Abstract
Purpose of Review
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a global public health issue. While cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma commonly affect patients with chronic HBV, extrahepatic manifestations are often unappreciated.
Recent Findings
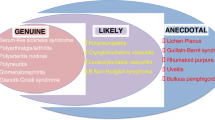
Extrahepatic manifestations can be variable in presentation but include several commonly described syndromes including HBV-related nephropathy, vasculitides, dermatitis, and arthritis. However, recently described entities include hematologic and neurologic manifestations.
Summary
The primary immune-mediated mechanism common to many extrahepatic manifestations involves viral antigen-triggered immune complex formation. Initiation of antiviral treatment is associated with clinical response in most cases of extrahepatic disease; thus, recognition of these manifestations is essential to mitigating associated morbidity and mortality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Vyas AK, Lslam M, Garg G, Singh AK, Trehanpati N. Humoral immune responses and hepatitis B infection. Dig Dis. 2021;39(5):516–25. https://doi.org/10.1159/000514274.
Yuen M-F, Chen D-S, Dusheiko GM, Janssen HLA, Lau DTY, Locarnini SA, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4(1):18035. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.35.
Sheena BS, Hiebert L, Han H, Ippolito H, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abbasi-Kangevari Z, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of hepatitis B, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7(9):796–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00124-8.
Rehermann B, Nascimbeni M. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(3):215–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1573.
Jennette JC, Falk R, Bacon P, Basu N, Cid M, Ferrario F, et al. 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. 2013.
Guillevin L, Mahr A, Callard P, Godmer P, Pagnoux C, Leray E, et al. Hepatitis B virus-associated polyarteritis nodosa: clinical characteristics, outcome, and impact of treatment in 115 patients. Medicine. 2005;84(5):313–22. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.md.0000180792.80212.5e.
Hočevar A, Tomšič M, Perdan PK. Clinical approach to diagnosis and therapy of polyarteritis nodosa. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(3):14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-021-00983-2.
Wang CR, Tsai HW. Human hepatitis viruses-associated cutaneous and systemic vasculitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27(1):19–36. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i1.19.
Pagnoux C, Seror R, Henegar C, Mahr A, Cohen P, Le Guern V, et al. Clinical features and outcomes in 348 patients with polyarteritis nodosa: a systematic retrospective study of patients diagnosed between 1963 and 2005 and entered into the French vasculitis study group database. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(2):616–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27240.
Trepo C, Guillevin LC. Polyarteritis nodosa and extrahepatic manifestations of HBV infection: the case against autoimmune intervention in pathogenesis. J Autoimmun. 2001;16(3):269–74. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaut.2000.0502.
Naniwa T, Maeda T, Shimizu S, Ito R. Hepatitis B virus-related polyarteritis nodosa presenting with multiple lung nodules and cavitary lesions. Chest. 2010;138(1):195–7. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.09-2579.
Nemoto M, Nishioka K, Fukuoka J, Aoshima M. Hepatitis B virus-associated vasculitis: multiple cavitary masses in the lung mimicking granulomatous polyangiitis. Intern Med. 2019;58(20):3013–7. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.3012-19.
Shields LBE, Burge M, Hunsaker JC. Sudden death due to polyarteritis nodosa. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2012;8(3):290–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-011-9290-1.
Iino T, Eguchi K, Sakai M, Nagataki S, Ishijima M, Toriyama K. Polyarteritis nodosa with aortic dissection: necrotizing vasculitis of the vasa vasorum. J Rheumatol. 1992;19(10):1632–6.
Sergent JS, Lockshin MD, Christian CL, Gocke DJ. Vasculitis with hepatitis B antigenemia: long-term Observations in Nine Patients. Medicine. 1976;55(1):1–18.
Duffy J, Lidsky MD, Sharp JT, Davis JS, Person DA, Hollinger FB, et al. Polyarthritis, polyarteritis and hepatitis B. Medicine. 1976;55(1):19–37.
Shusterman N, London WT. Hepatitis B and immune-complex disease. N Engl J Med. 1984;310(1):43–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198401053100110.
