Abstract
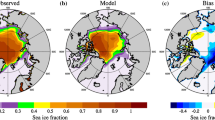
Sea ice is a sensitive indicator of climate change and an important component of climate system models. The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model 5.0 (CICE5.0) was introduced to the Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model (BCC_CSM) as a new alternative to the Sea Ice Simulator (SIS). The principal purpose of this paper is to analyze the impacts of these two sea ice components on simulations of basic Arctic sea ice, atmosphere, and ocean states. Two sets of experiments were conducted with the same configurations except for the sea ice component used, i.e., SIS and CICE. The distributions of sea ice concentration and thickness reproduced by the CICE simulations in both March and September were closer to actual observations than those reproduced by SIS simulations, which presented a very thin sea ice cover in September. Changes in sea ice conditions also brought about corresponding modifications to the atmosphere and ocean circulation. CICE simulations showed higher agreement with the reference datasets than did SIS simulations for surface air temperature, sea level pressure, and sea surface temperature in most parts of the Arctic Ocean. More importantly, compared with simulations with SIS, BCC_CSM with CICE revealed stronger Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC), which is more consistent with actual observations. Thus, CICE shows better performance than SIS in BCC_CSM. However, both components demonstrate a number of common weaknesses, such as overestimation of the sea ice cover in winter, especially in the Nordic Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk. Additional studies and improvements are necessary to develop these components further.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behrens, L. K., Martin, T., Semenov, V. A., and Latif, M., 2012. The Arctic sea ice in the CMIP3 climate model ensemble-variability and anthropogenic change. The Cryosphere Discussions, 6: 5317–5344, DOI: 10.5194/tcd-6-5317-2012.
Bitz, C. M., and Lipscomb, W. H., 1999. An energy-conserving thermodynamic model of sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104: 15669–15677.
Briegleb, B. P., and Light, B., 2007. A Delta-Eddington multiple scattering parameterization for solar radiation in the sea ice component of the Community Climate System Model. National Center for Atmospheric Research Technical Note N-CAR/TN-472+STR. Boulder, Colorado, 1-100.
Budikova, D., 2009. Role of Arctic sea ice in global atmospheric circulation: A review. Global and Planetary Change, 68: 149–163.
Budyko, M., 1969. The effect of solar radiation variations on the climate of the earth. Tellus, 21: 611–619.
Cavalieri, D. J., and Parkinson, C. L., 2012. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979-2010. The Cryosphere, 6: 881–889.
Chu, M., Fang, Y. J., Zhang, L. J., and Wu, T. W., 2018. Influence of albedo related parameters on the simulation of Arctic sea ice by CICE. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 76(3): 461–472.(in Chinese with English abstract).
Cohen, J., Screen, J. A., Furtado, J. C., Barlow, M., Whittleston, D., Coumou, D., Francis, J., Dethloff, K., Entekhabi, D., Overland, J., and Jones, J., 2014. Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather. Nature Geoscience, 7: 627–637.
Ding, Y. J., and Zhang, S. Q., 2015. The hydrological impact of cryosphere water cycle on global-scale water cycle. Chinese Science Bulletin, 60(7): 593–602.(in Chinese with English abstract).
Doscher, R., Vihma, T., and Maksimovich, E., 2014. Recent advances in understanding the Arctic climate system state and change from a sea ice perspective: A review. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14: 13571–13600.
Fang, Y. J., Chu, M., Wu, T. W., Zhang, L. J., and Nie, S. C., 2017. Coupling of CICE5.0 with BCC_CSM2.0 model and its performance evaluation on Arctic sea ice simulation. Haiyang Xuebao, 39(5): 33–43.(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ganachaud, A., 2003. Large-scale mass transports, water mass formation, and diffusivities estimated from World Ocean Circulation Experiment (WOCE) hydrographic data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108: 3213.
