Abstract
Purpose of Review
HBsAg has been an important serological marker for the diagnosis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Recently, HBsAg quantification has been utilized to predict the disease activity and the response to antiviral treatment. This review aims to update the clinical utility of HBsAg quantification in the management of chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
Recent Findings
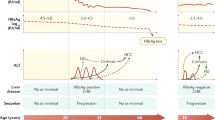
HBsAg level varies across different phases of the natural history of CHB, highest in the immune-tolerant phase and lowest in inactive carriers. HBsAg level is useful to stratify the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in low-viremic patients. HBsAg level also helps predict the HBsAg loss in HBeAg-negative patients. Moreover, baseline level and on-treatment kinetics of HBsAg are associated with the treatment response to pegylated interferon and nucleos(t)ide analogs in both HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative patients. Finally, HBsAg level can serve as a therapeutic endpoint marker for evaluating novel curative agents against HBV infection.
Summary
HBsAg quantification can help guide the management of CHB.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Blumberg BS, Gerstley BJ, Hungerford DA, London WT, Sutnick AI. A serum antigen (Australia antigen) in Down's syndrome, leukemia, and hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1967;66(5):924–31.
Kao JH, Chen DS. Global control of hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2(7):395–403.
• Raimondo G, Locarnini S, Pollicino T, Levrero M, Zoulim F, Lok AS et al. Update of the statements on biology and clinical impact of occult hepatitis b virus infection. J Hepatol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.034. Important consensus for occult hepatitis B infection with updated definition, biology, diagnosis, treatments, special topics and future research.
Kao JH. Role of viral factors in the natural course and therapy of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol Int. 2007;1(4):415–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-007-9033-2.
Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373(9663):582–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60207-5.
Kao JH, Chen PJ, Chen DS. Recent advances in the research of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiologic and molecular biological aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 2010;108:21–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-380888-2.00002-9.
•• Cornberg M, Wong VW, Locarnini S, Brunetto M, Janssen HLA, Chan HL. The role of quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen revisited. J Hepatol. 2017;66(2):398–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.08.009 Extensive review of the role of qHBsAg considering the role in HBV infection and the prediction of treatment response.
•• Revill PA, Chisari FV, Block JM, Dandri M, Gehring AJ, Guo H, et al. A global scientific strategy to cure hepatitis B. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30119-0 Shed light on the current and potential treatment strategies throughout HBV lifecycle.
Seeger C, Mason WS. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection. Virology. 2015;479–480:672–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.031.
Mason WS, Gill US, Litwin S, Zhou Y, Peri S, Pop O, et al. HBV DNA integration and clonal hepatocyte expansion in chronic hepatitis B patients considered immune tolerant. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(5):986–98e4. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.012.
Thompson AJ, Nguyen T, Iser D, Ayres A, Jackson K, Littlejohn M, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers: disease phase influences correlation with viral load and intrahepatic hepatitis B virus markers. Hepatology. 2010;51(6):1933–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23571.
Manesis EK, Papatheodoridis GV, Tiniakos DG, Hadziyannis ES, Agelopoulou OP, Syminelaki T, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen: relation to hepatitis B replication parameters in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2011;55(1):61–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.10.027.
Yang HC, Kao JH. Revisiting the natural history of chronic HBV infection. Curr Hepatol Rep. 2016;15(3):141–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-016-0304-z.
McMahon BJ, Holck P, Bulkow L, Snowball M. Serologic and clinical outcomes of 1536 Alaska natives chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(9):759–68.
Chu CM, Liaw YF. HBsAg seroclearance in asymptomatic carriers of high endemic areas: appreciably high rates during a long-term follow-up. Hepatology. 2007;45(5):1187–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21612.
Kim JH, Lee JH, Park SJ, Bae MH, Kim JH, Kim do Y, et al. factors associated with natural seroclearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and prognosis after seroclearance: a prospective follow-up study. Hepato-gastroenterology. 2008;55(82–83):578–81.
Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Lu SN, Jen CL, Wang LY, et al. Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: a community-based follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(2):474–82. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.048.