Guillevin L, Lhote F, Cohen P, Sauvaget F, Jarrousse B, Lortholary O, et al. Polyarteritis nodosa related to hepatitis B virus. A prospective study with long-term observation of 41 patients. Medicine. 1995;74(5):238–53. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005792-199509000-00002.
Michalak T. Immune complexes of hepatitis B surface antigen in the pathogenesis of periarteritis nodosa. A study of seven necropsy cases. Am J Pathol. 1978;90(3):619–32.
Fye KH, Becker MJ, Theofilopoulos AN, Moutsopoulos H, Feldman JL, Talal N. Immune complexes in hepatitis B antigen-associated periarteritis nodosa. Detection by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and the Raji cell assay. Am J Med. 1977;62(5):783–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(77)90884-1.
Gocke D, Hsu K, Morgan C, Bombardieri S, Lockshin M, Christian C. Association between polyarteritis and Australian antigen. Lancet. 1970;296(7684):1149–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(70)90339-9.
Sergent JS. Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis B infection. Bull Rheum Dis. 1983;33(6):1–6.
Rogers RB, Graham Smith JJ, Chalker DK. Hepatitis and the skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7(4):552–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(82)80257-0.
Mirise RT, Kitridou RC. Arthritis and hepatitis. West J Med. 1979;130(1):12–7.
Janssen HL, van Zonneveld M, van Nunen AB, Niesters HG, Schalm SW, de Man RA. Polyarteritis nodosa associated with hepatitis B virus infection. The role of antiviral treatment and mutations in the hepatitis B virus genome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;16(8):801–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.meg.0000108362.41221.57.
Tang MBY, Liew KVS, Ng PPL, Tan SH, Ng SK. Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa associated with precore mutant hepatitis B infection. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149(4):914–5. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05538.x.
Wartelle-Bladou C, Lafon J, Trépo C, Pichoud C, Picon M, Pellissier J-F, et al. Successful combination therapy of polyarteritis nodosa associated with a pre-core promoter mutant hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2001;34(5):774–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(00)00088-X.
Miguelez M, Bueno J, Laynez P. Polyarteritis nodosa associated with precore mutant hepatitis B virus infection. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57(3):173. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.57.3.173.
Dienstag JL. Immunopathogenesis of the extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis B virus infection. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1981;3(4):461–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01951493.
McElgunn PSJ. Dermatologic manifestations of hepatitis B virus infection. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1983;8(4):539–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(83)80058-9.
Stone JH. Polyarteritis nodosa. JAMA. 2002;288(13):1632–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.288.13.1632.
Hekali P, Kajander H, Pajari R, Stenman S, Somer T. Diagnostic significance of angiographically observed visceral aneurysms with regard to polyarteritis nodosa. Acta Radiol. 1991;32(2):143–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/028418519103200212.
Puéchal X. Polyarteritis nodosa: state of the art. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(4):105320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2021.105320.
Howard T, Ahmad K, Swanson JA, Misra S. Polyarteritis nodosa. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;17(4):247–51. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.tvir.2014.11.005.
Frohnert PP, Sheps SG. Long-term follow-up study of periarteritis nodosa. Am J Med. 1967;43(1):8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(67)90144-1.
Pinto PC, Hu E, Bernstein-Singer M, Pinter-Brown L, Govindarajan S. Acute hepatic injury after the withdrawal of immunosuppressive chemotherapy in patients with hepatitis B. Cancer. 1990;65(4):878–84.
Lam KC, Lai CL, Ng RP, Trepo C, Wu PC. Deleterious effect of prednisolone in HBsAg-positive chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1981;304(7):380–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198102123040702.
Guillevin L, Lhote F, Leon A, Fauvelle F, Vivitski L, Trepo C. Treatment of polyarteritis nodosa related to hepatitis B virus with short term steroid therapy associated with antiviral agents and plasma exchanges. A prospective trial in 33 patients. J Rheumatol. 1993;20(2):289–98.
Guillevin L, Lhote F, Sauvaget F, Deblois P, Rossi F, Levallois D, et al. Treatment of polyarteritis nodosa related to hepatitis B virus with interferon-alpha and plasma exchanges. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994;53(5):334–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.53.5.334.
