Abstract
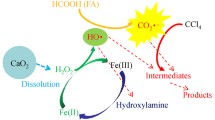
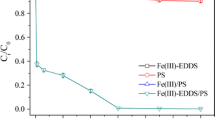
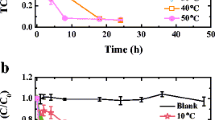
The thermally activated persulfate (PS) degradation of carbon tetrachloride (CT) in the presence of formic acid (FA) was investigated. The results indicated that CT degradation followed a zero order kinetic model, and CO –2 · was responsible for the degradation of CT confirmed by radical scavenger tests. CT degradation rate increased with increasing PS or FA dosage, and the initial CT had no effect on CT degradation rate. However, the initial solution pH had effect on the degradation of CT, and the best CT degradation occurred at initial pH 6. Cl– had a negative effect on CT degradation, and high concentration of Cl– displayed much strong inhibition. Ten mmol·L–1HCO –3 promoted CT degradation, while 100 mmol·L–1NO –3 inhibited the degradation of CT, but SO 2–4 promoted CT degradation in the presence of FA. The measured Cl–concentration released into solution along with CT degradation was 75.8% of the total theoretical dechlorination yield, but no chlorinated intermediates were detected. The split of C-Cl was proposed as the possible reaction pathways in CT degradation. In conclusion, this study strongly demonstrated that the thermally activated PS system in the presence of FA is a promising technique in in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) remediation for CT contaminated site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi J, Choi K, Lee W. Effects of transition metal and sulfide on the reductive dechlorination of carbon tetrachloride and 1,1,1-trichloroethane by FeS. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(2–3): 1151–1158
TÁmara M L, Butler E C. Effects of iron purity and groundwater characteristics on rates and products in the degradation of carbon tetrachloride by iron metal. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(6): 1866–1876
Buxton G V, Greenstock C L, Helman W P, Ross A B. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (·OH/·O–) in aqueous solution. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1988, 17(2): 513–886
Gu X G, Lu S G, Li L, Qiu Z F, Sui Q, Lin K F, Luo Q S. Oxidation of 1,1,1-trichloroethane stimulated by thermally activated persulfate. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(19): 11029–11036
Liang C, Bruell C J, Marley M C, Sperry K L. Persulfate oxidation for in situ remediation of TCE. I. Activated by ferrous ion with and without a persulfate-thiosulfate redox couple. Chemosphere, 2004, 55(9): 1213–1223
Fang G D, Dionysiou D D, Al-Abed S R, Zhou D M. Superoxide radical driving the activation of persulfate by magnetite nanoparticles: implications for the degradation of PCBs. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 129(2): 325–332
Fang G, Gao J, Dionysiou D D, Liu C, Zhou D. Activation of persulfate by quinones: free radical reactions and implication for the degradation of PCBs. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(9): 4605–4611
Ahmad M, Teel A L, Watts R J. Mechanism of persulfate activation by phenols. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(11): 5864–5871
Zhao J Y, Zhang Y B, Quan X, Chen S. Enhanced oxidation of 4- chlorophenol using sulfate radicals generated from zero-valent iron and peroxydisulfate at ambient temperature. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 71(3): 302–307
House D A. Kinetics and mechanism of oxidations by peroxydisulfate. Chemical Reviews, 1962, 62(3): 185–203
Pennington D E, Haim A. Stoichiometry and mechanism of the chromium(II)—peroxydisulfate reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 90(14): 3700–3704
Peyton G R. The free-radical chemistry of persulfate-based total organic carbon analyzers. Marine Chemistry, 1993, 41(1–3): 91–103
Kolthoff I M, Miller I K. The chemistry of persulfate. I. The kinetics and mechanism of the decomposition of the persulfate ion in aqueous medium1. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1951, 73(7): 3055–3059
Watts R J, Bottenberg B C, HessT F, Jensen M D, Teel A L. Role of reductants in the enhanced desorption and transformation of chloroaliphatic compounds by modified Fenton’s reactions. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(19): 3432–3437
Bielski B H, Cabelli D E, Arudi R L, Ross A B. Reactivity of HO2/O–2 radicals in aqueous solution. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1985, 14(4): 1041–1100
Liang C J, Bruell C J, Marley M C, Sperry K L. Thermally activated persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene (TCE) and 1,1,1-trichloroethane (TCA) in aqueous systems and soil slurries. Soil & Sediment Contamination, 2003, 12(2): 207–228
