Abstract
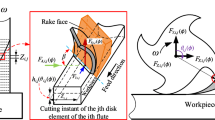
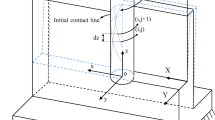
A three-dimensional finite element model was established for the milling of thin-walled parts. The physical model of the milling of the part was established using the AdvantEdge FEM software as the platform. The aluminum alloy impeller was designated as the object to be processed and the boundary conditions which met the actual machining were set. Through the solution, the physical quantities such as the three-way cutting force, the tool temperature, and the tool stress were obtained, and the calculation of the elastic deformation of the thin-walled blade of the free-form surface at the contact points between the tool and the workpiece was realized. The elastic deformation law of the thin-walled blade was then predicted. The results show that the maximum deviation between the predicted value and the actual measured machining value of the elastic deformation was 26.055 μm; the minimum deviation was 2.011 μm, with the average deviation being 10.154 μm. This shows that the prediction is in close agreement with the actual result.
摘要
建立了薄壁零件铣削加工的三维有限元模型。以AdvantEdge FEM 软件为平台,建立零件铣削 的物理模型。以铝合金叶轮为被加工对象,设定符合实际加工的仿真边界条件,通过求解得到三向切 削力、刀具温度及刀具应力等物理量,并计算自由曲面薄壁叶片实例在各个刀触点处的弹性变形量, 预 测了薄壁叶片实例的弹性变形规律。结果表明:弹性变形预测值与实际加工测量值之间的最大偏差为 26.055 μm,最小偏差为2.011 μm,平均偏差为10.154 μm,这表明预测结果与实际结果十分吻合。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ARMAREGO E J A, DESHPANDE N D. Force prediction models and CAD/CAM software for helical tooth milling processes III: End-milling and slot operations [J]. International Journal of Product Research, 1994, 32(7): 1715–1738.
BUDAK E, ALTINTAS Y, ARMOREGO E J A. Prediction of milling force coefficients from orthogonal cutting data [J]. ASME Journal of Manufacture Science and Engineering, 1996, 118(2): 216–224.
WEINERT K, BIERMANN D, KERSTING M, GRÜNERT S. Experimental and computational analysis of machining processes for light-weight aluminum structures [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2008, 43: 97–104.
LI Hong-qi, SHIN Y C. A comprehensive dynamic end milling simulation model [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2006, 128(1): 86–95.
GUO H, ZUO D W, WU H B, TONG G Q. Prediction on milling distortion for aero-multi-frame parts [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 499(1): 230–233.
RATCHEV S, LIU S, HUANG W, BECKER A A. Milling error prediction and compensation in machining of low-rigidity parts [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2004, 44(15): 1629–1641.
RATCHEV S, LIU S, BECHER A A. Error compensation strategy in milling flexible thin-wall parts [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 162(10): 673–681.
WANG Ling-yun, HUANG Hong-hui, Intelligent manufacturing system of impeller for computer numerical control (CNC) programming based on KBE [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(12): 4577–4584.
WANG Chun, CHENG Hao, SU Bin. Johnson cook material model and simulation experiment of aluminum alloy 6005A [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 472–475: 510–514.
RATCHEV S, LIU Shu-long, HUANG Wei. Machining simulation and system integration combining FE analysis and cutting mechanics modeling [J] International Journal of Advanced Manufacture, 2007, 35(1): 55–65.
CHEN Wei-fang, XUE Jian-bin. Deformation prediction and error compensation in multilayer milling processes fort hin-walled parts [J] International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2009, 49(11): 859–864.
WANG Y P, HAN Chun-jie, WANG Can, LI Shi-ke. A modified Johnson–Cook model for 30Cr2Ni4MoV rotor steel over a wide range of temperature and strain rate [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2011, 46(9): 2922–2927.
RATCHEV S, LIU S, HUANG W, BECKER A A. An advanced FEA based force induced error compensation strategy in milling [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2006, 46(5): 542–551.
SHROT A, BAKER M. Determination of Johnson-Cook parameters from machining simulations [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 52(1): 298–304.
EUN Y H, DONG W K, JONG Y L, LEE C S, CHEN F F. High speed pocket milling planning by feature-based machining area partitioning [J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2011, 27(4): 706–713.
GUO H, ZUO D W, WU H B, XU F, TONG G Q. Prediction on milling distortion for aero-multi-frame parts [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 499(1): 230–233.
YE G G, XUE S F, JIANG M Q. Modeling periodic adiabatic shear band evolution during high speed machining Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2013, 40(1): 39–55.
SONG Qing-hua, LIU Zhan-qiang, AI Xing, LIU Zhen-ling. Influence of chatter on machining distortion for thin-walled component peripheral milling [J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2014, Article ID329564. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/329564.
EUN Y H, DONG W K, JONG Y L, LEE C S, CHEN F F. High speed pocket milling planning by feature-based machining area partitioning [J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2011, 27(4): 706–713.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(U1530138) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(A1-8903-17-0103) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Ly., Huang, Hh., West, R.W. et al. A model of deformation of thin-wall surface parts during milling machining process. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 1107–1115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3810-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3810-z