Guillevin L, Mahr A, Cohen P, Larroche C, Queyrel V, Loustaud-Ratti V, et al. Short-term corticosteroids then lamivudine and plasma exchanges to treat hepatitis B virus–related polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Care Res. 2004;51(3):482–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20401.
Kruger M, Böker KH, Zeidler H, Manns MP. Treatment of hepatitis B-related polyarteritis nodosa with famciclovir and interferon alfa-2b. J Hepatol. 1997;26(4):935–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80263-2.
Erhardt A, Sagir A, Guillevin L, Neuen-Jacob E, Häussinger D. Successful treatment of hepatitis B virus associated polyarteritis nodosa with a combination of prednisolone, α-interferon and lamivudine. J Hepatol. 2000;33(4):677–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(00)80025-2.
Combes B, Shorey J, Barrera A, Stastny P, Eigenbrodt EH, Hull AR, et al. Glomerulonephritis with deposition of Australia antigen-antibody complexes in glomerular basement membrane. Lancet. 1971;2(7718):234–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92572-4.
Bhimma R, Coovadia HM. Hepatitis B virus-associated nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 2004;24(2):198–211. https://doi.org/10.1159/000077065.
Shah AS, Amarapurkar DN. Spectrum of hepatitis B and renal involvement. Liver Int. 2018;38(1):23–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13498.
Kupin WL. Viral-associated GN: hepatitis B and other viral infections. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(9):1529–33. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.09180816.
Wang R, Wu Y, Zheng B, Zhang X, An D, Guo N, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of hepatitis B associated membranous nephropathy and idiopathic membranous nephropathy complicated with hepatitis B virus infection. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):18407. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98010-y.
Jiang W, Liu T, Dong H, Xu Y, Liu LQ, Guan GJ, et al. Relationship between serum DNA replication, clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis with severe proteinuria by lamivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy. Biomed Environ Sci. 2015;28(3):206–13. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2015.027.
Fu B, Ji Y, Hu S, Ren T, Bhuva MS, Li G, et al. Efficacy and safety of anti-viral therapy for Hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0227532. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227532. Meta-analysis of seven clinical trials with 182 participants examining efficacy and safety of NRTI's and interferon therapy for HBV-GN
Takekoshi Y, Tanaka M, Miyakawa Y, Yoshizawa H, Takahashi K, Mayumi M. Free small and IgG-associated large hepatitis B e antigen in the serum and glomerular capillary walls of two patients with membranous glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1979;300(15):814–9. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm197904123001502.
Chen L, Wu C, Fan X, Gao J, Yin H, Wang T, et al. Replication and infectivity of hepatitis B virus in HBV-related glomerulonephritis. Int J Infect Dis. 2009;13(3):394–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2008.08.014.
Lai KN, Lai FM, Lo S, Ho CP, Chan KW. IgA nephropathy associated with hepatitis B virus antigenemia. Nephron. 1987;47(2):141–3. https://doi.org/10.1159/000184477.
Zhang L, Meng H, Han X, Han C, Sun C, Ye F, et al. The relationship between HBV serum markers and the clinicopathological characteristics of hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis (HBV-GN) in the northeastern chinese population. Virol J. 2012;9(1):200. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-9-200.
Gupta A, Quigg RJ. Glomerular diseases associated with hepatitis B and C. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015;22(5):343–51. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2015.06.003.
Hirose H, Udo K, Kojima M, Takahashi Y, Miyakawa Y, Miyamoto K, et al. Deposition of hepatitis B e antigen in membranous glomerulonephritis: identification by F(ab')2 fragments of monoclonal antibody. Kidney Int. 1984;26(3):338–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1984.178.
Zhu HL, Li X, Li J, Zhang ZH. Genetic variation of occult hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(13):3531–46. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3531.
Gherlan GS. Occult hepatitis B—the result of the host immune response interaction with different genomic expressions of the virus. World J Clin Cases. 2022;10(17):5518–30. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5518.
