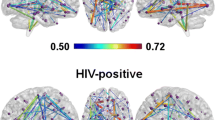
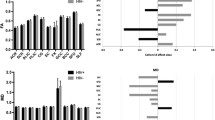
Abstract
In much of the developed world, the HIV epidemic has largely been controlled by antiretroviral treatment. Even so, there is growing concern that HIV-infected individuals may be at risk for accelerated brain aging and a range of cognitive impairments. What promotes or resists these changes is largely unknown. There is also interest in discovering factors that promote resilience to HIV and combat its adverse effects in children. Here, we review recent developments in brain imaging that reveal how the virus affects the brain. We relate these brain changes to changes in blood markers, cognitive function, and other patient outcomes or symptoms, such as apathy or neuropathic pain. We focus on new and emerging techniques, including new variants of brain MRI. Diffusion tensor imaging, for example, can map the brain’s structural connections, while fMRI can uncover functional connections. Finally, we suggest how large-scale global research alliances, such as ENIGMA, may resolve controversies over effects where evidence is now lacking. These efforts pool scans from tens of thousands of individuals and offer a source of power not previously imaginable for brain imaging studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Thompson PM, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Lopez OL, Aizenstein HJ, et al. Thinning of the cerebral cortex visualized in HIV/AIDS reflects CD4+ T lymphocyte decline. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15647. This paper provided the first 3D maps of cortical differences in HIV patients based on neuroimaging.
Chiang MC, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Lopez OL, Aizenstein HJ, Toga AW, et al. 3D pattern of brain atrophy in HIV/AIDS visualized using tensor-based morphometry. Neuroimage. 2007;34:44.
Moore RC, Fazeli PL, Jeste DV, Moore DJ, Grant I, Woods SP, et al. Successful cognitive aging and health-related quality of life in younger and older adults infected with HIV. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1186.
Puthanakit T, Saphonn V, Ananworanich J, Kosalaraksa P, Hansudewechakul R, Vibol U, et al. Early versus deferred antiretroviral therapy for children older than 1 year infected with HIV (PREDICT): a multicentre, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:933. This publication highlights the new PREDICT study, examining at childhood brain, behavior, and cognitive developmental effects of HIV exposure and immediate vs deferred treatment.
Wendelken LA, Valcour V. Impact of HIV and aging on neuropsychological function. J Neurovirol. 2012;18:256.
Nishijima T, Gatanaga H, Teruya K, Tajima T, Kikuchi Y, Hasuo K, et al. Brain magnetic resonance imaging screening is not useful for HIV-1-infected patients without neurological symptoms. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 2014;30:970.
Fennema-Notestine C, Ellis RJ, Archibald SL, Jernigan TL, Letendre SL, Notestine RJ, et al. Increases in brain white matter abnormalities and subcortical gray matter are linked to CD4 recovery in HIV infection. J Neurovirol. 2013;19:393.
Keltner JR, Fennema-Notestine C, Vaida F, Wang D, Franklin DR, Dworkin RH, et al. HIV-associated distal neuropathic pain is associated with smaller total cerebral cortical gray matter. J Neurovirol. 2014;20:209.
Becker JT, Martinson JJ, Penugonda S, Kingsley L, Molsberry S, Reynolds S, et al. No association between APOE - epsilon 4 alleles, HIV infection, age, neuropsychological outcome, or death. J Neurovirol. 2015;21:24.
Harezlak J, Cohen R, Gongvatana A, Taylor M, Buchthal S, Schifitto G, et al. Predictors of CNS injury as measured by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the setting of chronic HIV infection and CART. J Neurovirol. 2014;20:294.
Thompson PM, Stein JL, Medland SE, Hibar DP, Vasquez AA, Renteria ME, et al. The ENIGMA Consortium: large-scale collaborative analyses of neuroimaging and genetic data. Brain Imaging Behav. 2014;8:153. This paper describes the consortia work in neuroimaging and how one in particular, ENIGMA, and the network of researchers involved have combined their analyses to achieve enough statistical power to detect differences in brain volume associated with to single nucleotide variations in the human genome. This work is now being extended to study consistencies and differences in HIV effects on brain structure.