Simonetti J, Bulkow L, McMahon BJ, Homan C, Snowball M, Negus S, et al. Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 2010;51(5):1531–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23464.
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Su TH, Wang CC, Chen CL, Chen PJ, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels predict surface antigen loss in hepatitis B e antigen seroconverters. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(2):517–25, 25 e1–2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.046.
•• Yeo YH, Ho HJ, Yang HI, Tseng TC, Hosaka T, Trinh HN, et al. Factors Associated With Rates of HBsAg Seroclearance in Adults With Chronic HBV Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(3):635–46 e9. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.027 Provide updated data through large scale meta-analysis for HBsAg seroclerance rate and factors associated with HBsAg seroclerance.
Chan HL, Wong VW, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HY, Sung JJ. A longitudinal study on the natural history of serum hepatitis B surface antigen changes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;52(4):1232–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23803.
Jaroszewicz J, Calle Serrano B, Wursthorn K, Deterding K, Schlue J, Raupach R, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infection: a European perspective. J Hepatol. 2010;52(4):514–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.01.014.
Nguyen T, Thompson AJ, Bowden S, Croagh C, Bell S, Desmond PV, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen levels during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B: a perspective on Asia. J Hepatol. 2010;52(4):508–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.01.007.
New insights into HBV replication: new opportunities for improved therapies.
Brunetto MR, Oliveri F, Colombatto P, Moriconi F, Ciccorossi P, Coco B, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen serum levels help to distinguish active from inactive hepatitis B virus genotype D carriers. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(2):483–90. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.052.
Brouwer WP, Chan HL, Brunetto MR, Martinot-Peignoux M, Arends P, Cornberg M, et al. Repeated measurements of hepatitis B surface antigen identify carriers of inactive HBV during long-term follow-up. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(10):1481–9e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2016.01.019.
Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Jen CL, Batrla-Utermann R, Lu SN, et al. Serum levels of hepatitis B surface antigen and DNA can predict inactive carriers with low risk of disease progression. Hepatology. 2016;64(2):381–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28552.
Lin LY, Wong VW, Zhou HJ, Chan HY, Gui HL, Guo SM, et al. Relationship between serum hepatitis B virus DNA and surface antigen with covalently closed circular DNA in HBeAg-negative patients. J Med Virol. 2010;82(9):1494–500. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.21863.
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Yang WT, Chen CL, Yang HC, Su TH, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen level complements viral load in predicting viral reactivation in spontaneous HBeAg seroconverters. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29(6):1242–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12502.
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295(1):65–73. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.295.1.65.
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Yang HC, Su TH, Wang CC, Chen CL, et al. High levels of hepatitis B surface antigen increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low HBV load. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(5):1140–9 e3; quiz e13–4. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.02.007.
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Yang HC, Su TH, Wang CC, Chen CL, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels help predict disease progression in patients with low hepatitis B virus loads. Hepatology. 2013;57(2):441–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26041.
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Yang HC, Su TH, Wang CC, Chen CL, et al. Determinants of spontaneous surface antigen loss in hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients with a low viral load. Hepatology. 2012;55(1):68–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24615.
Chan HL, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HY, Wong VW. Viral determinants of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients. J Infect Dis. 2011;204(3):408–14. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jir283.
Liu J, Lee MH, Batrla-Utermann R, Jen CL, Iloeje UH, Lu SN, et al. A predictive scoring system for the seroclearance of HBsAg in HBeAg-seronegative chronic hepatitis B patients with genotype B or C infection. J Hepatol. 2013;58(5):853–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.12.006.
Sun J, Ma H, Xie Q, Xie Y, Sun Y, Wang H, et al. Response-guided peginterferon therapy in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomized controlled study. J Hepatol. 2016;65(4):674–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.024.
Chan HL, Wong VW, Chim AM, Chan HY, Wong GL, Sung JJ. Serum HBsAg quantification to predict response to peginterferon therapy of e antigen positive chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(11–12):1323–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04474.x.
