Abstract
Purpose of Review
For 30 years, ultrasound has been investigated as a means to evaluate salivary gland abnormalities in patients with autoimmune disease. We aim to review the test characteristics of ultrasound for diagnosing Sjögren’s syndrome, the scoring systems used for this purpose, and the ultrasound similarities and differences between Sjögren’s syndrome and some of its potential salivary gland mimics.
Recent Findings
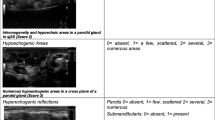
Hypo/anechoic glandular lesions are the major ultrasound characteristic found in Sjögren’s syndrome. Most studies have reported such ultrasound abnormalities to have a sensitivity and specificity in the range of 65–85% and 85–95%, respectively, as well as a positive likelihood ratio between 4 and 12. However, similar findings can also be seen in sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, IgG4-related disease, HIV, and lymphoma. A “nodal” pattern of involvement or the ultrasound artifact of “through transmission” can help distinguish some of these mimics from Sjogren’s syndrome.
Summary
Ultrasound can substantially influence the diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zeron P, Seror R, Bootsma H, Bowman SJ, Dorner T, et al. Characterization of systemic disease in primary Sjogren's syndrome: EULAR-SS task force recommendations for articular, cutaneous, pulmonary and renal involvements. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(12):2230–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kev200.
Shiboski CH, Shiboski SC, Seror R, Criswell LA, Labetoulle M, Lietman TM, et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjogren's syndrome: a consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(1):35–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39859.
Garberg H, Jonsson R, Brokstad KA. The serological pattern of autoantibodies to the Ro52, Ro60, and La48 autoantigens in primary Sjogren's syndrome patients and healthy controls. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005;34(1):49–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009740510017940.
Cornec D, Jousse-Joulin S, Marhadour T, Pers JO, Boisrame-Gastrin S, Renaudineau Y, et al. Salivary gland ultrasonography improves the diagnostic performance of the 2012 American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(9):1604–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keu037.
de Clerck LS, Corthouts R, Francx L, Brussaard C, de Schepper A, Vercruysse HA, et al. Ultrasonography and computer tomography of the salivary glands in the evaluation of Sjogren's syndrome. Comparison with parotid sialography. J Rheumatol. 1988;15(12):1777–81.
• van Nimwegen JF, Mossel E, Delli K, van Ginkel MS, Stel AJ, FGM K, et al. Incorporation of salivary gland ultrasonography into the ACR-EULAR criteria for primary Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Care Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.24017The most comprehensive assessment of integrating salivary gland ultraasound into the ACR-EULAR classification criteria for primary Sjogren's syndrome.
De Vita S, Lorenzon G, Rossi G, Sabella M, Fossaluzza V. Salivary gland echography in primary and secondary Sjogren's syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992;10(4):351–6.
• Hong X, Li W, Xie XY, Zhang ZY, Chen Y, Gao Y, et al. Differential diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis, primary Sjogren’s syndrome, and chronic obstructive submandibular sialadenitis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;55(2):179–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2016.10.021This study describes differences between IGG4 disease and Sjogren's syndrome on salivary gland ultrasound.
Bonavita JA, Mayo J, Babb J, Bennett G, Oweity T, Macari M, et al. Pattern recognition of benign nodules at ultrasound of the thyroid: which nodules can be left alone? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(1):207–13. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.08.1820.
Jara LJ, Navarro C, Brito-Zeron Mdel P, Garcia-Carrasco M, Escarcega RO, Ramos-Casals M. Thyroid disease in Sjogren's syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26(10):1601–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0638-6.
Baldini C, Luciano N, Tarantini G, Pascale R, Sernissi F, Mosca M, et al. Salivary gland ultrasonography: a highly specific tool for the early diagnosis of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0657-7.
Mossel E, Delli K, van Nimwegen JF, Stel AJ, Kroese FGM, Spijkervet FKL, et al. Ultrasonography of major salivary glands compared with parotid and labial gland biopsy and classification criteria in patients with clinically suspected primary Sjogren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(11):1883–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211250.
