Abstract
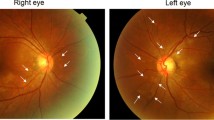
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) after heart transplantation is a rare, but serious complication, because of a high risk for permanent neurological deficits or allograft rejection. A 48-year-old female who underwent orthotropic heart transplantation presented with a sudden severe headache 10 days after transplantation. Although magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) findings at initial symptom onset were normal, MRA finding at the next day revealed multifocal vasoconstriction of cerebral arteries. Tacrolimus-induced RCVS was strongly suspected, and tacrolimus was immediately discontinued and basiliximab was added as an alternative immunosuppressant. Notably, neurological symptoms occurred at the time of sharp increase in serum tacrolimus levels and resolved when it decreased to low levels. Follow-up MRA showed complete remission and she recovered without any neurological symptom or allograft rejection. Our case suggests that prompt diagnosis with repeated MRA and immediate discontinuation of tacrolimus are essential to avoid severe neurological sequelae of RCVS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ducros A. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(10):906–17.
Ducros A, Fiedler U, Porcher R, Boukobza M, Stapf C, Bousser MG. Hemorrhagic manifestations of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: frequency, features, and risk factors. Stroke. 2010;41(11):2505–11.
Kodama S, Mano T, Masuzawa A, Hirata Y, Nagasako Y, Mano KK, et al. Tacrolimus-induced reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome with delayed multi-segmental vasoconstriction. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26(5):e75–7.
Ban SP, Hwang G, Kim CH, Kwon O. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome combined with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after heart transplantation. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;42:118–21.
Kumai Y, Seguchi O, Sato T, Wada K, Shiozawa M, Yokota C, et al. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome after heart transplantation: a case report. Transplant Proc. 2017;49(10):2415–8.
Park CS, Park JJ. Two rare neurologic complications after heart transplantation: posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, followed by reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016;35(7):940–3.
Kitamura S. Heart transplantation in Japan: a critical appraisal for the results and future prospects. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;60:639–44.
Sato M, Okada Y, Oto T, Minami M, Shiraishi T, Nagayasu T, et al. Registry of the Japanese Society of Lung and Heart-Lung Transplantation: official Japanese lung transplantation report. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:594–601.
Bechstein WO. Neurotoxicity of calcineurin inhibitors: impact and clinical management. Transpl Int. 2000;13:313–26.
Costanzo MR, Dipchand A, Starling R, et al. The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Guidelines for the care of heart transplant recipients. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010;29:914–56.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest existed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeda, S., Saito, S., Toda, K. et al. A case of tacrolimus-induced reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome after heart transplantation. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 68, 1483–1486 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01309-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-020-01309-2