Abstract
Purpose of Review
While anti-PD-1 antibodies have been a breakthrough in the treatment of patients with advanced melanoma, a substantial proportion of patients are still refractory to or progress after treatment with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Here, we review the post anti-PD-1 therapy alternatives that may be possible for patients with unresectable or metastatic stage 3 or 4 melanoma.
Recent Findings
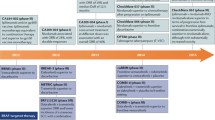
Currently available treatment options include BRAF-targeted and MEK inhibitor–targeted therapies for those with BRAFV600 mutant melanoma, while for patients with BRAF-WT melanoma or those who have already received prior BRAF-targeted therapy, options include anti-CTLA-4 therapy, alone or in combination with anti-PD-1 therapy, or for selected patients, clinical trials that may incorporate other immune checkpoint inhibitors or co-stimulatory agonists, oncolytic virotherapies, adoptive cellular therapies, or other novel agents.
Summary
Participation in clinical trials is critical in order to delineate what more effective treatment options are and which group of patients after receiving prior anti-PD-1 therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, Arance A, Grob JJ, Mortier L, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet (London, England). 2017;390(10105):1853–62.
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob J-J, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, et al. Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(16):1535–46.
O’Donnell JS, Smyth MJ, Teng MW. Acquired resistance to anti-PD1 therapy: checkmate to checkpoint blockade? Genome medicine. 2016;8(1):111.
Zaretsky JM, Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Escuin-Ordinas H, Hugo W, Hu-Lieskovan S, et al. Mutations associated with acquired resistance to PD-1 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(9):819–29.
Kuske M, Westphal D, Wehner R, Schmitz M, Beissert S, Praetorius C, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of BRAF and MEK inhibitors: implications for melanoma therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2018;136:151–9.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417(6892):949–54.
Ascierto PA, McArthur GA, Dreno B, Atkinson V, Liszkay G, Di Giacomo AM, et al. Cobimetinib combined with vemurafenib in advanced BRAF(V600)-mutant melanoma (coBRIM): updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(9):1248–60.
Long GV, Eroglu Z, Infante J, Patel S, Daud A, Johnson DB, et al. Long-term outcomes in patients with BRAF V600-mutant metastatic melanoma who received dabrafenib combined with trametinib. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(7):667–73.
• Dummer R, Ascierto PA, Gogas HJ, Arance A, Mandala M, Liszkay G, et al. Encorafenib plus binimetinib versus vemurafenib or encorafenib in patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma (COLUMBUS): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. This phase III randomized trial explored the latest BRAF and MEK inhibitor combination, encorafenib plus binimetinib compared with encorafenib or vemurafenib with quite a durable median progression-free and overall survival in BRAF mutant melanoma.
Johnson DB, Pectasides E, Feld E, Ye F, Zhao S, Johnpulle R, et al. Sequencing treatment in BRAFV600 mutant melanoma: anti-PD-1 before and after BRAF inhibition. J Immunother. 2017;40(1):31–5.
Saab KR, Mooradian MJ, Wang DY, Chon J, Xia CY, Bialczak A, et al. Tolerance and efficacy of BRAF plus MEK inhibition in patients with melanoma who previously have received programmed cell death protein 1-based therapy. Cancer. 2019;125(6):884–91.
Hugo W, Zaretsky Jesse M, Sun L, Song C, Moreno Blanca H, Hu-Lieskovan S, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic features of response to anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cell. 2016;165(1):35–44.
Burton EM, Amaria RN, Glitza IC, Shephard M, Diab A, Milton D, et al. 1312PD safety and efficacy of TRIplet combination of nivolumab (N) with dabrafenib (D) and trametinib (T) [TRIDeNT] in patients (pts) with BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma (MM): a single center phase II study. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(Supplement_5).
Jakob JA, Bassett RL Jr, Ng CS, Curry JL, Joseph RW, Alvarado GC, et al. NRAS mutation status is an independent prognostic factor in metastatic melanoma. Cancer. 2012;118(16):4014–23.
Sullivan RJ. Dual MAPK/CDK targeting in melanoma: new approaches, New Challenges. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(5):532–3.
Mendenhall WM, Amdur RJ, Hinerman RW, Werning JW, Villaret DB, Mendenhall NP. Head and neck mucosal melanoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2005;28(6):626–30.
Curtin JA, Busam K, Pinkel D, Bastian BC. Somatic activation of KIT in distinct subtypes of melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(26):4340–6.
Hodi FS, Corless CL, Giobbie-Hurder A, Fletcher JA, Zhu M, Marino-Enriquez A, et al. Imatinib for melanomas harboring mutationally activated or amplified KIT arising on mucosal, acral, and chronically sun-damaged skin. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(26):3182–90.
