Abstract
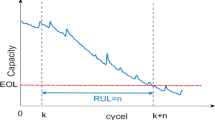
Reliability and remaining useful life (RUL) estimation for a satellite rechargeable lithium battery (RLB) are significant for prognostic and health management (PHM). A novel Bayesian framework is proposed to do reliability analysis by synthesizing multisource data, including bivariate degradation data and lifetime data. Bivariate degradation means that there are two degraded performance characteristics leading to the failure of the system. First, linear Wiener process and Frank Copula function are used to model the dependent degradation processes of the RLB’s temperature and discharge voltage. Next, the Bayesian method, in combination with Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) simulations, is provided to integrate limited bivariate degradation data with other congeneric RLBs’ lifetime data. Then reliability evaluation and RUL prediction are carried out for PHM. A simulation study demonstrates that due to the data fusion, parameter estimations and predicted RUL obtained from our model are more precise than models only using degradation data or ignoring the dependency of different degradation processes. Finally, a practical case study of a satellite RLB verifies the usability of the model.
摘要
卫星蓄电池剩余剩余寿命预测是卫星系统故障诊断与健康管理的重要一环。 本文创新性的提出了一个融合二元性能退化数据和寿命数据的可靠性分析贝叶斯模型, 对卫星锂电池的剩余寿命进行预测。 二元性能退化是指系统存在两个相关的性能退化现象, 二者的共同作用下可能导致系统故障。 模型中首先利用 Copula 函数和线性维纳过程对锂电池的二元性能退化数据进行建模。 而后, 利用贝叶斯模型融合小子样寿命数据, 采用马尔科夫蒙特卡洛仿真估计模型参数, 从而对剩余寿命进行预测, 并通过仿真和实例分析对所提模型的性能进行分析。 结果表明融合了二元性能退化数据和寿命数据后, 剩余寿命的预测精度能够有效提高。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GAO Li-jun, LIU Sheng-yi, DOUGAL R A. Dynamic lithium-ion battery model for system simulation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Components and Packaging Technologies, 2002, 25(3): 495–505.
ERDINC O, VURAL B, UZUNOGLU M. A dynamic lithium-ion battery model considering the effects of temperature and capacity fading [C]//International Conference on Clean Electrical Power. Capri, Italy: IEEE, 2009: 383–386.
JIN Guang, MATTHEWS D E, ZHOU Zhong-bao. A Bayesian framework for on-line degradation assessment and residual life prediction of secondary batteries in spacecraft [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2013, 113: 7–20.
PATEL M R. Spacecraft power systems [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2005.
SI Xiao-sheng. An adaptive prognostic approach via nonlinear degradation modelling: Application to battery data [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 62(8): 5082–5096.
TANG Sheng-jin, YU Chuan-qiang, WANG Xue, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on the Wiener process with measurement error [J]. Energies, 2014, 7(2): 520–547.
HU Chao, JAIN G, TAMIRISA P, et al. Method for estimating capacity and predicting remaining useful life of lithium-ion battery [J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 126: 182–189.
SONG L, EVANS J W. Electrochemical-thermal model of lithium polymer batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(6): 2086–2095.
GU W B, WANG C Y. Thermal-electrochemical modeling of battery systems [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(8): 2910–2922.
LIAW B Y, JUNGST R G, NAGASUBRAMANIAN G, et al. Modeling capacity fade in lithium-ion cells [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 140(1): 157–161.
SHIM J, KOSTECKI R, RICHARDSON T, et al. Electrochemical analysis for cycle performance and capacity fading of a lithium-ion battery cycled at elevated temperature [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 112(1): 222–230.
SPOTNITZ R. Simulation of capacity fade in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 113(1): 72–80.
LIU Da-tong, WANG Hong, PENG Yu, et al. Satellite lithium-ion battery remaining cycle life prediction with novel indirect health indicator extraction [J]. Energies, 2013, 6(8): 3654–3668.
VETTER J, NOV K P, WAGNER M R, et al. Ageing mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 147(1): 269–281.
WANG Xiao-lin, GUO Bo, CHENG Zhi-jun. Residual life estimation based on bivariate Wiener degradation process with time-scale transformations [J]. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 2012, 84(3): 545–563.
CHEN S C, WAN C C, WANG Y Y. Thermal analysis of lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 140(1): 11–24.
ZHANG Jing-liang, LEE J. A review on prognostics and health monitoring of Li-ion battery [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(15): 6007–6014.