Yu F, Li G, Hao W, Hu W. Hepatitis B virus-related glomerulonephritis with positive and negative serum HBsAg: different clinicopathologic characteristics of two clinical subtypes. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14:3069–77. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.S318087. Retrospective review of 101 renal biopsies of patients with HBV-GN showing that serum HBsAg positivity is associated with a more severe disease course
Lai KN, Ho RTH, Tam JS, Lai FM. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA and RNA in kidneys of HBV-related glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1996;50(6):1965–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1996.519.
Diao Z, Ding J, Yin C, Wang L, Liu W. Purified hepatitis B virus induces human Mesangial cell proliferation and extracellular matrix expression In Vitro. Virol J. 2013;10(1):300. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-422X-10-300.
KDIGO. 2021 Clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 2021;100(4s):S1–s276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.05.021.
Lai KN, Li PKT, Lui SF, Au TC, Tam JSL, Tong KL, et al. Membranous nephropathy related to hepatitis B virus in adults. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(21):1457–63. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199105233242103.
Huang C-W, Lin C-H, Chuang Y-W, Yang S-S, Lee T-Y, Yeh H-Z, et al. Association of hepatitis B virus infection and glomerulonephritis in a HBV-endemic area: a population-based study. Adv Dig Med. 2018;5(4):121–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/aid2.13092.
Su C-W. Hepatitis B virus and glomerulonephritis: two silent killers. Adv Dig Med. 2018;5(4):111–2. https://doi.org/10.1002/aid2.13100.
Lai KN, Lai FM, Tam JS, Vallance-Owen J. Strong association between IgA nephropathy and hepatitis B surface antigenemia in endemic areas. Clin Nephrol. 1988;29(5):229–34.
Iida H, Izumino K, Asaka M, Fujita M, Takata M, Sasayama S. IgA nephropathy and hepatitis B virus. IgA nephropathy unrelated to hepatitis B surface antigenemia. Nephron. 1990;54(1):18–20. https://doi.org/10.1159/000185803.
Elewa U, Sandri AM, Kim WR, Fervenza FC. Treatment of hepatitis B virus-associated nephropathy. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;119(1):c41–9; discussion c9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324652.
Wang NS, Wu ZL, Zhang YE, Liao LT. Existence and significance of hepatitis B virus DNA in kidneys of IgA nephropathy. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(5):712–6. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i5.712.
Lai FM, Li PK, Suen MW, Lui SF, Lai KN. Crescentic glomerulonephritis related to hepatitis B virus. Mod Pathol. 1992;5(3):262–7.
Nasri H, Mubarak M. Sudden deterioration of renal function in a patient with nephrotic syndrome and a very high hepatitis B viral DNA load. J Renal Inj Prev. 2012;1(1):39–41. https://doi.org/10.12861/jrip.2012.14.
Mareddy AS, Rangaswamy D, Vankalakunti M, Attur RP, Nagaraju SP, Koti N. Immune mediated crescentic MPGN secondary to HBV infection: a rare presentation for a common infection. Australas Med J. 2016;9(1):12–6. https://doi.org/10.4066/amj.2015.2568.
Li S-j, Xu S-t, Chen H-p, Zhang M-c, Xu F, Cheng S-q, et al. Clinical and morphologic spectrum of renal involvement in patients with HBV-associated cryoglobulinaemia. Nephrology. 2017;22(6):449–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.12795.
Mazzaro C, Dal Maso L, Gragnani L, Visentini M, Saccardo F, Filippini D, et al. Hepatitis B virus-related cryoglobulinemic vasculitis: review of the literature and long-term follow-up analysis of 18 patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues from the Italian Study Group of Cryoglobulinemia (GISC). Viruses. 2021;13(6) https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061032.
Sakai K, Morito N, Usui J, Hagiwara M, Hiwatashi A, Fukuda K, et al. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis as a complication of hepatitis B virus infection. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;26(1):371–3. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq600.
Unverdi S, Ceri M, Köklü S, Unverdi H, Koçak E, Duranay M. Tenofovir as a first line option for prophylaxis in a patient with hepatitis B virus associated nephrotic syndrome. Ann Hepatol. 2011;10(3):372–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31554-6.
Harzallah A, Rahma K, Hafedh H, Mariem H, Rim G, Fethi BH, Imen G, Ezzeddine A. Hepatitis B virus-associated focal and segmental glomerular sclerosis: a rare case of tip variant. Clin Case Rep J. 2022;3(4):1–5.