Gao, Y. Q., Sun, J. Q., Li, F., He, S. P., Sandven, S., Yan, Q., Zhang, Z. S., Lohmann, K., Keenlyside, N., Furevik, T., and Suo, L. L., 2015. Arctic sea ice and Eurasian climate: A review. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 32(1): 92–114.
Griffies, S. M., Gnanadesikan, A., Dixon, K. W., Dunne, J. P., Gerdes, R., Harrison, M. J., Rosati, A., Russell, J. L., Samuels, B. L., Spelman, M. J., Winton, M., and Zhang, R., 2005. Formulation of an ocean model for global climate simulations. Ocean Science, 1: 45–79.
Hunke, E. C., and Dukowicz, J. K., 1997. An elastic-viscous-plastic model for sea ice dynamics. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 27: 1849–1867.
Hunke, E. C., Hebert, D. A., and Lecomte, O., 2013. Level-ice melt ponds in the Los Alamos sea ice model, CICE. Ocean Modelling, 71: 26–42.
Jahn, A., and Holland, M. M., 2013. Implications of Arctic sea ice changes for North Atlantic deep convection and the meridional overturning circulation in CCSM4-CMIP5 simulations. Geophysical Research Letters, 40: 1206–1211.
Kanamitsu, M., Ebisuzaki, W., Woollen, J., Yang, S. K., Hnilo, J. J., Fiorino, M., and Potter, G. L., 2002. NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bulletin of American Meteorological Society, 83: 1631–1643.
Kiehl, J. T., and Gent, P. R., 2004. The community climate system model, version 2. Journal of Climate, 17: 3666–3682.
Kobayashi, S., Ota, Y., Harada, Y., Ebita, A., Moriya, M., Onoda, H., Onogi, K., Kamahori, H., Kobayashi, C., Endo, H., Mi-yaoka, K., and Takahashi, K., 2015. The JRA-55 reanalysis: General specifications and basic characteristics. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 93(1): 5–48.
Kug, J. S., Jeong, J. H., Jang, Y. S., Kim, B. M., Folland, C. K., Min, S. K., and Son, S. W., 2015. Two distinct influences of Arctic warming on cold winters over North America and East Asia. Nature Geoscience, 8: 759–763.
Levermann, A., Mignot, J., Nawrath, S., and Rahmstorf, S., 2007. The role of northern sea ice cover for the weakening of the thermohaline circulation under global warming. Journal of Climate, 20: 4160–4171.
Lipscomb, W. H., 2001. Remapping the thickness distribution in sea ice models. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 106: 13989–14000.
Lipscomb, W. H., Hunke, E. C., Maslowski, W., and Jakacki, J., 2007. Ridging, strength, and stability in high-resolution sea ice models. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112: C03S91.
Lovely, A., Loose, B., Schlosser, P., McGillis, W., Zappa, C., Perovich, D., Brown, S., Morell, T., Hsueh, D., and Friedrich, R., 2015. The gas transfer through polar sea ice experiment: Insights into the rates and pathways that determine geoche-mical fluxes. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 120: 8177–8194.
McCusker, K. E., Fyfe, J. C., and Sigmond, M., 2016. Twenty-five winters of unexpected Eurasian cooling unlikely due to Arctic sea-ice loss. Nature Geoscience, 9: 838–843.
Meier, W. N., Hovelsrud, G. K., Oort, B. E., Key, J. R., Kovacs, K. M., Michel, C., Haas, C., Granskog, M. A., Gerland, S., Perovich, D. K., Makshtas, A., and Reist, J. D., 2014. Arctic sea ice in transformation: A review of recent observed changes and impacts on biology and human activity. Review of Geophysics, 51: 185–217.
Mori, M., Watanabe, M., Shiogama, H., Inoue, J., and Kimoto, M., 2014. Robust Arctic sea-ice influence on the frequent Eurasian cold winters in past decades. Nature Geoscience, 7: 1–5.
Nakamura, T., Yamazaki, K., Iwamoto, K., Honda, M., Miyoshi, Y., Ogawa, Y., Tomikawa, Y., and Ukita, J., 2016. The stratospheric pathway for Arctic impacts on midlatitude climate. Geophysical Research Letters, 43: 3494–3501.