Jousse-Joulin S, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Cornec D, Marhadour T, Bressollette L, Gestin S, et al. Brief report: ultrasonographic assessment of salivary gland response to rituximab in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(6):1623–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39088.
Salaffi F, Argalia G, Carotti M, Giannini FB, Palombi C. Salivary gland ultrasonography in the evaluation of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Comparison with minor salivary gland biopsy. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(5):1229–36.
Cornec D, Jousse-Joulin S, Pers JO, Marhadour T, Cochener B, Boisrame-Gastrin S, et al. Contribution of salivary gland ultrasonography to the diagnosis of Sjogren's syndrome: toward new diagnostic criteria? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2013;65(1):216–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37698.
Milic VD, Petrovic RR, Boricic IV, Radunovic GL, Pejnovic NN, Soldatovic I, et al. Major salivary gland sonography in Sjogren's syndrome: diagnostic value of a novel ultrasonography score (0-12) for parenchymal inhomogeneity. Scand J Rheumatol. 2010;39(2):160–6. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009740903270623.
Hocevar A, Ambrozic A, Rozman B, Kveder T, Tomsic M. Ultrasonographic changes of major salivary glands in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Diagnostic value of a novel scoring system. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44(6):768–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh588.
• Martel A, Coiffier G, Bleuzen A, Goasguen J, de Bandt M, Deligny C, et al. What is the best salivary gland ultrasonography scoring methods for the diagnosis of primary or secondary Sjogren's syndromes? Joint Bone Spine. 2019;86(2):211–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2018.06.014This study compares the test charecteristiscs of various salivary gland ultrasound scoring systems in the same patient cohort.
Shimizu M, Okamura K, Yoshiura K, Ohyama Y, Nakamura S. Sonographic diagnosis of Sjogren syndrome: evaluation of parotid gland vascularity as a diagnostic tool. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106(4):587–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.11.007.
Omotehara S, Nishida M, Satoh M, Inoue M, Kudoh Y, Horie T, et al. Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing sialadenitis. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2016;43(2):257–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-015-0693-6.
Law ST, Jafarzadeh SR, Govender P, Sun X, Sanchorawala V, Kissin EY. Comparison of ultrasound features of major salivary glands in Sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, and Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Care Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.24029.
Lee KA, Lee SH, Kim HR. Diagnostic and predictive evaluation using salivary gland ultrasonography in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36 Suppl 112(3):165–72.
Hofauer B, Mansour N, Heiser C, Gahleitner C, Thuermel K, Bas M, et al. Sonoelastographic modalities in the evaluation of salivary gland characteristics in Sjogren's syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(9):2130–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2016.04.011.
Dejaco C, De Zordo T, Heber D, Hartung W, Lipp R, Lutfi A, et al. Real-time sonoelastography of salivary glands for diagnosis and functional assessment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014;40(12):2759–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2014.06.023.
• Carotti M, Salaffi F, Di Carlo M, Barile A, Giovagnoni A. Diagnostic value of major salivary gland ultrasonography in primary Sjogren's syndrome: the role of grey-scale and colour/power Doppler sonography. Gland Surg. 2019;8(Suppl 3):S159–S67. https://doi.org/10.21037/gs.2019.05.03The most recent meta-analysis of salivary gland ultrasound for Sjogren's syndrome.
Zhou M, Song S, Wu S, Duan T, Chen L, Ye J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of salivary gland ultrasonography with different scoring systems in Sjogren's syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17128. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35288-5.
Delli K, Dijkstra PU, Stel AJ, Bootsma H, Vissink A, Spijkervet FK. Diagnostic properties of ultrasound of major salivary glands in Sjogren's syndrome: a meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2015;21(6):792–800. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12349.
Hocevar A, Rainer S, Rozman B, Zor P, Tomsic M. Ultrasonographic changes of major salivary glands in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Evaluation of a novel scoring system. Eur J Radiol. 2007;63(3):379–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.02.003.
Takagi Y, Kimura Y, Nakamura H, Sasaki M, Eguchi K, Nakamura T. Salivary gland ultrasonography: can it be an alternative to sialography as an imaging modality for Sjogren's syndrome? Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(7):1321–4. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.123836.
