Abstract
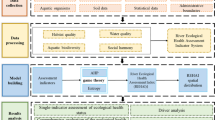
Previous studies on river health evaluation mainly focused on characterizations at a river-corridor scale and ignored the complex interactions between the river ecosystem and other components of the river basin. Based on the consideration of the interactions among rivers, associated river basin and habitats, an assessment framework with multi-scale indicators was developed. An index system divided among these three scales to characterize the health of river ecosystems in China’s Liao River Basin was established. Set pair analysis was applied to integrate the multi-scale indicators and determine the health classes. The evaluation results indicated that the rivers in the western and eastern zones of the Liao River were classified as sick, and rivers in the main stream of the Liao and Huntai rivers were classified as unhealthy. An excessive level of disturbances, such as large pollution loads and dense construction of water conservation projects within the river basin, were the main causes of the river health deterioration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Townsend C R. Concepts in river ecology: pattern and progress in the catchment hierarchy. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie (Suppl. 113). Large Rivers, 1996, 10: 3–12
Chang Q, Zhang Y F. Theory and practice of aquatic ecosystem Restoration. In: Li H Y, Ju M T, eds. Theory and Practice of Ecological Restoration. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005, 90–91 (in Chinese)
Zhao YW, Yang Z F. River health: concept, assessment method and direction. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2005, 25(1): 119–124 (in Chinese)
Maddock I. The importance of physical habitat assessment for evaluating river health. Freshwater Biology, 1999, 41(2): 373–391
Gao Y S, Wang H, Wang F. Construction of evaluation index system for river’s healthy life. Advances in Water Science, 2007, 18(2): 252–257 (in Chinese)
Liu C M, Liu X Y. Healthy river and its indication, criteria and standards. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2009, 19(1): 3–11
Boulton A J. An overview of river health assessment: philosophies, practice, problems and prognosis. Freshwater Biology, 1999, 41(2): 469–479
Wu A N, Yang K, Che Y, Yuan W. Characterization of rivers health status and its assessment. Advances in Water Science, 2005, 16(4): 602–607 (in Chinese)
Huang Y, Wen H, Cai J L. Research progress on river health assessment based on environmental management. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(4): 967–973 (in Chinese)
Karr J K. Assessments of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries (Bethesda), 1981, 6: 21–27
Oberdorff T, Pont D, Hugueny B, Porcher J P. Development and validation of a fish-based index for the assessment of ‘river health’ in France. Freshwater Biology, 2002, 47(9): 1720–1734
Silveira M P, Baptista D F, Buss D F, Nessimian J L, Egler M. Application of biological measures for stream integrity assessment in south-east Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2005, 101(1–3): 117–128
Zhang Y, Xu C B, Ma X P, Zhang Z, Wang J C. Biotic integrity index and criteria of benthic organisms in Liao River Basin. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2007, 27(6): 919–927 (in Chinese)
Robert C, Petersen J R. The RCE: a Riparian, Channel, and Environmental Inventory for small streams in the agricultural landscape. Freshwater Biology, 1992, 27(2): 295–306
Ladson A R, White L J, Doolan J A, Finlayson B L, Hart B T, Lake P S, Tilleard J W. Development and testing of an index of stream condition for waterway management in Australia. Freshwater Biology, 1999, 41(2): 453–468
Zhao Y W, Yang Z F, Yao C Q. Basic frameworks of health assessment and restoration of Yellow River. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 19(5): 131–134 (in Chinese)
Meng W, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Zheng B H. Integrated assessment of river health based on water quality, aquatic life and physical habitat. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2009, 21(8): 1017–1027
Zhang F L, Liu J L, Yang Z F, Li Y L. Ecosystem health assessment of urban rivers and lakes-Case study of “the six lakes” in Beijing, China. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China, 2008, 2(2): 209–217
Zhao Y W, Yang Z F. Integrative fuzzy hierarchical model for river health assessment: A case study of Yong River in Ningbo City, China. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2009, 14(4): 1729–1736
Zheng B H, Zhang Y, Li Y B. Study of indicators and methods for river habitat assessment of Liao River Basin. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2007, 27(6): 928–936 (in Chinese)
Su M R, Yang Z F, Chen B, Ulgiati S. Urban ecosystem health assessment based on emergy and set pair analysis-A comparative study of typical Chinese cities. Ecological Modelling, 2009, 220 (18): 2341–2348
Zou Z H, Sun J N, Ren G P. Study and application on the entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2005, 25(4): 552–556 (in Chinese)
Simpson J, Norris R, Barmuta L. AusRivAS-National River Health Program. User Manual Website version, 1999
Beijing Normal University. Water Ecological Protection and Restoration Plan in Liao River Basin. School of Environment, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 2008 (in Chinese)
Zhang Y. Aquatic ecosystem zone and river health assessment in Liao River Basin, China. Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences, 2006 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Zhao, Y., Yang, Z. et al. Multi-scale evaluation of river health in Liao River Basin, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 5, 227–235 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-010-0219-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-010-0219-9