Parkinson, C. L., and Cavalieri, D. J., 2008. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979-2006. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113: C07003.
Qiu, B., Zhang, L. J., Chu, M., Wu, T. W., and Tan, H. H., 2015. Performance analysis of Arctic sea ice simulation in climate system models. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 27(1): 47–55.(in Chinese with English abstract).
Rayner, N. A., Parker, D. E., Horton, E. B., Folland, C. K., Alexander, L. V., Rowell, D. P., Kent, E. C., and Kaplan, A., 2003. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(D14): 4407.
Rysgaard, S., Bendtsen, J., Pedersen, L. T., Ramlov, H., and Glud, R. N., 2009. Increased CO2 uptake due to sea ice growth and decay in the Nordic Seas. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114: C09011.
Semtner, A. J., 1976. A model for the thermodynamics growth of sea ice in numerical investigations of climate. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 6: 27–37.
Stephens, G. L., O’Brien, D., Webster, P. J., Pilewski, P., Kato, S., and Li, J. L., 2015. The albedo of earth. Reviews of Geophysics, 53(1): 141–163.
Stroeve, J. C., Kattsov, V., Barrett, A., Serreze, M., Pavlova, T., Holland, M., and Meier, W. N., 2012. Trends in Arctic sea ice extent from CMIP5, CMIP3 and observations. Geophysical Research Letters, 39: L16502.
Tan, H. H., Zhang, L. J., Chu, M., Wu, T. W., Qiu, B., and Li, J. L., 2015. An analysis of simulated global sea ice extent, thickness and causes of error with the BCC_CSM model. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 39: 1–13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tietsche, S., Balmaseda, M. A., Zuo, H., and Mogensen, K., 2014. Arctic sea ice in the ECMWF MyOcean2 ocean re-analysis ORAP5. Technical Memorandum No.737. European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, Reading, 1-36.
Vihma, T., 2014. Effects of Arctic sea ice decline on weather and climate: A review. Surveys in Geophysics, 35: 1175–1214.
Walsh, J. E., 1983. The role of sea ice in climate variability: Theories and evidence. Atmosphere-Ocean, 21: 229–242.
Walsh, J. E., 2014. Intensified warming of the Arctic: Causes and impacts on middle latitudes. Global and Planetary Change, 117: 52–63.
Winton, M. A., 2000. Reformulated three-layer sea ice model. Journal of Atmospheric Oceanic Technology, 17: 525–531.
Wu, F. M., He, J. H., and Qi, L., 2014. Arctic sea ice declining and its impact on the cold Eurasian winters: A review. Advances in Earth Science, 29(8): 913–921.(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu, T. W., Yu, R. C., Zhang, F., Wang, Z. Z., Dong, M., Wang, L. N., Jin, X., Chen, D. L., and Li, L., 2010. The Beijing Climate Center atmospheric general circulation model: Description and its performance for the present-day climate. Climate Dynamics, 34: 123–147.
Wu, T., Song, L., Li, W., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Xin, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Li, J., Wu, F., Liu, Y., Zhang, F., Shi, X., Chu, M., Zhang, J., Fang, Y., Wang, F., Lu, Y., Liu, X., Wei, M., Liu, Q., Zhou, W., Dong, M., Zhao, Q., Ji, J., Li, L., and Zhou, M., 2014. An overview of BCC climate system model development and application for climate change studies. Journal of Meteorological Research, 28(1): 34–56.
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2015CB953904), the Welfare Program of Meteorology (No. GYHY201506011), and the National Key R&D Program (Nos. 2016YFA060 2602, 2018YFC1407104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, M., Shi, X., Fang, Y. et al. Impacts of SIS and CICE as Sea Ice Components in BCC_CSM on the Simulation of the Arctic Climate. J. Ocean Univ. China 18, 553–562 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-019-3862-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-019-3862-1