Mora V C, Rosso J A, Carrillo Le Roux G, Mártire D O, Gonzalez M C. Thermally activated peroxydisulfate in the presence of additives: a clean method for the degradation of pollutants. Chemosphere, 2009, 75(10): 1405–1409
Lin M Z, Katsumura Y, Muroya Y, He H, Miyazaki T, Hiroishi D. Pluse radiolysis of sodium formate aqueous solution up to 400°C: absorption spectra, kinetics and yield of carboxyl radical CO –2 ·. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2008, 77(10–12): 1208–1212
Liang C, Huang C F, Mohanty N, Kurakalva R M. A rapid spectrophotometric determination of persulfate anion in ISCO. Chemosphere, 2008, 73(9): 1540–1543
Xu M, Gu X, Lu S, Qiu Z, Sui Q, Miao Z, Zang X, Wu X. Degradation of carbon tetrachloride in aqueous solution in the thermally activated persulfate system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 286: 7–14
Neta P, Huie R E, Ross A B. Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1988, 17(3): 1027–1284
Mulazzani Q G, D’Angelantonio M, Venturi M, Hoffman M Z, Rodgers MA. Interaction of formate and oxalate ions with radiationgenerated radicals in aqueous solution. Methylviologen as a mechanistic probe. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1986, 90(21): 5347–5352
Berkovic A M, Gonzalez MC, Russo N, Michelini MC, Pis Diez R, Mártire D O. Reduction of mercury(II) by the carbon dioxide radical anion: a theoretical and experimental investigation. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2010, 114(49): 12845–12850
Das T N, Ghanty T K, Pal H. Reactions of methyl viologen dication (MV2+) with H atoms in aqueous solution: mechanism derived from pulse radiolysis measurements and ab initio mo calculations. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2003, 107(31): 5998–6006
Gonzalez M C, Le Roux G C, Rosso J A, Braun A M. Mineralization of CCl4 by the UVC-photolysis of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of methanol. Chemosphere, 2007, 69(8): 1238–1244
CooperW J, Cramer C J, Martin N H, Mezyk S P, O’Shea K E, von Sonntag C. Free radical mechanisms for the treatment of methyl tertbutyl ether (MTBE) via advanced oxidation/reductive processes in aqueous solutions. Chemical Reviews, 2009, 109(3): 1302–1345
Flyunt R, Schuchmann M N, von Sonntag C. A common carbanion intermediate in the recombination and proton-catalysed disproportionation of the carboxyl radical anion, CO –2 ·, in aqueous solution. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2001, 7(4): 796–799
Morkovinik A F, Okhlobystin O Y. Inorganic radical-ions and their organic reactions. Russian Chemical Reviews, 1979, 48(11): 1055–1075
Buxton G V, Bydder M, Salmon G A. The reactivity of chlorine atoms in aqueous solution, Part II. The reactivity of chlorine atoms in aqueous solution II: The equilibrium SO –4 · + Cl–↔SO 2–4 + Cl·. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 1999, 1(2): 269–273
Regino C A, Richardson D E. Bicarbonate-catalyzed hydrogen peroxide oxidation of cysteine and related thiols. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 2007, 360(14): 3971–3977
Draganic Z D, Negrón-Mendoza A, Sehested K, Vujoševic S I, Navarro-Gonzáles R, Albarrán-SanchezM G, Draganic I G. Radiolysis of aqueous solutions of ammonium bicarbonate over a large dose range. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation Part C Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 1991, 38(3): 317–321
Padmaja S, Neta P, Huie R E. Rate constants for some reactions of inorganic radicals with inorganic ions. Temperature and solvent dependence. International Journal of Chemical Kinetics, 1993, 25 (6): 445–455
Neta P, Grodkowsk J, Ross A B. Rate constants for reactions of aliphatic carbon-centered radicals in aqueous solution. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1996, 25(3): 709–1050
McCormick M L, Adriaens P. Carbon tetrachloride transformation on the surface of nanoscale biogenic magnetite particles. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(4): 1045–1053
McCormick M L, Bouwer E J, Adriaens P. Carbon tetrachloride transformation in a model iron-reducing culture: relative kinetics of biotic and abiotic reactions. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(3): 403–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Gu, X., Lu, S. et al. Degradation of carbon tetrachloride in thermally activated persulfate system in the presence of formic acid. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 10, 438–446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0798-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0798-6