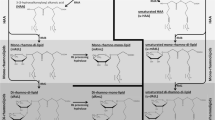
Abstract
Sugar fatty acid nonionic surfactants have attracted great attention due to their good biodegradability, biocompatibility, and bio-based characteristics. Regioselective sugar acylation is difficult to control for chemical reactions. The immiscible nature between hydrophilic sugars and hydrophobic fatty acids also negatively affects the reaction efficiency. In the present study, a group of sugar fatty acid nonionic surfactants, ethyl di-rhamnolipids, was synthesized. Di-rhamnolipids were isolated from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa fermentation broth containing a rhamnolipid mixture with about 64 % di-rhamnolipids, and then purified by silica gel chromatography. Di-rhamnolipids were successfully ethylated at 0 °C for 24 h, confirmed by HPLC–MS and 1H-NMR analyses. Preliminary emulsification test indicated that ethyl di-rhamnolipids were a potential class of useful sugar fatty acid nonionic surfactants. The synthesis process was mild, did not require regioselective sugar acylation, and offered a new way of developing novel sugar fatty acid nonionic surfactants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foley P, pour AK, Beach ES, Zimmerman JB (2012) Derivation and synthesis of renewable surfactants. Chem Soc Rev 41:1499–1518
Machut C, Mouri-Belabdelli F, Cavrot J-P, Sayede A, Monflier E (2010) New supramolecular amphiphiles based on renewable resources. Green Chem 12:772–775
Lee M, Gwak HS, Park BD, Lee S-T (2005) Synthesis of mycolic acid biosurfactants and their physical and surface-active properties. J Am Oil Chem Soc 82:181–188
Wadekar S, Kale S, Lali A, Bhowmick D, Pratap A (2012) Sophorolipid production by Starmerella bombicola (ATCC 22214) from virgin and waste frying oils, and the effects of activated earth treatment of the waste oils. J Am Oil Chem Soc 89:1029–1039
Crosman JT, Pinchuk RJ, Cooper DG (2002) Enhanced biosurfactant production by Corynebacterium alkanolyticum ATCC 21511 using self-cycling fermentation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 79:467–472
Baker IJ, Matthews B, Suares H, Krodkiewska I, Furlong DN, Grieser F, Drummond CI (2000) Sugar fatty acid ester surfactants: structure and ultimate aerobic biodegradability. J Surfactants Deterg 3:1–11
Pepić I, Hafner A, Lovrić J, Pirkić B, Filipović-Grčić J (2010) A nonionic surfactant/chitosan micelle system in an innovative eye drop formulation. J Pharm Sci 99:4317–4325
Flower DR, Perrie Y (2013) Immunomic discovery of adjuvants and candidate subunit vaccines. Springer, New York
Polat T, Linhardt RJ (2001) Syntheses and applications of sucrose-based esters. J Surfactants Deterg 4:415–421
van den Broek LA, Boeriu CG (2013) Enzymatic synthesis of oligo- and polysaccharide fatty acid esters. Carbohydr Polym 93:65–72
Gumel A, Annuar M, Heidelberg T, Chisti Y (2011) Lipase mediated synthesis of sugar fatty acid esters. Process Biochem 46:2079–2090
Ruiz CC (2010) Sugar-based surfactants: fundamentals and applications. CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, Florida
Fregapane G, Sarney DB, Vulfson EN (1991) Enzymic solvent-free synthesis of sugar acetal fatty acid esters. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:796–800
Plou FJ, Cruces M, Ferrer M, Fuentes G, Pastor E, Bernabé M, Christensen M, Comelles F, Parra JL, Ballesteros A (2002) Enzymatic acylation of di- and trisaccharides with fatty acids: choosing the appropriate enzyme, support and solvent. J Biotechnol 96:55–66
Tsuzuki W, Kitamura Y, Suzuki T, Kobayashi S (1999) Synthesis of sugar fatty acid esters by modified lipase. Biotechnol Bioeng 64:267–271
Ganske F, Bornscheuer UT (2005) Lipase-catalyzed glucose fatty acid ester synthesis in ionic liquids. Org Lett 7:3097–3098
Ye R, Pyo S-H, Hayes DG (2010) Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of saccharide-fatty acid esters using suspensions of saccharide crystals in solvent-free media. J Am Oil Chem Soc 87:281–293
Lee SH, Dang DT, Ha SH, Chang W-J, Koo Y-M (2008) Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of fatty acid sugar ester using extremely supersaturated sugar solution in ionic liquids. Biotechnol Bioeng 99:1–8
Degn P, Zimmermann W (2001) Optimization of carbohydrate fatty acid ester synthesis in organic media by a lipase from Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Bioeng 74:483–491
Ferrer M, Soliveri J, Plou FJ, Lopez-Cortes N, Reyes-Duarte D, Christensen M, Copa-Patiño JL, Ballesteros A (2005) Synthesis of sugar esters in solvent mixtures by lipases from Thermomyces lanuginosus and Candida antarctica B, and their antimicrobial properties. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:391–398
Ganske F, Bornscheuer UT (2005) Optimization of lipase-catalyzed glucose fatty acid ester synthesis in a two-phase system containing ionic liquids and t-BuOH. J Mol Catal B Enzym 36:40–42
Wang X, Miao S, Wang P, Zhang S (2012) Highly efficient synthesis of sucrose monolaurate by alkaline protease Protex 6L. Bioresource Technol 109:7–12
Henkel M, Müller MM, Kügler JH, Lovaglio RB, Contiero J, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2012) Rhamnolipids as biosurfactants from renewable resources: concepts for next-generation rhamnolipid production. Process Biochem 47:1207–1219