Zhou T-B, Jiang Z-P. Is there an association of hepatitis B virus infection with minimal change disease of nephrotic syndrome? A clinical observational report. Ren Fail. 2015;37(3):459–61. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2014.1001711.
Fabrizi F, Dixit V, Martin P. Meta-analysis: anti-viral therapy of hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24(5):781–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03041.x.
Yi Z, Wei Jie Y, Nan Z. The efficacy of anti-viral therapy on hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hepatol. 2011;10(2):165–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31565-0.
Yang Y, Ma Y-p, Chen D-p, Zhuo L, Li W-g. A meta-analysis of antiviral therapy for hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy. PLoS One. 2016;11(9):e0160437. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160437.
Sun IO, Hong YA, Park HS, Choi SR, Chung BH, Park CW, et al. Experience of anti-viral therapy in hepatitis B-associated membranous nephropathy, including Lamivudine-resistant strains. Korean J Intern Med. 2012;27(4):411–6. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2012.27.4.411.
Cozzani E, Herzum A, Burlando M, Parodi A. Cutaneous manifestations of HAV, HBV, HCV. Ital J Dermatol Venereol. 2021;156:5–12. https://doi.org/10.23736/S2784-8671.19.06488-5.
Jones AM, Warken K, Tyring SK. The cutaneous manifestations of viral hepatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20(2):233–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0733-8635(01)00010-9.
Csepregi A, Nemesanszky E, Rojkovich B, Poor G. Rheumatoid arthritis and hepatitis B virus: evaluating the pathogenic link. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(3):474–7.
Scully LJ, Karayiannis P, Thomas HC. Interferon therapy is effective in treatment of hepatitis B-induced polyarthritis. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37(11):1757–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01299871.
Kikuchi K, Fukuda K, Hayashi S, Maeda T, Takashima Y, Fujita M, et al. Polyarthritis presented in a patient with untreated chronic hepatitis B infection. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2022;7(1):320–3. https://doi.org/10.1093/mrcr/rxac075.
Hsu CS, Lang HC, Huang KY, Lin HH, Chen CL. Association of rheumatoid arthritis and hepatitis B Infection: a nationwide nested case-control study from 1999 to 2009 in Taiwan. Medicine. 2016;95(18):e3551. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000003551.
Chen Y-L, Jing J, Mo Y-Q, Ma J-D, Yang L-J, Chen L-F, et al. Presence of hepatitis B virus in synovium and its clinical significance in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1623-y.
Zheng B, Li T, Lin Q, Huang Z, Wang M, Deng W, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and its association with HLA-B27: a retrospective study from south China. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(7):2011–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-1934-7.
Mihas AA, Kirby JD, Kent SP. Hepatitis B antigen and polymyositis. JAMA. 1978;239(3):221–2. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1978.03280300053021.
Bacon PA, Doherty SM, Zuckerman AJ. Hepatitis-B antibody in polymyalgia Rheumatica. Lancet. 1975;2(7933):476–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90547-4.
Elling H, Skinhøj P, Elling P. Hepatitis B virus and polymyalgia rheumatica: a search for HBsAg, HBsAb, HBcAb, HBeAg, and HBeAb. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980;39(5):511–3. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.39.5.511.
Levo Y, Gorevic PD, Kassab HJ, Zucker-Franklin D, Franklin EC. Association between hepatitis B virus and essential mixed cryoglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1977;296(26):1501–4. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm197706302962605.
Mazzaro C, Bomben R, Visentini M, Gragnani L, Quartuccio L, Saccardo F, et al. Hepatitis B virus-infection related cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Clinical manifestations and the effect of antiviral therapy: A review of the literature. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1095780. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1095780. Review of clinical manifestations and treatment of HBV-related cryoglobulinemia
Alfraji N, Upadhyaya VD, Bekampis C, Kuzyshyn H. Mixed Cryoglobulinemia syndrome (MCS) due to untreated hepatitis B with uncommon presentation: case report and literature review. BMC Rheumatol. 2020;4(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41927-020-00159-y.