CHOI Young-jin, WANG Jin-suk. Stability analysis of a voltage-temperature (V/T) limit circuit for satellite power system [C]//Proceedings of the Energy Conversion Engineering Conference (IECEC 1996). Washington, DC, USA: IEEE, 1996, 1: 316–321.
COX D R, MILLER H D. The theory of stochastic process [M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1965.
PAN Zheng-qiang, BALAKRISHNAN N, SUN Q, et al. Bivariate degradation analysis of products based on Wiener processes and copulas [J]. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 2013, 83(7): 1316–1329.
WANG Xiao-lin, GUO Bo, CHENG Zhi-jun, et al. Residual life estimation based on bivariate Wiener degradation process with measurement errors [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(1): 844–851.
SAHA B, GOEBEL K, POLL S, et al. Prognostics methods for battery health monitoring using a Bayesian framework [J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2009, 58(2): 291–296.
HE Wei, WILLIARD N, OSTERMAN M, et al. Prognostics of lithium-ion batteries based on Dempster–Shafer theory and the Bayesian Monte Carlo method [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(23): 10314–10321.
WANG Li-zhi, PAN Rong, LI Xiao-yang, et al. A Bayesian reliability evaluation method with integrated accelerated degradation testing and field information [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2013, 112: 38–47.
LEHMANN A. Joint modeling of degradation and failure time data [J]. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2009, 139(5): 1693–1706.
GUO Ji-qiang, WILSON A G. Bayesian methods for estimating system reliability using heterogeneous multilevel information [J]. Technometrics, 2013, 55(4): 461–472.
NELSEN R B. An introduction to copulas [M]. Second ed. New York: Springer Science+Business Media, Inc, 2006.
PENG Wei-wen, HUANG Hong-zhong, LI Yan-feng, et al. Life cycle reliability assessment of new products—A Bayesian model updating approach [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2013, 112(10): 9–19.
SKLAR A. Random variables, joint distributions, and copulas [J]. Kybernetica, 1973, 9(6): 449–460.
SAHA B, GOEBEL K. Modeling Li-ion battery capacity depletion in a particle filtering framework [C]//The Annual Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society. San Diego, CA: PHMsociety, 2009: 2909–2924.
PENG C Y, TSENG S T. Mis-specification analysis of linear prediction models [J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2009, 58(3): 444–455.
NTZOUFRAS I. Bayesian modeling using WinBUGS [M]. Canada: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2009.
PENG Wei-wen, LIU Yu, LI Yan-feng, et al. A Bayesian optimal design for degradation tests based on the inverse Gaussian process [J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2014, 28(10): 3937–3946.
WANG Zhong-lai, HUANG Hong-zhong, DU Li. Reliability analysis on competitive failure processes under fuzzy degradation data [J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2011, 11(3): 2964–2973.
YUAN T, JI Y. A Hierarchical bayesian degradation model for heterogeneous data [J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2015, 64(1): 63–70.
PAN Zheng-qiang, BALAKRISHNAN N, SUN Quan. Bivariate constant-stress accelerated degradation model and inference [J]. Communications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation, 2010, 40(2): 247–257.
SPIEGELHALTER D J, BEST N G, CARLIN B P, et al. Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit [J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 2002, 64(4): 583–639.
SPIEGELHALTER D J, BEST N G, CARLIN B P, et al. The deviance information criterion: 12 years on [J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 2014, 76(3): 485–493.
HAO Hui-bing, SU Chun. A Bayesian framework for reliability assessment via wiener process and MCMC [J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014, 2014 Article ID 486368. DOI: 101155120141486368.
SANTOS C A, ACHCAR J A. A Bayesian analysis in the presence of covariates for multivariate survival data: An example of application [J]. Revista Colombinana De Estadistica, 2011, 34(1): 111–131.
TSAI C C, TSENG S T, BALAKRISHNAN N. Mis-specification analyses of gamma and Wiener degradation processes [J]. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2011, 141(12): 3725–3735.
MASSEY J R, FRANK J. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for goodness of fit [J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1951, 46(253): 68–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(71371182) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Jia, X. & Guo, B. Bayesian framework for satellite rechargeable lithium battery synthesizing bivariate degradation and lifetime data. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 418–431 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3747-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3747-2
Key words
- rechargeable lithium battery
- Bayesian framework
- bivariate degradation
- lifetime data
- remaining useful life
- reliability evaluation