Masters MC, Ances BM. Role of neuroimaging in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Semin Neurol. 2014;34:89.
Thompson PM, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Lu A, Lee SE, Lee JY, et al. 3D mapping of ventricular and corpus callosum abnormalities in HIV/AIDS. Neuroimage. 2006;31:12.
Wang Y, Zhang J, Gutman B, Chan TF, Becker JT, Aizenstein HJ, et al. Multivariate tensor-based morphometry on surfaces: application to mapping ventricular abnormalities in HIV/AIDS. Neuroimage. 2010;49:2141.
Fischl B, van der Kouwe A, Destrieux C, Halgren E, Segonne F, Salat DH, et al. Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2004;14:11.
Patenaude B, Smith SM, Kennedy DN, Jenkinson M. A Bayesian model of shape and appearance for subcortical brain segmentation. Neuroimage. 2011;56:907.
Hibar DP, Stein JL, Renteria ME, Arias-Vasquez A, Desrivieres S, Jahanshad N, et al. : Common genetic variants influence human subcortical brain structures. Nature 2015. This paper is the largest neuroimaging paper to date, pooling together information from over 30,000 brain scans to discover multiple genetic markers that influence brain structure across over 50 sites in the world.
Nir TM, Fouche J-P, Valcour VG, Shikuma CM, Kallianpur KJ, Ananworanich J, et al. CD4 counts predict brain white matter integrity in people living with HIV: a meta-analysis by the ENIGMA HIV working group. San Francisco, CA, USA: CNS (Cognitive Neuroscience Society); 2015.
Cohen RA, Harezlak J, Schifitto G, Hana G, Clark U, Gongvatana A, et al. Effects of nadir CD4 count and duration of human immunodeficiency virus infection on brain volumes in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era. J Neurovirol. 2010;16:25.
Kallianpur KJ, Shikuma C, Kirk GR, Shiramizu B, Valcour V, Chow D, et al. Peripheral blood HIV DNA is associated with atrophy of cerebellar and subcortical gray matter. Neurology. 2013;80:1792.
Heaps JM, Sithinamsuwan P, Paul R, Lerdlum S, Pothisri M, Clifford D, et al.: Association between brain volumes and HAND in cART-naive HIV+ individuals from Thailand. J Neurovirol 2015.
Cysique LA, Brew BJ. The effects of HIV and aging on brain functions: proposing a research framework and update on last 3 years’ findings. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2014;9:355.
Pfefferbaum A, Rogosa DA, Rosenbloom MJ, Chu W, Sassoon SA, Kemper CA, et al. Accelerated aging of selective brain structures in human immunodeficiency virus infection: a controlled, longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35:1755.
Chen L, Perlina A, Lee CJ. Positive selection detection in 40,000 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 sequences automatically identifies drug resistance and positive fitness mutations in HIV protease and reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 2004;78:3722.
Klunder AD, Chiang MC, Dutton RA, Lee SE, Toga AW, Lopez OL, et al. Mapping cerebellar degeneration in HIV/AIDS. Neuroreport. 2008;19:1655.
Hua X, Boyle CP, Harezlak J, Tate DF, Yiannoutsos CT, Cohen R, et al. Disrupted cerebral metabolite levels and lower nadir CD4+ counts are linked to brain volume deficits in 210 HIV-infected patients on stable treatment. Neuroimage Clin. 2013;3:132.
Lepore N, Brun C, Chou YY, Chiang MC, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, et al. Generalized tensor-based morphometry of HIV/AIDS using multivariate statistics on deformation tensors. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2008;27:129.
Jahanshad N, Hibar D, Faskowitz J, Medland S, McMahon K, de Zubicaray G, et al. Voxelwise meta analysis for multi-site brain mapping. Honolulu, Hawaii: Organization for Human Brain Mapping (OHBM); 2015.