Guo J, Carvajal RD, Dummer R, Hauschild A, Daud A, Bastian BC, et al. Efficacy and safety of nilotinib in patients with KIT-mutated metastatic or inoperable melanoma: final results from the global, single-arm, phase II TEAM trial. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(6):1380–7.
Lezcano C, Shoushtari AN, Ariyan C, Hollmann TJ, Busam KJ. Primary and metastatic melanoma with NTRK fusions. Am J Surg Pathol. 2018;42(8):1052–8.
Drilon A, Laetsch TW, Kummar S, DuBois SG, Lassen UN, Demetri GD, et al. Efficacy of larotrectinib in TRK fusion–positive cancers in adults and children. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(8):731–9.
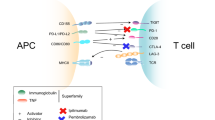
Melero I, Hervas-Stubbs S, Glennie M, Pardoll DM, Chen L. Immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(2):95–106.
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):711–23.
Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, Arance A, Grob JJ, Mortier L, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(26):2521–32.
Zimmer L, Apuri S, Eroglu Z, Kottschade LA, Forschner A, Gutzmer R, et al. Ipilimumab alone or in combination with nivolumab after progression on anti-PD-1 therapy in advanced melanoma. Eur J Cancer. 2017;75:47–55.
Long GV, Robert C, Blank CU, Ribas A, Mortier L, Schachter J, et al. Outcomes in patients (pts) treated with ipilimumab (ipi) after pembrolizumab (pembro) in KEYNOTE-006. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2017;30(1):118.
Olson D, Luke JJ, Hallmeyer S, Bajaj M, Carll T, Krausz T, et al. Phase II trial of pembrolizumab (pembro) plus 1 mg/kg ipilimumab (ipi) immediately following progression on anti-PD-1 Ab in melanoma (mel). J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15_suppl):9514.
Ascierto PA, Melero I, Bhatia S, Bono P, Sanborn RE, Lipson EJ, et al. Initial efficacy of anti-lymphocyte activation gene-3 (anti–LAG-3; BMS-986016) in combination with nivolumab (nivo) in pts with melanoma (MEL) previously treated with anti–PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(15_suppl):9520.
Mach N, Curigliano G, Santoro A, Kim D-W, Tai DWM, Hodi S, et al. 1202P phase (Ph) II study of MBG453 + spartalizumab in patients (pts) with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and melanoma pretreated with anti–PD-1/L1 therapy. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(Supplement_5).
Papadopoulos KP, Autio KA, Golan T, Dobrenkov K, Chartash E, Li XN, et al. Phase 1 study of MK-4166, an anti-human glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) antibody, as monotherapy or with pembrolizumab (pembro) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(15_suppl):9509.
Ribas A, Medina T, Kummar S, Amin A, Kalbasi A, Drabick JJ, et al. SD-101 in combination with pembrolizumab in advanced melanoma: results of a phase Ib, Multicenter Study. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(10):1250–7.
Milhem M, Gonzales R, Medina T, Kirkwood JM, Buchbinder E, Mehmi I, et al. Abstract CT144: Intratumoral toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonist, CMP-001, in combination with pembrolizumab can reverse resistance to PD-1 inhibition in a phase Ib trial in subjects with advanced melanoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78(13 Supplement):CT144-CT.
• Diab A, Haymaker C, Bernatchez C, Andtbacka RHI, Shaheen M, Johnson D, et al. 1245PD intratumoral (IT) injection of the TLR9 agonist tilsotolimod (IMO-2125) in combination with ipilimumab (ipi) triggers durable responses in PD-1 inhibitor refractory metastatic melanoma (rMM): Results from a multicenter, phase I/II study. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(suppl_8). Preliminary data from the ILLUMINATE 204 trial show a promising response rate in patients who received prior anti-PD-1 therapy, suggesting an effective regimen in those eligible for intratumoral injections.
Meric-Bernstam F, Sandhu SK, Hamid O, Spreafico A, Kasper S, Dummer R, et al. Phase Ib study of MIW815 (ADU-S100) in combination with spartalizumab (PDR001) in patients (pts) with advanced/metastatic solid tumors or lymphomas. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(15_suppl):2507.
Parkinson DR, Abrams JS, Wiernik PH, Rayner AA, Margolin KA, Van Echo DA, et al. Interleukin-2 therapy in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8(10):1650–6.
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, Weber JS, Parkinson DR, et al. Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2. Jama. 1994;271(12):907–13.
