The long-term follow-up results after steroid treatment in patients with autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006;47(6):440–8.
Tanaka S et al. Corticosteroid-responsive diabetes mellitus associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Lancet. 2000;356(9233):910–1.
Brunicardi FC et al. Pancreatic polypeptide administration improves abnormal glucose metabolism in patients with chronic pancreatitis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(10):3566–72.
Rabiee A et al. Pancreatic polypeptide administration enhances insulin sensitivity and reduces the insulin requirement of patients on insulin pump therapy. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;5(6):1521–8.
Hammel P, Malca D, Levy P, et al. Influence of elective pancreatic surgery on the occurrence of diabetes in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gatroenterology. 1996;110:A396. abstract.
Brand B et al. Prospective evaluation of morphology, function, and quality of life after extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy and endoscopic treatment of chronic calcific pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(12):3428–38.
Adams DB, Ford MC, Anderson MC. Outcome after lateral pancreaticojejunostomy for chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1994;219(5):481–7. discussion 487–9.
Aspelund G et al. Improved outcomes for benign disease with limited pancreatic head resection. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005;9(3):400–9.
Mehrabi A et al. Expanding the indications of pancreas transplantation alone. Pancreas. 2014;43(8):1190–3.
Dong M et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: islet autotransplantation after pancreatectomy for minimizing diabetes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2011;75(6):771–9.
Sutherland DE et al. Total pancreatectomy and islet autotransplantation for chronic pancreatitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;214(4):409–24. discussion 424–6.
Bellin MD et al. Islet autotransplantation to preserve beta cell mass in selected patients with chronic pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus undergoing total pancreatectomy. Pancreas. 2013;42(2):317–21.
Gruessner RW et al. Pancreas allotransplants in patients with a previous total pancreatectomy for chronic pancreatitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;206(3):458–65.
Sato Y et al. Heterotopic pancreas autotransplantation with spleen for uncontrollable hemorrhagic pseudocyst and disabling pain in chronic pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60(123):425–7.
Ricordi C et al. Outcome of human islet isolation and allotransplantation in 20 consecutive cases. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 1992;5 Suppl 1:193–8.
Shalimov A A, et al. [Experience in xenografts of pancreatic islet cell cultures after surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis]. Klin Khir, 1990(11): 1–2.
Rajesh G et al. Diet, nutrient deficiency and chronic pancreatitis. Trop Gastroenterol. 2013;34(2):68–73.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Yu Kuei Lin, Philip C. Johnston, Karla Arce, and Betul A. Hatipoglu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Pancreas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y.K., Johnston, P.C., Arce, K. et al. Chronic Pancreatitis and Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Treat Options Gastro 13, 319–331 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-015-0055-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-015-0055-x