Cohen RA, Harezlak J, Gongvatana A, Buchthal S, Schifitto G, Clark U, et al. Cerebral metabolite abnormalities in human immunodeficiency virus are associated with cortical and subcortical volumes. J Neurovirol. 2010;16:435.
Anderson AM, Harezlak J, Bharti A, Mi D, Taylor MJ, Daar ES, et al.: Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers predict cerebral injury in HIV-infected individuals on stable combination antiretroviral therapy. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2015.
Zahr NM, Mayer D, Rohlfing T, Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A. Imaging neuroinflammation? A perspective from MR spectroscopy. Brain Pathol. 2014;24:654.
Madsen SK, Ver Steeg G, Mezher A, Jahanshad N, Nir TM, Hua X, et al. Information-theoretic characterization of blood panel predictors for brain atrophy and cognitive decline in the elderly. Brooklyn, NY, USA: International Symposium for Biomedical Imaging; 2015.
Ver Steeg G, Madsen SK, Mezher A, Jahanshad N, Nir TM, Hua X, et al.: Correlation explanation for multi-modal brain data. Mach Learn Comput Biol, 2014.
Jahanshad N, Nir TM, Toga AW, Jack Jr CR, Bernstein MA, Weiner MW, et al. Seemingly unrelated regression empowers detection of network failure in dementia. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36 Suppl 1:S103.
Hua X, Leow AD, Levitt JG, Caplan R, Thompson PM, Toga AW. Detecting brain growth patterns in normal children using tensor-based morphometry. Hum Brain Mapp. 2009;30:209.
Thompson PM, Giedd JN, Woods RP, MacDonald D, Evans AC, Toga AW. Growth patterns in the developing brain detected by using continuum mechanical tensor maps. Nature. 2000;404:190.
Nir TM, Jahanshad N, Busovaca E, Wendelken L, Nicolas K, Thompson PM, et al. Mapping white matter integrity in elderly people with HIV. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014;35:975.
Jahanshad N, Couture M-C, Prasitsuebsai W, Nir TM, Aurpibul L, Thompson PM, et al.: Brain imaging and neurodevelopment in HIV-uninfected Thai children born to HIV-infected mothers. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2015; In Press.
Jahanshad N, Valcour VG, Nir TM, Kohannim O, Busovaca E, Nicolas K, et al. Disrupted brain networks in the aging HIV+ population. Brain Connect. 2012;2:335.
Thomason ME, Thompson PM. Diffusion imaging, white matter, and psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011;7:63.
Wilson TW, Heinrichs-Graham E, Becker KM, Aloi J, Robertson KR, Sandkovsky U, et al.: Multimodal neuroimaging evidence of alterations in cortical structure and function in HIV-infected older adults. Hum Brain Mapp 2014.
Dahiya S, Irish BP, Nonnemacher MR, Wigdahl B. Genetic variation and HIV-associated neurologic disease. Adv Virus Res. 2013;87:183.
Van Manen D, van't Wout AB, Schuitemaker H. Genome-wide association studies on HIV susceptibility, pathogenesis and pharmacogenomics. Retrovirology. 2012;9:70.
Chang L, Andres M, Sadino J, Jiang CS, Nakama H, Miller E, et al. Impact of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 and HIV on cognition and brain atrophy: antagonistic pleiotropy and premature brain aging. Neuroimage. 2011;58:1017.
Chang L, Jiang C, Cunningham E, Buchthal S, Douet V, Andres M, et al. Effects of APOE epsilon4, age, and HIV on glial metabolites and cognitive deficits. Neurology. 2014;82:2213.
Hoare J, Fouche JP, Phillips N, Joska JA, Donald KA, Thomas Ket al.: Clinical associations of white matter damage in cART-treated HIV-positive children in South Africa. J Neurovirol 2015.