Buchbinder EI, Dutcher JP, Daniels GA, Curti BD, Patel SP, Holtan SG, et al. Therapy with high-dose Interleukin-2 (HD IL-2) in metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma following PD1 or PDL1 inhibition. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):49.
Bentebibel S-E, Hurwitz ME, Bernatchez C, Haymaker C, Hudgens CW, Kluger HM, et al. A first-in-human study and biomarker analysis of NKTR-214, a novel IL2Rβγ-biased cytokine, in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Cancer Discov. 2019;9(6):711–21.
Kaufman HL, Kim DW, DeRaffele G, Mitcham J, Coffin RS, Kim-Schulze S. Local and distant immunity induced by intralesional vaccination with an oncolytic herpes virus encoding GM-CSF in patients with stage IIIc and IV melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(3):718–30.
Andtbacka RHI, Collichio F, Harrington KJ, Middleton MR, Downey G, Ӧhrling K, et al. Final analyses of OPTiM: a randomized phase III trial of talimogene laherparepvec versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in unresectable stage III–IV melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):145.
• Chesney J, Puzanov I, Collichio F, Singh P, Milhem MM, Glaspy J, et al. Randomized, open-label phase II study evaluating the efficacy and safety of talimogene laherparepvec in combination with ipilimumab versus ipilimumab alone in patients with advanced, unresectable melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1658–67. This phase II randomized trial was the first randomized trial to evaluate addition of an oncolytic virus to a checkpoint inhibitor. The trial demonstrated that the objective response rate was significantly higher with T-VEC plus ipilimumab vs ipilimumab alone.
Ribas A, Dummer R, Puzanov I, VanderWalde A, Andtbacka RHI, Michielin O, et al. Oncolytic virotherapy promotes intratumoral T cell infiltration and improves anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Cell. 2017;170(6):1109–19.e10.
Andtbacka RHI, Curti BD, Kaufman H, Daniels GA, Nemunaitis JJ, Spitler LE, et al. Final data from CALM: a phase II study of Coxsackievirus A21 (CVA21) oncolytic virus immunotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(15_suppl):9030.
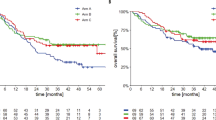
•• Goff SL, Dudley ME, Citrin DE, Somerville RP, Wunderlich JR, Danforth DN, et al. Randomized, prospective evaluation comparing intensity of lymphodepletion before adoptive transfer of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(20):2389–97. This trial explored adoptive cellular therapy with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in 101 patients with metastatic melanoma, showing promising results in patients, including in those who had received prior therapy.
Sarnaik A, Khushalani NI, Chesney JA, Kluger HM, Curti BD, Lewis KD, et al. Safety and efficacy of cryopreserved autologous tumor infiltrating lymphocyte therapy (LN-144, lifileucel) in advanced metastatic melanoma patients who progressed on multiple prior therapies including anti-PD-1. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(15_suppl):2518.
Crosby T, Fish R, Coles B, Mason MD. Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):Cd001215.
Wilson MA, Schuchter LM. Chemotherapy for melanoma. Cancer Treat Res. 2016;167:209–29.
Zimpfer-Rechner C, Hofmann U, Figl R, Becker JC, Trefzer U, Keller I, et al. Randomized phase II study of weekly paclitaxel versus paclitaxel and carboplatin as second-line therapy in disseminated melanoma: a multicentre trial of the Dermatologic Co-operative Oncology Group (DeCOG). Melanoma Res. 2003;13(5):531–6.
Kim KB, Sosman JA, Fruehauf JP, Linette GP, Markovic SN, McDermott DF, et al. BEAM: a randomized phase II study evaluating the activity of bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin plus paclitaxel in patients with previously untreated advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(1):34–41.
Hauschild A, Agarwala SS, Trefzer U, Hogg D, Robert C, Hersey P, et al. Results of a phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of sorafenib in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel as second-line treatment in patients with unresectable stage III or stage IV melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(17):2823–30.
Giles MH, Coventry BJ. Isolated limb infusion chemotherapy for melanoma: an overview of early experience at the Adelaide Melanoma Unit. Cancer Manag Res. 2013;5:243–9.
Steinman J, Ariyan C, Rafferty B, Brady MS. Factors associated with response, survival, and limb salvage in patients undergoing isolated limb infusion. J Surg Oncol. 2014;109(5):405–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Nalan Akgul Babacan declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Zeynep Eroglu has received research funding from Novartis and has received compensation from Regeneron and ArrayBioPharma for participation on advisory boards.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Melanoma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babacan, N.A., Eroglu, Z. Treatment Options for Advanced Melanoma After Anti-PD-1 Therapy. Curr Oncol Rep 22, 38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-020-0894-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-020-0894-z