Abstract
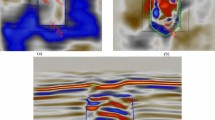
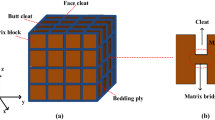
Water flooding disasters are one of the five natural coal-mining disasters that threaten the lives of coal miners. The main causes of this flooding are water-conducting fractured zones within coal seams. However, when resistivity methods are used to detect water-conducting fractured zones in coal seams, incorrect conclusions can be drawn because of electrical anisotropy within the water-conducting fractured zones. We present, in this paper, a new geo–electrical model based on the geology of water-conducting fractured zones in coal seams. Factors that influence electrical anisotropy were analyzed, including formation water resistivity, porosity, fracture density, and fracture surface roughness, pressure, and dip angle. Numerical simulation was used to evaluate the proposed electrical method. The results demonstrate a closed relationship between the shape of apparent resistivity and the strike and dip of a fracture. Hence, the findings of this paper provide a practical resistivity method for coal-mining production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brace, W. F., and Orange A. F., 1968, Electrical resistivity changes in saturation rocks during fracture and frictional sliding: J. Geophysics. Res., 73 1433–1445.
Brown, S. R., 1995, Simple mathematical model of a rough fracture: Journal of Geophysical Research, 100(B4), 5941–5952.
Cheng, J. L., Li, F., Peng, S. P., et al., 2015, Joint inversion of TEM and DC in roadway advanced detection based on particle swarm optimization.: Journal of Applied Geophysics, 123 30–35.
Chang, J. H., Yu, J. C., and Liu, Z. X., 2016, Threedimensional numerical modeling of full-space transient electromagnetic responses of water in goaf: Applied Geophysics, 13(3), 539–552.
Dong, N. G., Pan, L. Y., and Li, J. B., 2011, Talk about of control measures of major hazard sources: Shandong Coal Science and Technology, 1 200–201.
Keller, G. V., and Frischknecht, F. C., 1900, Electrical methods in geophysical prospecting: Pergamon Press, 190066.
Li, D. C., Ge, B. T., and Hu, J. W., 1999, Predictedmechanism and experiment of resistivity method for the coal mine: Coal Geology and Exploration, 27(6), 62–64.
Li, J. M., 2005, Geoelectric field and exploration of electrical method: The Geological Publishing House, Beijing.
Liu, S. D., Wu, R. X., Zhang, P. S., and Cao, Y., 2009, Three dimension parallel electric surveying and iIts applications in water disaster exploration in coal mines: Journal of China Coal society, 34(7), 927–932.
Liu, T. M. and Qin, H. l., 2006, Economic analysis of safety accidents in China coal mining: Coal Mine Safety, Total (377), 70–72.
Power, W. L., Tullis T. E., et al., 1987, Roughness of natural faults surface: Geophysics Research Letter, 14 29–32.
Sui W. H., et al., 2015, Interactions of overburden failure zones due to multiple-seam mining using longwall caving: Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 74(3), 1019–1035.
Said, A. H., 1994, Electric study of fracture anisotropy at Falkenberg: Geophysics, 59(6), 881–888.
Shen, J. S., et al., 2010, Analysis of the mechanism of the effects of secondary porosities on the cementation factor and saturation index in reservoir formation with vuggs and fractures: Well Logging Technology, 34(1), 9–15.
Shen, J. S., et al., 2009, Study on the anisotropic characteristics of the electric response to fractures reservoir: Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(11), 2903–2912.
Stesky, R. M., 1986, Electrical conductivity of brine saturated fractured rock: Geophysics, 51(8), 1585–1593.
Yue, J. H., and Li, Z. D., 1997, Mine DC Electrical Methods and Application to Coal Floor Water Invasion Detecting: Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 26(1), 94–98.
Yin, C., and Hodges, G., 2003, Identification of Electrical Anisotropy from Helicopter EM Data. Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, 419–431.
Yan, S., Xue, G. Q., Qiu, W. Z., et al., 2016, Feasibility of central loop TEM method for prospecting multilayer water-filled goaf. Applied Geophysics, 13(4), 587–597.
Yin, C., and Weidelt, P., 1999, Geoelectrical fields in a layered earth with arbitrary anisotropy: Geophysics, 64(2), 426–434.
Zhao, G. M., Li, T. L., Xu, K. J., and Li, J. P., 2007, The study and application of well-surface resistivity method in the safety at coal field: Progress in Geophysics, 22(6), 1895–1899.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities 2014QNA88 as well as the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 41674133).
Su Ben-Yu, graduated from Northeast Petroleum University in Exploration Technology and Engineering in 2006. He received a master’s degree from China University of Petroleum (Beijing) in Earth Exploration & Information Technology in 2009. He pursued his Ph. D. degree from 2009 to 2012 in geophysics in Kyushu University. Currently he is teaching and doing research at China University of Mining and Technology as a geophysical associated professor. His main research field is forward and inverse numerical simulation of mining geophysics.
Yue Jian-Hua, Professor and doctoral supervisor, graduated from the Tongji University in marine geophysics in 1986. He received a master’ s degree in geophysics from the China University of Mining and Technology in 1991 and a Ph. D. degree in coal, oil, and gas geology and exploration in 1997. He pursued post-doctoral studies on mechanics from 1998 to 2001. His main research interests include coal field and mine geophysics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, BY., Yue, JH. Research of the electrical anisotropic characteristics of water-conducting fractured zones in coal seams. Appl. Geophys. 14, 216–224 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-017-0620-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-017-0620-2