Sonneveld MJ, Hansen BE, Piratvisuth T, Jia JD, Zeuzem S, Gane E, et al. Response-guided peginterferon therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels. Hepatology. 2013;58(3):872–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26436.
Marcellin P, Bonino F, Yurdaydin C, Hadziyannis S, Moucari R, Kapprell HP, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen levels: association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative patients. Hepatol Int. 2013;7(1):88–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-012-9343-x.
Brunetto MR, Moriconi F, Bonino F, Lau GK, Farci P, Yurdaydin C, et al. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen levels: a guide to sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009;49(4):1141–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22760.
Brunetto MR, Marcellin P, Cherubini B, Yurdaydin C, Farci P, Hadziyannis SJ, et al. Response to peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) in HBeAg-negative CHB: on-treatment kinetics of HBsAg serum levels vary by HBV genotype. J Hepatol. 2013;59(6):1153–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.017.
Rijckborst V, Hansen BE, Cakaloglu Y, Ferenci P, Tabak F, Akdogan M, et al. Early on-treatment prediction of response to peginterferon alfa-2a for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B using HBsAg and HBV DNA levels. Hepatology. 2010;52(2):454–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23722.
Marcellin P, Buti M, Krastev Z, de Man RA, Zeuzem S, Lou L, et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen loss in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. J Hepatol. 2014;61(6):1228–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.019.
•• Liu J, Li T, Zhang L, Xu A. The Role of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Cessation among Asian Chronic Hepatitis B Patients: A Systematic Review. Hepatology. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30474. Systemic review for optimal cutoff value in EOT HBsAg level regarding NA cessation.
Lo GH. Therapy of hepatitis B: is it really not associated with HBsAg seroclearance ? Gastroenterology. 2019;157:267. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.069.
Piratvisuth T, Marcellin P, Popescu M, Kapprell HP, Rothe V, Lu ZM. Hepatitis B surface antigen: association with sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients. Hepatol Int. 2013;7(2):429–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-011-9280-0.
Sonneveld MJ, Rijckborst V, Boucher CA, Hansen BE, Janssen HL. Prediction of sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2b for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using on-treatment hepatitis B surface antigen decline. Hepatology. 2010;52(4):1251–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23844.
Rijckborst V, Hansen BE, Ferenci P, Brunetto MR, Tabak F, Cakaloglu Y, et al. Validation of a stopping rule at week 12 using HBsAg and HBV DNA for HBeAg-negative patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a. J Hepatol. 2012;56(5):1006–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.007.
Chevaliez S, Hezode C, Bahrami S, Grare M, Pawlotsky JM. Long-term hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) kinetics during nucleoside/nucleotide analogue therapy: finite treatment duration unlikely. J Hepatol. 2013;58(4):676–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.11.039.
Wooddell CI, Yuen MF, Chan HL, Gish RG, Locarnini SA, Chavez D et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(409). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aan0241.
Zoulim F, Carosi G, Greenbloom S, Mazur W, Nguyen T, Jeffers L, et al. Quantification of HBsAg in nucleos(t)ide-naive patients treated for chronic hepatitis B with entecavir with or without tenofovir in the BE-LOW study. J Hepatol. 2015;62(1):56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.031.
Wursthorn K, Jung M, Riva A, Goodman ZD, Lopez P, Bao W, et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen decline during 3 years of telbivudine treatment in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients. Hepatology. 2010;52(5):1611–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23905.
Jeng WJ, Chen YC, Chang ML, Liaw YF. Alpha-fetoprotein level-dependent early hepatitis B surface antigen decline during entecavir therapy in chronic hepatitis B with hepatitis flare. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(6):1601–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkw019.
Chen YC, Jeng WJ, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Decreasing levels of HBsAg predict HBsAg seroclearance in patients with inactive chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10(3):297–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2011.08.029.
Seto WK, Wong DK, Fung J, Hung IF, Fong DY, Yuen JC, et al. A large case-control study on the predictability of hepatitis B surface antigen levels three years before hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. Hepatology. 2012;56(3):812–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.25718.