Nakamoto BK, Jahanshad N, McMurtray A, Kallianpur KJ, Chow DC, Valcour VG, et al. Cerebrovascular risk factors and brain microstructural abnormalities on diffusion tensor images in HIV-infected individuals. J Neurovirol. 2012;18:303.
Wright PW, Vaida FF, Fernandez RJ, Rutlin J, Price RW, Lee E, et al. Cerebral white matter integrity during primary HIV infection. AIDS. 2015;29:433.
Kamat R, Brown GG, Bolden K, Fennema-Notestein C, Archibald S, Marcotte TD, et al. Apathy is associated with white matter abnormalities in anterior, medial brain regions in persons with HIV infection. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2014;36:854.
Ernst T, Yakupov R, Nakama H, Crocket G, Cole M, Watters M, et al. Declined neural efficiency in cognitively stable human immunodeficiency virus patients. Ann Neurol. 2009;65:316.
van den Heuvel MP, Hulshoff Pol HE. Exploring the brain network: a review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;20:519.
Thomas JB, Brier MR, Snyder AZ, Vaida FF, Ances BM. Pathways to neurodegeneration: effects of HIV and aging on resting-state functional connectivity. Neurology. 2013;80:1186.
Ances BM, Hammoud DA. Neuroimaging of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2014;9:545.
Weiner MW, Veitch DP, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Cairns NJ, Green RC, et al. The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: a review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:e111.
Weiner M, Veitcha DP, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Cairns NJ, Cedarbaum J, et al.: Impact of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, 2004–2014. 2015; Submitted.
Jahanshad N, Kochunov PV, Sprooten E, Mandl RC, Nichols TE, Almasy L, et al. Multi-site genetic analysis of diffusion images and voxelwise heritability analysis: a pilot project of the ENIGMA-DTI working group. Neuroimage. 2013;81:455.
Stein JL, Medland SE, Vasquez AA, Hibar DP, Senstad RE, Winkler AM, et al. Identification of common variants associated with human hippocampal and intracranial volumes. Nat Genet. 2012;44:552.
van Erp TGM, Hibar DP, Rasmussen JM, Glahn DC, D.Pearlson G, Andreassen OA, et al.: Subcortical brain volume abnormalities in 2,028 patients with schizophrenia and 2,540 healthy controls via the ENIGMA consortium. Mol Psychiatry 2015; In Press.
Hibar DP, Westlye LT, Erp TGMv, Rasmussen J, Leonardo CD, Haukvik UK, et al.: Robust subcortical volumetric reductions in bipolar disorder: findings from the ENIGMA bipolar disorder working group including 1,745 cases and 2,613 controls. JAMA Psychiatry 2015; In Press.
Schmaal L, Veltman DJ, Erp TGMv, Sämann P, Frodl T, Jahanshad N, et al.: Subcortical brain volume abnormalities in major depressive disorder: prospective meta-analytic findings from the ENIGMA major depressive disorder working group including 1,808 cases and 7,223 controls. Molecular Psychiatry 2015; In Submission.
Fouche J, Jahanshad N, Ching C, Joska J, Paul R, Hoare J, et al. A meta-analysis by the ENIGMA-HIV working group: CD4 counts predict subcortical volume loss in HIV-positive individuals. Honolulu, Hawaii: Organization for Human Brain Mapping annual meeting; 2015.
Acknowledgments
PT and NJ are supported in part by grants from the NIH, including the NIH Big Data to Knowledge (BD2K) Initiative under U54 EB020403 (PI: Thompson); Neurodevelopment and imaging among HIV-infected Children from the PREDICT study, R01 MH089722; Predicting Brain Changes in HIV/AIDS, R01 NS080655; and Determinants of Resilience in Youth with HIV Infection and Youth Affected by HIV, R01 MH102151.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Paul Thompson and Neda Jahanshad declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Central Nervous System and Cognition
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, P.M., Jahanshad, N. Novel Neuroimaging Methods to Understand How HIV Affects the Brain. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 12, 289–298 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11904-015-0268-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11904-015-0268-6