Abstract
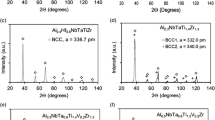
Effects of heat treatment on borides precipitation and mechanical properties of arc-melted and laser-cladded CoCrNiFeAl1.8Cu0.7B0.3Si0.1 high-entropy alloys were comparatively studied. The arc-melted alloy contains lots of long strip borides distributed in the body-centered cubic phase, with a hardness about 643 HV0.5. Laser-cladding can effectively inhibit the boride precipitation and the laser-cladded alloy is mainly composed of a simple bcc solid solution, with a high hardness about 769 HV0.5, indicating the strengthening effect by interstitial boron atoms is greater than the strengthening by borides precipitation. Heat treatments between 800°C and 1200°C can simultaneously improve the hardness and fracture toughness of arc-melted alloys, owing to the boride spheroidization, dissolution, re-precipitation, and hence the increased boron solubility and nano-precipitation in the bcc solid solution. By contrast, the hardness of laser-cladded alloys reduce after heat treatments in the same temperature range, due to the decreased boron solubility in the matrix.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Prog. Mater Sci. 61, 1 (2014).
H. Zhang, W.F. Wu, Y.Z. He, M.X. Li, and S. Guo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 363, 543 (2016).
N. Yu, N.D. Yurchenko, D.G. Stepanov, M.A. Shaysultanov, G.A. Tikhonovsky, and S. Salishchev, Mater. Charact. 121, 125 (2016).
M.H. Chuang, M.H. Tsai, W.R. Wang, S.J. Lin, and J.W. Yeh, Acta Mater. 59, 6308 (2011).
Z.M. Li, C.C. Tasan, H. Springer, B. Gault, and D. Raabe, Sci. Rep. 7, 40704 (2017).
Z.D. Wang and I. Baker, Mater. Lett. 180, 153 (2016).
H. Zhang, Y.Z. He, and Y. Pan, Scr. Mater. 69, 342 (2013).
G.J. Chen, C. Zhang, and Q.H. Tang, Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 44, 1418 (2015).
C.P. Lee, Y.Y. Chen, and C.Y. Hsu, J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, 424 (2007).
H. Zhang, Y. Pan, Y.Z. He, J.L. Wu, T.M. Yue, and S. Guo, JOM 66, 2057 (2014).
T.M. Yue, H. Xie, X. Lin, H.O. Yang, and G.H. Meng, J. Alloy Comp. 587, 588 (2014).
N. Aleksandra, A. Merati, B. Mariusz, B. Manon, F. Olaniyi, and N. Michel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, 773 (2015).
R.F. Zhang, S.H. Sheng, and B.X. Liu, Chem. Phys. Lett. 442, 511 (2007).
Y.T. Wang, Y. Adachi, K. Nakajima, and Y. Sugimoto, Acta Mater. 58, 4849 (2010).
H.L. Yi, Z.Y. Hou, Y.B. Xu, D. Wu, and G.D. Wang, Scr. Mater. 67, 645 (2012).
A. Munitza, L. Meshi, and M.J. Kaufman, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 689, 384 (2017).
A. Munitz, S. Salhov, S. Hayun, and N. Frage, J Alloy Compd. 683, 221 (2016).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 51271001 and Joint Fund of Iron and Steel Research by NSFC under Grant No. U1560105, the University Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province of China under Grant No. KJ2014A029, and the Tribology Science Fund of State Key Laboratory of Tribology under Grant No. SKLTKF14B02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Tang, H., He, Y.Z. et al. Effect of Heat Treatment on Borides Precipitation and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiAl1.8Cu0.7B0.3Si0.1 High-Entropy Alloy Prepared by Arc-Melting and Laser-Cladding. JOM 69, 2078–2083 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2381-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2381-z