Abstract
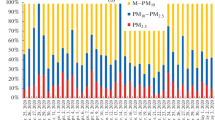
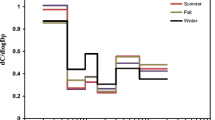
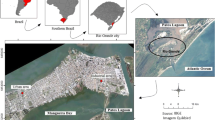
The temporal variation of aerosol size distribution in León, Spain, was analyzed with an optical spectrometer, in order to identify changes associated with the summer-autumn transition. For each hour and day of the week, we have studied the temporal variation of the particle number during the day. As the summer progresses, the total particle number increases from 1000 ± 600 in August to 1500 ± 1000 particles cm−3 in October, mainly due to more intense road traffic after the summer holidays and to the beginning of the new academic year in the study area in September. The particle number was higher on weekdays than on weekends in September and October. However, in August the values were similar, due to lower activity in the city, coinciding with the main holiday period. The aerosol size distributions were bimodal. In the fine mode, both the highest concentration (573 particles cm−3) and the lowest count median diameter (0.08 μm) were recorded in October. The contribution of particles from forest fires and Saharan dust intrusions had a negative impact on the air quality of the city during the summer. Considering the estimated respirable fraction in healthy adults (after the Standard ISO 7708:1995), on weekdays the highest values are obtained between 0600 and 1000 UTC (around 15 μg m−3) and in the afternoon, between 1700 and 2000 UTC (around 12 μg m−3), coinciding with the rush hour.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalto P, Hämeri K, Paatero P, Kulmala M, Bellander T, Berglind N, Bouso L, Castaño-Vinyals G, Sunyer J, Cattani G, Marconi A, Cyrys J, Klot S, Peters A, Zetzsche K, Lanki T, Pekkanen J, Nyberg F, Sjövall B, Forastiere F (2005) Aerosol particle number concentration measurements in five European cities using TSI-3022 condensation particle counter over a three-year period during health effects of air pollution on susceptible subpopulations. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 55:1064–1076. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2005.10464702
Alonso-Blanco E, Calvo AI, Fraile R, Castro A (2012) The influence of wildfires on aerosol size distributions in rural areas. Sci World J 2012:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/735697
Alonso-Blanco E, Castro A, Calvo AI, Pont V, Mallet M, Fraile R (2018) Wildfire smoke plumes transport under a subsidence inversion: climate and health implications in a distant urban area. Sci Total Environ 619–620:988–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.142
Analitis A, Katsouyanni K, Dimakopoulou K, Samoli E, Nikoloulopoulos AK, Petasakis Y, Touloumi G, Schwartz J, Anderson HR, Cambra K, Forastiere F, Zmirou D, Vonk JM, Clancy L, Kriz B, Bobvos J, Pekkanen J (2006) Short-term effects of ambient particles on cardiovascular and respiratory mortality. Epidemiology 17:230–233. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ede.0000199439.57655.6b
Artíñano B, Salvador P, Alonso DG et al (2003) Anthropogenic and natural influence on the PM10 and PM2.5 aerosol in Madrid (Spain). Analysis of high concentration episodes. Environ Pollut 125:453–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00078-2
Brown J, Gordon T, Price O, Asgharian B (2013) Thoracic and respirable particle definitions for human health risk assessment. Part Fibre Toxicol 10(1):12
Calvo AI, Alves C, Castro A, Pont V, Vicente AM, Fraile R (2013a) Research on aerosol sources and chemical composition: past, current and emerging issues. Atmos Res 120–121:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.09.021
Calvo AI, Pont V, Castro A, Mallet M, Palencia C, Roger JC, Dubuisson P, Fraile R (2010) Radiative forcing of haze during a forest fire in Spain. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD012172
Calvo AI, Pont V, Liousse C, Dupré B, Mariscal A, Zouiten C, Gardrat E, Castera P, Lacaux CG, Castro A, Fraile R (2008) Chemical composition of urban aerosols in Toulouse, France during CAPITOUL experiment. Meteorol Atmos Phys 102:307–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-008-0319-2
Calvo AI, Tarelho LAC, Teixeira ER, Alves C, Nunes T, Duarte M, Coz E, Custodio D, Castro A, Artiñano B, Fraile R (2013b) Particulate emissions from the co-combustion of forest biomass and sewage sludge in a bubbling fluidised bed reactor. Fuel Process Technol 114:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2013.03.021
Castro A, Alonso-Blanco E, González-Colino M, Calvo AI, Fernández-Raga M, Fraile R (2010) Aerosol size distribution in precipitation events in León, Spain. Atmos Res 96:421–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.01.014
Castro A, Calvo AI, Alves C, Alonso-Blanco E, Coz E, Marques L, Nunes T, Fernández-Guisuraga JM, Fraile R (2015) Indoor aerosol size distributions in a gymnasium. Sci Total Environ 524–525:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.118
Chaloulakou A, Kassomenos P, Spyrellis N, Demokritou P, Koutrakis P (2003) Measurements of PM10 and PM2.5 particle concentrations in Athens, Greece. Atmos Environ 37:649–660
Cheng Y, Lee S, Gu Z, Ho K, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Chow JC, Watson JG, Cao J, Zhang R (2015) PM2.5 and PM10-2.5 chemical composition and source apportionment near a Hong Kong roadway. Particuology 18:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2013.10.003
Cyrys J, Pitz M, Heinrich J, Wichmann HE, Peters A (2008) Spatial and temporal variation of particle number concentration in Augsburg, Germany. Sci Total Environ 401:168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.03.043