Hsu YC, Mo LR, Chang CY, Wu MS, Kao JH, Wang WL, et al. Association between serum level of hepatitis B surface antigen at end of Entecavir therapy and risk of relapse in E antigen-negative patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(10):1490–8e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2016.03.024.
Wang CC, Tseng KC, Hsieh TY, Tseng TC, Lin HH, Kao JH. Assessing the durability of Entecavir-treated hepatitis B using quantitative HBsAg. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(9):1286–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2016.109.
•• Jeng WJ, Chang ML, Liaw YF. Off-therapy precipitous HBsAg decline predicts HBsAg loss after finite entecavir therapy in HBeAg-negative patients. J Viral Hepat. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.13114. HBsAg seroconversion after cessation of NAs required a precipitous decline. Sooner HBsAg loss was predicted by lower EOT HBsAg in sustained remission group and qHBsAg<100 IU/mL.
Chang ML, Liaw YF, Hadziyannis SJ. Systematic review: cessation of long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42(3):243–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13272.
Papatheodoridis G, Vlachogiannakos I, Cholongitas E, Wursthorn K, Thomadakis C, Touloumi G, et al. Discontinuation of oral antivirals in chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. Hepatology. 2016;63(5):1481–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28438.
Wang CC, Kao JH. The role of hepatitis B surface antigen in Nucleos(t)ide analogue cessation among Asian chronic hepatitis B patients: friend or foe? Hepatology. 2019;69(4):1843. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30532.
Chien NH, Huang YT, Wu CY, Chang CY, Wu MS, Kao JH, et al. Time-varying serum gradient of hepatitis B surface antigen predicts risk of relapses after off-NA therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017;17(1):154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-017-0697-3.
Wu D, Ning Q. Toward a Cure for Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Combination Therapy Involving Viral Suppression and Immune Modulation and Long-term Outcome. J Infect Dis. 2017;216(suppl_8):S771–S7. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jix355.
Zhang Y, Chen B, Wang L, Chi J, Song S, Liu M, et al. HBsAg seroclearance or seroconversion induced by peg-interferon alpha and lamivudine or adefovir combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B treatment: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2016;108(5):263–70. https://doi.org/10.17235/reed.2016.3995/2015.
• Qiu K, Liu B, Li SY, Li H, Chen ZW, Luo AR, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: combination treatment of regimens based on pegylated interferon for chronic hepatitis B focusing on hepatitis B surface antigen clearance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47(10):1340–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14629 Meta-analysis revealed the more effective combination therapy based on pegylated IFN ("NA-experienced" vs. "De novo", "switch to" vs. "add-on") for achieving HBsAg seroclearance.
Hu P, Shang J, Zhang W, Gong G, Li Y, Chen X, et al. HBsAg Loss with Peg-interferon Alfa-2a in Hepatitis B Patients with Partial Response to Nucleos(t)ide Analog: New Switch Study. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2018;6(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2017.00072.
Ning Q, Han M, Sun Y, Jiang J, Tan D, Hou J, et al. Switching from entecavir to PegIFN alfa-2a in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised open-label trial (OSST trial). J Hepatol. 2014;61(4):777–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.044.
Hsu CW, Su WW, Lee CM, Peng CY, Chuang WL, Kao JH, et al. Phase IV randomized clinical study: Peginterferon alfa-2a with adefovir or entecavir pre-therapy for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. J Formos Med Assoc. 2018;117(7):588–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2017.12.007.
Hsu CW, Chien RN, Liaw YF. Reply to "letter to the editor"-combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B: the future and beyond. J Formos Med Assoc. 2018;117(8):747–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2018.05.022.
Lin CL. Combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B: the future and beyond. J Formos Med Assoc. 2018;117(8):745–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2018.04.006.
• Mavilia MG, Wu GY. HBV-HCV Coinfection: Viral Interactions, Management, and Viral Reactivation. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2018;6(3):296–305. https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2018.00016 Comoprehensive review of HBV and HCV coinfection.