Viganò M, Martin P, Cappelletti M, Fabrizi F. HBV-associated cryoglobulinemic vasculitis: remission after antiviral therapy with entecavir. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014;39(1):65–73. https://doi.org/10.1159/000355778.
Popp JW Jr, Harrist TJ, Dienstag JL, Bhan AK, Wands JR, LaMont JT, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis associated with acute and chronic hepatitis. Arch Intern Med. 1981;141(5):623–9.
Moro F, Fania L, Sinagra JLM, Salemme A, Di Zenzo G. Bullous pemphigoid: trigger and predisposing factors. Biomolecules. 2020;10(10):1432.
Lai YR, Chang YL, Lee CH, Tsai TH, Huang KH, Lee CY. Risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma among patients with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis c virus in Taiwan: a nationwide cohort study. Cancers. 2022;14(3) https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030583. Large Taiwanese cohort study examining the risk of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma in 37,656 patients with HBV
Ulcickas Yood M, Quesenberry CP Jr, Guo D, Caldwell C, Wells K, Shan J, et al. Incidence of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma among individuals with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2007;46(1):107–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21642.
Dogan B. Dermatological manifestations in hepatitis B surface antigen carriers in east region of Turkey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005;19(3):323–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.01185.x.
Song J, Zhang Z, Ji X, Su S, Liu X, Xu S, et al. Lack of evidence of hepatitis in patients with oral lichen planus in China: a case control study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016;21(2):e161–8. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.20812.
Bokor-Bratic M. Lack of evidence of hepatic disease in patients with oral lichen planus in Serbia. Oral Dis. 2004;10(5):283–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-0825.2004.01029.x.
Nath A, Agarwal R, Malhotra P, Varma S. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern Med J. 2010;40(9):633–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-5994.2009.02060.x.
Su T-H, Liu C-J, Tseng T-C, Chou S-W, Liu C-H, Yang H-C, et al. Chronic hepatitis B is associated with an increased risk of B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49(5):589–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.15132.
Cheng CL, Huang SC, Chen JH, Wei CH, Fang WQ, Su TH, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen positivity is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. Oncologist. 2020;25(9):793–802. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0756. Retrospective cohort study evaluating chronic hepatitis B as a prognostic marker in DLBCL
Marcucci F, Spada E, Mele A, Caserta CA, Pulsoni A. The association of hepatitis B virus infection with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma - a review. Am J Blood Res. 2012;2(1):18–28.
Gonzalez Casas R, Garcia-Buey L, Jones EA, Gisbert JP, Moreno-Otero R. Systematic review: hepatitis-associated aplastic anaemia—a syndrome associated with abnormal immunological function. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;30(5):436–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04060.x.
Hendren N, Moore J, Hofmann S, Rambally S. Resolution of acute hepatitis B-associated aplastic anaemia with antiviral therapy. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-221503.
Zeldis JB, Mugishima H, Steinberg HN, Nir E, Gale RP. In vitro hepatitis B virus infection of human bone marrow cells. J Clin Invest. 1986;78(2):411–7. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI112591.
Yimam KK, Merriman RB, Todd FR. A rare case of acute hepatitis B virus infection causing guillain-barré syndrome. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;9(2):121–3.
Wei J, Duan S. Severe Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with chronic hepatitis B: A case report and literature review. Medicine. 2021;100(48):e27989. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000027989. Literature review of Guillan-Barre syndrome association with HBV infection
Tsukada N, Koh C-S, Inoue A, Yanagisawa N. Demyelinating neuropathy associated with hepatitis B virus infection: detection of immune complexes composed of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J Neurol Sci. 1987;77(2):203–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510X(87)90123-7.
Penner E, Maida E, Mamoli B, Gangl A. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid immune complexes containing hepatitis B surface antigen in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1982;82(3):576–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5085(82)80411-3.
Cacoub P, Terrier B. Hepatitis B-related autoimmune manifestations. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009;35(1):125–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2009.03.006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Najafian declares that she has no conflict of interest. Dr. Han declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Najafian, N., Han, SH. Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis B. Curr Hepatology Rep 22, 147–157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-023-00603-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-023-00603-w