Deshmukh DK, Deb MK, Mkoma SL (2013) Size distribution and seasonal variation of size-segregated particulate matter in the ambient air of Raipur city, India. Air Qual Atmos Heal 6:259–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-011-0169-9
Dunn OJ (1964) Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1964.10490181
Gerasopoulos E, Kouvarakis G, Babasakalis P et al (2006) Origin and variability of particulate matter (PM10) mass concentrations over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos Environ 40:4679–4690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.04.020
Gomišček B, Hauck H, Stopper S, Preining O (2004) Spatial and temporal variations of PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and particle number concentration during the AUPHEP—project. Atmos Environ 38:3917–3934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.03.056
Goudie A (2014) Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ Int 63:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.10.011
Gugamsetty B, Wei H, Liu CN et al (2012) Source characterization and apportionment of PM10, PM2.5 and PM0.1 by using positive matrix factorization. Aerosol Air Qual Res 12:476–491. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2012.04.0084
Held A, Zerrath A, Mckeon U et al (2008) Aerosol size distributions measured in urban, rural and high-alpine air with an electrical low pressure impactor (ELPI). Atmos Environ 42:8502–8512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.06.015
Hieu NT, Lee BK (2010) Characteristics of particulate matter and metals in the ambient air from a residential area in the largest industrial city in Korea. Atmos Res 98:526–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.08.019
Hussein T, Puustinen A, Aalto PP, Mäkelä JM, Hämeri K, Kulmala M (2003) Urban aerosol number size distributions. Atmos Chem Phys Discuss 3:5139–5184. https://doi.org/10.5194/acpd-3-5139-2003
International Organization for Standarization (ISO) (1995) ISO 7708:1995 (E): air quality—particle size fraction definitions for health related sampling. ISO publications, 1st edition, 1995-04-01
Jacob D (1999) Introduction to atmospheric chemistry. Princeton University Press
Johansson C, Norman M, Gidhagen L (2007) Spatial & temporal variations of PM10 and particle number concentrations in urban air. Environ Monit Assess 127:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9296-4
Khanum F, Chaudhry MN, Kumar P (2017) Characterization of five-year observation data of fine particulate matter in the metropolitan area of Lahore. Air Qual Atmos Heal 10:725–736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-017-0464-1
Kim KH, Kabir E, Kabir S (2015) A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ Int 74:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.10.005
Kim YJ, Boatman JF (1990) Size calibration corrections for the active scattering aerosol spectrometer probe (ASASP-100X). Aerosol Sci Technol 12:665–672. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786829008959381
Kim Oanh NT, Upadhyay N, Zhuang YH, Hao ZP, Murthy DVS, Lestari P, Villarin JT, Chengchua K, Co HX, Dung NT (2006) Particulate air pollution in six Asian cities: spatial and temporal distributions, and associated sources. Atmos Environ 40:3367–3380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.01.050
Klejnowski K, Krasa A, Rogula-Kozłowska W, Błaszczak B (2013) Number size distribution of ambient particles in a typical urban site: the first polish assessment based on long-term (9 months) measurements. Sci World J 2013:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/539568
Kruskal WH, Wallis WA (1952) Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 47:583–621. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1952.10483441
Kuzu SL (2016) Compositional variation of PCBs, PAHs, and OCPs at gas phase and size segregated particle phase during dust incursion from the Saharan Desert in the Northwestern Anatolian Peninsula. Adv Meteorol 2016:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7153286
Kuzu SL, Saral A (2017) The effect of meteorological conditions on aerosol size distribution in Istanbul. Air Qual Atmos Heal 10:1029–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-017-0491-y
Lelieveld J, Evans JS, Fnais M, Giannadaki D, Pozzer A (2015) The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 525:367–371. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15371
Lonati G, Crippa M, Gianelle V, Van Dingenen R (2011) Daily patterns of the multi-modal structure of the particle number size distribution in Milan, Italy. Atmos Environ 45:2434–2442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.02.003
Lyamani H, Olmo FJ, Alados-Arboledas L (2005) Saharan dust outbreak over southeastern Spain as detected by sun photometer. Atmos Environ 39:7276–7284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.09.011
Monsalve F, Tomás C, Fraile R (2013) Influence of meteorological parameters and air pollutants onto the morbidity due to respiratory diseases in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain. Aerosol Air Qual Res 13:1297–1312. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2012.12.0348
Morawska L, Salthammer T (2004) Indoor environment: airborne particles and settled dust. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinhelim
Pascal M, Falq G, Wagner V, Chatignoux E, Corso M, Blanchard M, Host S, Pascal L, Larrieu S (2014) Short-term impacts of particulate matter (PM10, PM10–2.5, PM2.5) on mortality in nine French cities. Atmos Environ 95:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.06.030
Pérez N, Pey J, Querol X, Alastuey A, López JM, Viana M (2008) Partitioning of major and trace components in PM10–PM2.5–PM1 at an urban site in Southern Europe. Atmos Environ 42:1677–1691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.11.034