Wernicke D, Hess H, Gromnica-Ihle E, Krause A, Schmidt WA. Ultrasonography of salivary glands -- a highly specific imaging procedure for diagnosis of Sjogren's syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(2):285–93.
Delli K, Arends S, van Nimwegen JF, Dijkstra PU, Stel AJ, Spijkervet FKL, et al. Ultrasound of the major salivary glands is a reliable imaging technique in patients with clinically suspected primary Sjogren's syndrome. Ultraschall Med. 2018;39(3):328–33. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-104631.
Jousse-Joulin S, Nowak E, Cornec D, Brown J, Carr A, Carotti M, et al. Salivary gland ultrasound abnormalities in primary Sjogren's syndrome: consensual US-SG core items definition and reliability. RMD Open. 2017;3(1):e000364. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000364.
Couderc M, Tournadre A, Mathieu S, Pereira B, Soubrier M, Dubost JJ. Do the salivary glands of patients with systemic sclerosis show ultrasonographic modifications suggestive of Sjogren's syndrome? Ann Rheum Dis. 2019:annrheumdis-2019-215777. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215777.
La Paglia GMC, Sanchez-Pernaute O, Alunno A, Martinez-Becerra MJ, Romero-Bueno F, Recuero S, et al. Ultrasound salivary gland involvement in Sjogren's syndrome vs. other connective tissue diseases: is it autoantibody and gland dependent? Clin Rheumatol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04780-2.
Jazzar A, Manoharan A, Brown JE, Shirlaw PJ, Carpenter GH, Challacombe SJ, et al. Predictive value of ultrasound scoring in relation to clinical and histological parameters in xerostomia patients. Oral Dis. 2019;25(1):150–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12959.
Orita Y, Sato Y, Kimura N, Marunaka H, Tachibana T, Yamashita Y, et al. Characteristic ultrasound features of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the salivary and thyroid gland. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014;134(1):93–9. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2013.831994.
Ning XR, Wang ZQ, Zhang SS, Zhang X, Tang SM, Liu YY. Application of ultrasonography scoring system in the assessment of IgG4-related sialadenitis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019;51(6):1032–5.
Shimizu M, Okamura K, Kise Y, Takeshita Y, Furuhashi H, Weerawanich W, et al. Effectiveness of imaging modalities for screening IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialadenitis (Mikulicz's disease) and for differentiating it from Sjogren's syndrome (SS), with an emphasis on sonography. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:223. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0751-x.
Shimizu M, Moriyama M, Okamura K, Kawazu T, Chikui T, Goto TK, et al. Sonographic diagnosis for Mikulicz disease. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108(1):105–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.02.032.
Asai S, Okami K, Nakamura N, Shiraishi S, Sugimoto R, Anar D, et al. Localized or diffuse lesions of the submandibular glands in immunoglobulin G4-related disease in association with differential organ involvement. J Ultrasound Med. 2013;32(5):731–6. https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.32.5.731.
Li W, Xie XY, Su JZ, Hong X, Chen Y, Gao Y, et al. Ultrasonographic features of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(1):167–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.09.014.
Takano S, Sato T, Fukasawa M, Shindo H, Takahashi E, Yokota Y, et al. Hypoechoic lesions in submandibular glands are diagnostic markers of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2016;45(1):e8–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000442.
Wang ZJ, Zheng LY, Pu YP, Zhou HH, Xie LS, Shi H, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing sialadenitis. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(6):2089–93. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001016.
Takagi Y, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, Miyashita T, Kawakami A, Sumi M, et al. IgG4-related Mikulicz's disease: ultrasonography of the salivary and lacrimal glands for monitoring the efficacy of corticosteroid therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013;31(5):773–5.
Schiodt M, Greenspan D, Daniels TE, Nelson J, Leggott PJ, Wara DW, et al. Parotid gland enlargement and xerostomia associated with labial sialadenitis in HIV-infected patients. J Autoimmun. 1989;2(4):415–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-8411(89)90170-4.
Soberman N, Leonidas JC, Berdon WE, Bonagura V, Haller JO, Posner M, et al. Parotid enlargement in children seropositive for human immunodeficiency virus: imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157(3):553–6. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.157.3.1651645.
Vargas PA, Mauad T, Bohm GM, Saldiva PH, Almeida OP. Parotid gland involvement in advanced AIDS. Oral Dis. 2003;9(2):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1601-0825.2003.02868.x.
Kabenge C, Ng S, Muyinda Z, Ameda F. Diagnostic ultrasound patterns of parotid glands in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients in Mulago, Uganda. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2010;39(7):389–99. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr/23992216.
Martinoli C, Pretolesi F, Del Bono V, Derchi LE, Mecca D, Chiaramondia M. Benign lymphoepithelial parotid lesions in HIV-positive patients: spectrum of findings at gray-scale and Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995;165(4):975–9. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.165.4.7677004.
Corthouts B, De Clerck LS, Francx L, De Schepper A, Vercruysse HA, Stevens WJ. Ultrasonography of the salivary glands in the evaluation of Sjogren's syndrome. Comparison with sialography. J Belg Radiol. 1991;74(3):189–92.
Napoli V, Tozzini A, Neri E, Calderazzi A, Gabriele M, Bonaretti S, et al. The imaging diagnosis of Sjogren's syndrome: echography, sialography and scintigraphy compared in the study of the salivary glands. Minerva Stomatol. 1996;45(4):141–8.
Kawamura H, Taniguchi N, Itoh K, Kano S. Salivary gland echography in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(4):505–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780330407.
Carotti M, Salaffi F, Manganelli P, Argalia G. Ultrasonography and colour Doppler sonography of salivary glands in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2001;20(3):213–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100670170068.
Giuseppetti GM, Argalia G, Salera D, Ranaldi R, Danieli G, Cappelli M. Ultrasonographic contrast-enhanced study of sicca syndrome. Eur J Radiol. 2005;54(2):225–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.04.018.
Poul JH, Brown JE, Davies J. Retrospective study of the effectiveness of high-resolution ultrasound compared with sialography in the diagnosis of Sjogren's syndrome. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008;37(7):392–7. https://doi.org/10.1259/dmfr/50668408.
Yoshiura K, Yuasa K, Tabata O, Araki K, Yonetsu K, Nakayama E, et al. Reliability of ultrasonography and sialography in the diagnosis of Sjogren's syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1997;83(3):400–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1079-2104(97)90249-3.
Xu. Value of sonographic score in the diagnosis of salivary gland involvement in patients with Sj(o)gren's syndrome. Chin J Ultrason. 2010;19:977–80.
Obinata K, Sato T, Ohmori K, Shindo M, Nakamura M. A comparison of diagnostic tools for Sjogren syndrome, with emphasis on sialography, histopathology, and ultrasonography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(1):129–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.08.033.
Shimizu M, Okamura K, Yoshiura K, Ohyama Y, Nakamura S, Kinukawa N. Sonographic diagnostic criteria for screening Sjogren's syndrome. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102(1):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.09.012.
Niemela RK, Takalo R, Paakko E, Suramo I, Paivansalo M, Salo T, et al. Ultrasonography of salivary glands in primary Sjogren's syndrome. A comparison with magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance sialography of parotid glands. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43(7):875–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh187.
Makula E, Pokorny G, Kiss M, Voros E, Kovacs L, Kovacs A, et al. The place of magnetic resonance and ultrasonographic examinations of the parotid gland in the diagnosis and follow-up of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000;39(1):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/39.1.97.
Astorri E, Sutcliffe N, Richards PS, Suchak K, Pitzalis C, Bombardieri M, et al. Ultrasound of the salivary glands is a strong predictor of labial gland biopsy histopathology in patients with sicca symptoms. J Oral Pathol Med. 2016;45(6):450–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12387.
Chen S, Wang Y, Zhang G, Chen S. Combination of salivary gland ultrasonography and virtual touch quantification for diagnosis of Sjogren's syndrome: a preliminary study. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2793898–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2793898.
El Miedany YM, Ahmed I, Mourad HG, Mehanna AN, Aty SA, Gamal HM, et al. Quantitative ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging of the parotid gland: can they replace the histopathologic studies in patients with Sjogren's syndrome? Joint Bone Spine. 2004;71(1):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2003.04.003.
Chikui T, Okamura K, Tokumori K, Nakamura S, Shimizu M, Koga M, et al. Quantitative analyses of sonographic images of the parotid gland in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32(5):617–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2006.01.013.
Lin D, Yang W, Guo X, Cao J, Lv Q, Jin O, et al. Cross-sectional comparison of ultrasonography scoring systems for primary Sjogren's syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):19065–71.
Andretta M, Sfriso P, Botsios C, Ostuni PA, Grava C, Tregnaghi A, et al. Comparison of ultrasonography and sialography vs. magnetic resonance in the diagnosis of the primary Sjogren's syndrome. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2001;21(1):22–31.
Kim JW, Lee H, Park SH, Kim SK, Choe JY, Kim JK. Salivary gland ultrasonography findings are associated with clinical, histological, and serologic features of Sjogren's syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(4):303–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009742.2017.1374451.
Luciano N, Baldini C, Tarantini G, Ferro F, Sernissi F, Varanini V, et al. Ultrasonography of major salivary glands: a highly specific tool for distinguishing primary Sjogren's syndrome from undifferentiated connective tissue diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(12):2198–204. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kev253.
Milic VD, Petrovic RR, Boricic IV, Marinkovic-Eric J, Radunovic GL, Jeremic PD, et al. Diagnostic value of salivary gland ultrasonographic scoring system in primary Sjogren's syndrome: a comparison with scintigraphy and biopsy. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(7):1495–500. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.081267.
Ariji Y, Ohki M, Eguchi K, Izumi M, Ariji E, Mizokami A, et al. Texture analysis of sonographic features of the parotid gland in Sjogren's syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166(4):935–41. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.166.4.8610577.
Makula E, Pokorny G, Rajtar M, Kiss I, Kovacs A, Kovacs L. Parotid gland ultrasonography as a diagnostic tool in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Br J Rheumatol. 1996;35(10):972–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.972.
Salaffi F, Carotti M, Iagnocco A, Luccioli F, Ramonda R, Sabatini E, et al. Ultrasonography of salivary glands in primary Sjogren's syndrome: a comparison with contrast sialography and scintigraphy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(8):1244–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ken222.
Theander E, Mandl T. Primary Sjogren's syndrome: diagnostic and prognostic value of salivary gland ultrasonography using a simplified scoring system. Arthritis Care Res. 2014;66(7):1102–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22264.
Zhang X, Zhang S, He J, Hu F, Liu H, Li J, et al. Ultrasonographic evaluation of major salivary glands in primary Sjogren's syndrome: comparison of two scoring systems. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(9):1680–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kev103.
Zhou MSS, Chen L, Liu X, Duan T. Study on the value of salivary gland ultrasonography in Sjogren's syndrome. Chin J Rheumatol. 2016;20:317–20.
Takagi Y, Sumi M, Nakamura H, Iwamoto N, Horai Y, Kawakami A, et al. Ultrasonography as an additional item in the American College of Rheumatology classification of Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(11):1977–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keu238.
Milic V, Petrovic R, Boricic I, Radunovic G, Marinkovic-Eric J, Jeremic P, et al. Ultrasonography of major salivary glands could be an alternative tool to sialoscintigraphy in the American-European classification criteria for primary Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51(6):1081–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ker431.
Qi X, Sun C, Tian Y, Han Y, Peng C, Jin H, et al. Comparison of the diagnostic value of four scoring systems in primary sjogren's syndrome patients. Immunol Lett. 2017;188:9–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2017.05.009.
Yonetsu K, Takagi Y, Sumi M, Nakamura T, Eguchi K. Sonography as a replacement for sialography for the diagnosis of salivary glands affected by Sjogren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61(3):276–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.61.3.276.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Tracian James-Goulbourne, Vagishwari Murugesan, and Eugene Y. Kissin declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Imaging
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
James-Goulbourne, T., Murugesan, V. & Kissin, E.Y. Sonographic Features of Salivary Glands in Sjögren’s Syndrome and its Mimics. Curr Rheumatol Rep 22, 36 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-020-00914-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-020-00914-7