Abstract
Purpose of Review
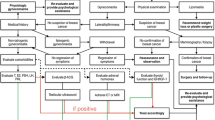
Our aim is to review the steps of diagnosis and management of gynecomastia with a special focus on treatment of gynecomastia associated with androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer.
Recent Findings
Recent studies investigating tamoxifen and radiation therapy for both therapy and prophylaxis of bicalutamide-induced gynecomastia are reviewed.
Summary
Gynecomastia is a common clinical problem, affecting between one and two thirds of middle-aged men. Diagnosis is typically made by history and physical exam. Common causes include chronic medical conditions and medications; however, unexplained gynecomastia should prompt laboratory work-up, followed by appropriate imaging studies to evaluate for hormone producing cancers. For patients taking bicalutamide for treatment of prostate cancer, tamoxifen or radiation therapy for gynecomastia are excellent options.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Sansone A, Romanelli F, Sansone M, Lenzi A, Di Luigi L. Gynecomastia and hormones. Endocrine. 2017;55:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0975-9.
Cuhaci N, Polat S, Evranos B, Ersoy R, Cakir B. Gynecomastia: clinical evaluation and management. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2014;18:150–8. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.129104.
Ordaz D, Thompson J. Gynecomastia and psychological functioning: a review of the literature. Body Image. 2015;15:141–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2015.08.004.
Pusl T, Stoemmer P. Gynecomastia: look beyond the obvious. Am J Med. 2017;130:e439–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.04.021.
Yousef AJ. Male breast cancer: epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Oncol. 2017;44:267–72. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.seminoncol.2017.11.002.
Braunstein GD. Gynecomastia. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1229–37. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp070677.
Doyle S, Steel J, Porter G. Imaging male breast cancer. Clin Radiol. 2011;66:1079–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2011.05.004.
Evans G, Anthony T, Appelbaum AH, Schumpert TD, Levy KR, Amirkhan RH, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of mammography in the evaluation of male breast disease. Am J Surg. 2001;181:96–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9610(00)00571-7.
Bannayan G, Hajdu S. Gynecomastia: clinicopathologic study of 351 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972;57:431–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/57.4.431.
Sinclair M, Grossmann M, Gow PJ, Angus PW. Testosterone in men with advanced liver disease: abnormalities and implications. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30:244–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12695.
Iglesias P, Carrero JJ, Diez JJ. Gonadal dysfunction in men with chronic kidney disease: clinical features, prognostic implications and therapeutic options. J Nephrol. 2012;25:31–42. https://doi.org/10.5301/JN.2011.8481.
Thompson DF, Carter JR. Drug-induced gynecomastia. Pharmacotherapy. 1993;13:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1875-9114.1993.tb02688.x.
• Ali SN, Jayasena CN, Sam AH. Which patients with gynaecomastia require more detailed investigation? Clin Endocrinol. 2018;88:360–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13526. A recent, concise review of the management strategy for patients with gynecomastia and suspected underlying malignancy.
Narula HS, Carlson HE. Gynaecomastia—pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10:684–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2014.139.
Rohrich RJ, Ha RY, Kenkel JM, Adams WP Jr. Classification and management of gynecomastia: defining the role of ultrasound-assisted liposuction. Plastic Reconstr Surg. 2003;111:909–23. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000042146.40379.25.
Hanavadi S, Banerjee D, Monypenny IJ, Mansel RE. The role of tamoxifen in the management of gynaecomastia. Breast. 2006;15:276–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2005.04.007.
Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2014;65:467–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.002.
Davanço RAS, Neto MS, Garcia ÉB, Matsuoka PK, Huijsmans JP, Ferreira LM. Quality of life in the surgical treatment of gynecomastia. Aesthet Plast Surg. 2009;33:514–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9213-z.
• Nguyen P, Alibhai S, Shehzad B, D’Amico A, Kantoff PW, Keating NL, et al. Adverse effects of androgen deprivation therapy and strategies to mitigate them. Eur Urol. 2015;67:825–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.07.010. Up to date review of the clinical effectiveness of available treatment strategies for all side effects of ADT for prostate cancer.
Saltzstein D, Sieber P, Morris T, Gallo J. Prevention and management of bicalutamide-induced gynecomastia and breast pain: randomized endocrinologic and clinical studies with tamoxifen and anastrozole. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2005;8:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500782.
•• Serretta V, Altieri V, Morgia G, Nicolosi F, De Grande G, Mazza R, et al. A randomized trial comparing tamoxifen therapy vs. tamoxifen prophylaxis in bicalutamide-induced gynecomastia. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2012;10:174–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2012.03.002. One hundred seventy-six patients with prostate cancer receiving bicalutamide monotherapy were randomized to receive tamoxifen therapeutically or prophylactically. Four percent of the therapeutic group discontinued bicalutamide due to painful gynecomastia, whereas no patients in the prophylactic group did. The authors conclude that bicalutamide-induced gynecomastia can be prevented to a significant degree by prophylaxis with tamoxifen.
Tunio MA, Al-Asiri M, Al-Amro A, Bayoumi Y, Fareed M. Optimal prophylactic and definitive therapy for bicalutamide-induced gynecomastia: results of a meta-analysis. Curr Oncol. 2012;19:280–8. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.19.993.
Widmark A, Fosså SD, Lundmo P, Damber JE, Vaage S, Damber L, et al. Does prophylactic breast irradiation prevent antiandrogen-induced gynecomastia? Evaluation of 253 patients in the randomized Scandinavian trial SPCG-7/SFUO-3. Urology. 2003;61:145–51. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000069500.65586.e5.
Boccardo F, Rubagotti A, Battaglia M, di Tonno P, Selvaggi FP, Conti G, et al. Evaluation of tamoxifen and anastrozole in the prevention of gynecomastia and breast pain induced by bicalutamide monotherapy of prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.12.013.
•• Wibowo E, Pollock PA, Hollis N, Wassersug RJ. Tamoxifen in men: a review of adverse events. Andrology. 2016;4:776–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12197. Systematic review of adverse events of tamoxifen for men. It is a well-tolerated medication with less than 5% of men discontinue tamoxifen due to side effects.
• Viani GA, Bernardes da Silva LG, Stefano EJ. Prevention of gynecomastia and breast pain caused by androgen deprivation therapy in prostate cancer: tamoxifen or radiotherapy? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:e519–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.01.036. Meta-analysis of 6 trials with 777 patients shows that tamoxifen prophylaxis is about twice as effective (absolute risk reduction of 64%) as radiation prophylaxis (ARR of 30%) in preventing breast pain and gynecomastia. Authors conclude that radiation is an acceptable alternative for patients at high risk of tamoxifen induced cardiac side effects.
Ozen H, Akyol F, Toktas G, Eskicorapci S, Unluer E, Kuyumcuoglu U, et al. Is prophylactic breast radiotherapy necessary in all patients with prostate cancer and gynecomastia and/or breast pain? J Urol. 2010;184:519–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.03.137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Lee Baumgarten declares no potential conflicts of interest. Ali A. Dabaja is a section editor for Current Urology Reports.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Men's Health
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumgarten, L., Dabaja, A.A. Diagnosis and Management of Gynecomastia for Urologists. Curr Urol Rep 19, 46 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-018-0796-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-018-0796-x