Pope CA, Dockery DW (2006) Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: lines that connect. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 56:709–742. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2006.10464485
Puustinen A, Hämeri K, Pekkanen J, Kulmala M, de Hartog J, Meliefste K, ten Brink H, Kos G, Katsouyanni K, Karakatsani A, Kotronarou A, Kavouras I, Meddings C, Thomas S, Harrison R, Ayres JG, van der Zee S, Hoek G (2007) Spatial variation of particle number and mass over four European cities. Atmos Environ 41:6622–6636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.04.020
Querol X, Alastuey A, Viana MM, Rodriguez S, Artiñano B, Salvador P, Garcia do Santos S, Fernandez Patier R, Ruiz CR, de la Rosa J, Sanchez de la Campa A, Menendez M, Gil JI (2004) Speciation and origin of PM10 and PM2.5 in Spain. J Aerosol Sci 35:1151–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2004.04.002
Rashki A, Rautenbach CJ d W, Eriksson PG, Kaskaoutis DG, Gupta P (2013) Temporal changes of particulate concentration in the ambient air over the city of Zahedan, Iran. Air Qual Atmos Heal 6:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-011-0152-5
Reizer M, Juda-Rezler K (2016) Explaining the high PM10concentrations observed in Polish urban areas. Air Qual Atmos Heal 9:517–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-015-0358-z
Ren-Jian Z, Kin-Fai H, Zhen-Xing S (2012) The role of aerosol in climate change, the environment, and human health. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 5:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2012.11446983
Salvador P, Artíñano B, Viana MM, Querol X, Alastuey A, González-Fernández I, Alonso R (2011) Spatial and temporal variations in PM10 and PM2.5 across Madrid metropolitan area in 1999-2008. Procedia Environ Sci 4:198–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2011.03.024
Samek L, Stegowski Z, Furman L, Fiedor J (2017) Chemical content and estimated sources of fine fraction of particulate matter collected in Krakow. Air Qual Atmos Heal 10:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0407-2
Samet J, Dominici F, Curriero F et al (2000) Fine particulate air pollution and mortality in 20 U.S. cities, 1987-1994. N Engl J Med 343:1742–1749
Stanier CO, Khlystov AYAY, Pandis SN (2004) Ambient aerosol size distributions and number concentrations measured during the Pittsburgh Air Quality Study (PAQS). Atmos Environ 38:3275–3284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.03.020
Tan WC, Qiu D, Liam BL et al (2000) The human bone marrow response to acute air pollution caused by forest fires. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:1213–1217. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.161.4.9904084
Wehner B, Wiedensohler A (2002) Long term measurements of submicrometer urban aerosols: statistical analysis for correlations with meteorological conditions and trace gases. Atmos Chem Phys Discuss 2:1699–1733. https://doi.org/10.5194/acpd-2-1699-2002
Wilson WE, Suh HH (1997) Fine particles and coarse particles: concentration relationships relevant to epidemiologic studies. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 47:1238–1249. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.1997.10464074
Woo KS, Chen DR, Pui DYH, McMurry PH (2001) Measurement of Atlanta aerosol size distributions: observations of ultrafine particle events. Aerosol Sci Technol 34:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/027868201300082049
Wu Z, Hu M, Lin P, Liu S, Wehner B, Wiedensohler A (2008) Particle number size distribution in the urban atmosphere of Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 42:7967–7980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.06.022
Zhang KM, Wexler AS (2004) Evolution of particle number distribution near roadways—Part I: analysis of aerosol dynamics and its implications for engine emission measurement. Atmos Environ 38:6643–6653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.06.043
Zhang KM, Wexler AS, Zhu YF, Hinds WC, Sioutas C (2004) Evolution of particle number distribution near roadways. Part II: the “Road-to-Ambient” process. Atmos Environ 38:6655–6665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.06.044
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Darrel Baumgardner for his help with the code developed by Bohern and Huffman. F. Oduber acknowledges the grant BES-2015-074473 from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness. C. Blanco-Alegre acknowledges the grant FPU16-05764 from the Spanish Ministry of Education, Culture and Sport. Noelia Ramón patiently revised the final version in English. The data from the CALIMA network are property of the Office for Quality and Environmental Evaluation (DGCEA, in its Spanish acronym), belonging to the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and the Environment. The data were supplied as a result of an agreement between the Spanish Ministry of Agriculture, Food and the Environment and the Scientific Research Council for sponsoring studies related to air pollution by particulate matter and metals in Spain.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Grant TEC2014-57821-R), the University of León (Programa Propio 2015/00054/001) and the AERORAIN project (Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness, Grant CGL2014-52556-R, co-financed with European FEDER funds).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oduber, F., Castro, A., Calvo, A. et al. Summer-autumn air pollution in León, Spain: changes in aerosol size distribution and expected effects on the respiratory tract. Air Qual Atmos Health 11, 505–520 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0556-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0556-6