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Lépine F, Déziel E (2010) Rhamnolipids: diversity of structures, microbial origins and roles. Appl Microbiol Biot 86:1323–1336
Mulligan CN (2009) Recent advances in the environmental applications of biosurfactants. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 14:372–378
Müller MM, Kügler JH, Henkel M, Gerlitzki M, Hörmann B, Pöhnlein M, Syldatk C, Hausmannb R (2012) Rhamnolipids–next generation surfactants? J Biotechnol 162:366–380
Pratap A, Wadekar S, Kale S, Lali A, Bhowmick DN (2011) Non-traditional oils as newer feedstock for rhamnolipids production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 10145). J Am Oil Chem Soc 88:1935–1943
Heyd M, Kohnert A, Tan T-H, Nusser M, Kirschhöfer F, Brenner-Weiss G, Franzreb M, Berensmeier S (2008) Development and trends of biosurfactant analysis and purification using rhamnolipids as an example. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1579–1590
Yan P, Lu M, Yang Q, Zhang H-L, Zhang Z-Z, Chen R (2012) Oil recovery from refinery oily sludge using a rhamnolipid biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas. Bioresource Technol 116:24–28
Zeftawy E, Monem M, Mulligan CN (2011) Use of rhamnolipid to remove heavy metals from wastewater by micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration (MEUF). Sep Purif Technol 77:120–127
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2009) Rhamnolipid biosurfactant-enhanced soil flushing for the removal of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings. Process Biochem 44:296–301
Nayak AS, Vijaykumar M, Karegoudar T (2009) Characterization of biosurfactant produced by Pseudoxanthomonas sp. PNK-04 and its application in bioremediation. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:73–79
Cameotra SS, Makkar RS (2010) Biosurfactant-enhanced bioremediation of hydrophobic pollutants. Pure Appl Chem 82:97–116
Lovaglio RB, dos Santos FJ, Jafelicci M, Contiero J (2011) Rhamnolipid emulsifying activity and emulsion stability: pH rules. Colloids Surf B 85:301–305
Sodagari M, Wang H, Ju L-K, Newby B-M (2012) Effect of rhamnolipids on initial attachment of bacteria on glass and octadecyltrichlorosilane-modified glass. Colloids Surf B 101:121–128
Chayabutra C, Ju LK (2001) Polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and rhamnolipids are synthesized sequentially in hexadecane fermentation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145. Biotechnol Progr 17:419–423
Pinzon NM, Ju L-K (2009) Improved detection of rhamnolipid production using agar plates containing methylene blue and cetyl trimethylammonium bromide. Biotechnol Lett 31:1583–1588
Sodagari M, Ju L-K (2014) Cells were a more important foaming factor than free rhamnolipids in fermentation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa E03-40 for high rhamnolipid production. J Surfactants Deterg 17:573–582
Déziel E, Lépine F, Milot S, Villemur R (2000) Mass spectrometry monitoring of rhamnolipids from a growing culture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 57RP. Biochim Biophys Acta 1485:145–152
Ye R, Hayes DG (2012) Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of saccharide-fatty acid esters utilizing solvent-free suspensions: effect of acyl donors and acceptors, and enzyme activity retention. J Am Oil Chem Soc 89:455–463
Davies J (1957) A quantitative kinetic theory of emulsion type, I. Physical chemistry of the emulsifying agent. Gas/liquid and liquid/liquid interface. Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress of Surface Activity, Butterworths, London
Bourrel M, Salager J, Schechter R, Wade W (1980) A correlation for phase behavior of nonionic surfactants. J Colloid Inter Sci 75:451–461
Salager J-L, Forgiarini AM, Bullón J (2013) How to attain ultralow interfacial tension and three-phase behavior with surfactant formulation for enhanced oil recovery: a review. Part 1. Optimum formulation for simple surfactant–oil–water ternary systems. J Surfactants Deterg 16:449–472
Salager J-L, Manchego L, Márquez L, Bullón J, Forgiarini A (2014) Trends to attain a lower interfacial tension in a revisited pure alkyl polyethyleneglycol surfactant–alkane–water ternary system. Basic concepts and straightforward guidelines for improving performance in enhanced oil recovery formulations. J Surfactants Deterg 17:199–213
Cayias J, Schechter R, Wade W (1976) Modeling crude oils for low interfacial tension. Soc Petrol Eng J 16:351–357
Queste S, Salager J, Strey R, Aubry J (2007) The EACN scale for oil classification revisited thanks to fish diagrams. J Colloid Inter Sci 312:98–107
Bouton F, Durand M, Nardello-Rataj V, Serry M, Aubry J-M (2009) Classification of terpene oils using the fish diagrams and the equivalent alkane carbon (EACN) scale. Colloid Surf A 338:142–147
Pérez MM, Salager J-L, Miñana-Pérez M, Graciaa A, Lachaise J (1995) Solubilization of polar oils in microemulsion systems. Springer, Berlin
Ontiveros JF, Pierlot C, Catté M, Molinier V, Pizzino A, Salager J-L, Aubry J-M (2013) Classification of ester oils according to their Equivalent alkane carbon number (EACN) and asymmetry of fish diagrams of C10E4/ester oil/water systems. J Colloid Inter Sci 403:67–76
Baran JR Jr, Pope GA, