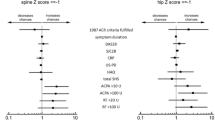
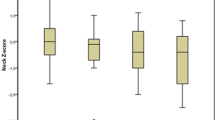
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized by bone loss. Degree of inflammation and autoantibody positivity have both been identified as important initiators of skeletal damage in RA. Whereas it is well appreciated that inflammation initiates bone loss via the action of cytokines, the effect of autoantibodies in initiating bone destruction has long been underestimated. It has, nonetheless, been known for years that antibodies against citrullinated proteins (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor are associated with a more destructive disease course. It was recently shown that ACPA bind osteoclast precursor cells and directly promote their differentiation into bone-resorbing osteoclasts. Other results have shown that in ACPA-positive individuals bone loss starts even before the onset of clinical disease; this is indicative of the independent effect of these antibodies in initiating skeletal damage. The observation that the mere presence of ACPA is associated with pathological changes suggests that these antibodies have functional properties and initiate the onset of disease long before patients consult the rheumatologist because of symptomatic joint disease. These findings also indicate that “RA” is a syndrome rather than a single disease, suggesting that autoantibody-positive patients are both genetically and clinically distinct phenotypes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205–19.
Schett G, Gravallese E. Bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8:656–64.
Schett G, Teitelbaum SL. Osteoclasts and arthritis. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24:1142–6.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/ European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1580–8.
Klareskog L, Stolt P, Lundberg K, et al. A new model for an etiology of rheumatoid arthritis: smoking may trigger HLA-DR (shared epitope)-restricted immune reactions to autoantigens modified by citrullination. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:38–46.
Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, et al. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2741–9.
van der Woude D, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Ioan-Facsinay A, et al. Epitope spreading of the anti-citrullinated protein antibody response occurs before disease onset and is associated with the disease course of early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1554–61.
Nielen MM, van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, et al. Simultaneous development of acute phase response and autoantibodies in preclinical rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:535–7.
Hughes-Austin JM, Deane KD, Derber LA, Kolfenbach JR, Zerbe GO, Sokolove J, et al. Multiple cytokines and chemokines are associated with rheumatoid arthritis-related autoimmunity in first-degree relatives without rheumatoid arthritis: Studies of the Aetiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis (SERA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Jun;72(6):901–7.
•• Harre U, Georgess D, Bang H, et al. Induction of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss by human autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1791–802. This paper attributed a functional property to anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, showing that they can directly initiate differentiation of bone-resorbing osteoclasts.
van Schaardenburg D, Nielen MM, Lems WF, et al. Bone metabolism is altered in preclinical rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1173–4.
• Guler-Yuksel M, Allaart CF, Goekoop-Ruiterman YPM, deVries-Bouwstra JK, vanGroenendael JHLM, et al. Changes in hand and generalised bone mineral density in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:330. Important paper showing that bone changes are frequently found in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting that skeletal damage starts at the clinical onset of rheumatoid arthritis, if not before.
De Rooy DPC, Johan Kalvesten J, Huizinga1 TWJ, et al. Loss of metacarpal bone density predicts RA development in recent-onset arthritis. Rheumatology 2012.
Gerlag DM, Raza K, van Baarsen LG, et al. EULAR recommendations for terminology and research in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis: report from the Study Group for Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:638–41.
• Kleyer A, Finzel S, Rech J, Manger B, Krieter M, Faustini F, Araujo E, Hueber AJ, Harre U, Engelke K, Schett G. Bone loss before the clinical onset of rheumatoid arthritis in subjects with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Mar 21. First evidence that bone loss starts before the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. The manuscript shows that healthy individuals with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies.
Hetland ML, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Junker P, et al. Radiographic progression and remission rates in early rheumatoid arthritis - MRI bone oedema and anti-CCP predicted radiographic progression in the 5-year extension of the double-blind randomised CIMESTRA trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1789–95.
Mustila A, Korpela M, Haapala AM, et al. Anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies and the progression of radiographic joint erosions in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated with FIN-RACo combination and single disease-modifying antirheumatic drug strategies. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:500–5.
Guler H, Turhanoglu AD, Ozer B, et al. The relationship between anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide and bone mineral density and radiographic damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2008;37:337–42.
Kroot EJ, de Jong BA, van Leeuwen MA, et al. The prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1831–5.
Guler-Yuksel M, Klarenbeek NB, Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, et al. Accelerated hand bone mineral density loss is associated with progressive joint damage in hands and feet in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R96.
Syversen SW, Goll GL, van der Heijde D, et al. Prediction of radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis and the role of antibodies against mutated citrullinated vimentin: results from a 10-year prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:345–51.
Saeki Y, Kudo-Tanaka E, Ohshima S, et al. Baseline anti-citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA) titers and serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels possibly predict progression of bone destruction in early stages of rheumatoid arthritis (ERA). Rheumatol Int. 2013;33:451–6.
van der Woude D, Syversen SW, van der Voort EI, et al. The ACPA isotype profile reflects long-term radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1110–6.
Vencovsky J, Machacek S, Sedova L, et al. Autoantibodies can be prognostic markers of an erosive disease in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:427–30.
Stach CM, Bauerle M, Englbrecht M, et al. Periarticular bone structure in rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy individuals assessed by high-resolution computed tomography. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:330–9.
Hecht C, Finzel S, Englbrecht M, et al. Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies but Not Rheumatoid Factor Are Associated with Larger Bone Erosions in rheumatoid arthritis patients a Cross-Sectional Micro Computed Tomography Study. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64 Suppl:2581.
Boyesen P, Hoff M, Odegard S, et al. Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate predict hand bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of short duration: a longitudinal study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R103.
Griffith JF, Genant HK. New imaging modalities in bone. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011;13:241–50.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Roland Kocijan, Ulrike Harre, and Georg Schett declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocijan, R., Harre, U. & Schett, G. ACPA and Bone Loss in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 15, 366 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-013-0366-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-013-0366-7