•• European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, European Association for the Study of the L. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017;67(2):370–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.021 Summary current consensus on the issue related to HBV infection.
•• Terrault NA, Lok ASF, McMahon BJ, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology. 2018;67(4):1560–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29800 Summary current consensus on the issue related to HBV infection.
Calvaruso V, Craxi A. HBV recurrence after HCV clearance on DAAs: sometimes they come back. J Hepatol. 2017;67(5):898–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.08.017.
Yu ML, Lee CM, Chuang WL, Lu SN, Dai CY, Huang JF, et al. HBsAg profiles in patients receiving peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for the treatment of dual chronic infection with hepatitis B and C viruses. J Infect Dis. 2010;202(1):86–92. https://doi.org/10.1086/653209.
Yen YH, Kee KM, Kuo FY, Chang KC, Hu TH, Lu SN, et al. A scoring system to predict HBsAg seroclearance in hepatitis B and C coinfected patients treated with interferon and ribavirin in an Asian cohort. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(50):e13383. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000013383.
Farci P, Anna NG. Current and future Management of Chronic Hepatitis D. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2018;14(6):342–51.
Keskin O, Wedemeyer H, Tuzun A, Zachou K, Deda X, Dalekos GN, et al. Association Between Level of Hepatitis D Virus RNA at Week 24 of Pegylated Interferon Therapy and Outcome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(13):2342–49 e1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2015.05.029.
Niro GA, Smedile A, Fontana R, Olivero A, Ciancio A, Valvano MR, et al. HBsAg kinetics in chronic hepatitis D during interferon therapy: on-treatment prediction of response. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44(6):620–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13734.
Chen GY, Su TH, Kao JH. Successful treatment of chronic hepatitis B and D with pegylated-interferon plus entecavir. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015;114(11):1140–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2013.05.011, 1141.
Kao CN, Su TH, Kao JH. Letter: HBsAg kinetics-guided interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis D. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45(3):480–1. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13872.
Jaroszewicz J, Reiberger T, Meyer-Olson D, Mauss S, Vogel M, Ingiliz P, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen concentrations in patients with HIV/HBV co-infection. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43143. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043143.
Arendt E, Jaroszewicz J, Rockstroh J, Meyer-Olson D, Zacher BJ, Mederacke I, et al. Improved immune status corresponds with long-term decline of quantitative serum hepatitis B surface antigen in HBV/HIV co-infected patients. Viral Immunol. 2012;25(6):442–7. https://doi.org/10.1089/vim.2012.0036.
Zoutendijk R, Zaaijer HL, de Vries-Sluijs TE, Reijnders JG, Mulder JW, Kroon FP, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen declines and clearance during long-term tenofovir therapy in patients coinfected with HBV and HIV. J Infect Dis. 2012;206(6):974–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jis439.
Strassl R, Reiberger T, Honsig C, Payer BA, Mandorfer M, Grabmeier-Pfistershammer K, et al. Viral determinants predicting hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance in HIV-/HBV-coinfected patients. J Viral Hepat. 2014;21(7):508–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.12175.
Lucifora J, Trepo C. Hepatitis: after HCV cure, HBV cure? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12(7):376–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2015.103.
Yang HC, Kao JH. Persistence of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA in hepatocytes: molecular mechanisms and clinical significance. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2014;3(9):e64. https://doi.org/10.1038/emi.2014.64.
Cornberg M, Manns MP. Hepatitis: no cure for hepatitis B and D without targeting integrated viral DNA? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15(4):195–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.185.
•• Lok AS, Zoulim F, Dusheiko G, Ghany MG. Hepatitis B cure: From discovery to regulatory approval. Hepatology. 2017;66(4):1296–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29323 A comprehensive review oncurrent novel treatment and the response evaluation for chronic HBV infection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Tzu-Chan Hong, Hung-Chih Yang and Jia-Horng Kao each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Hepatitis B
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, TC., Yang, HC. & Kao, JH. Role of HBsAg Testing in the Management of Patients with Chronic HBV. Curr Hepatology Rep 18, 331–341 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-019-00484-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-019-00484-y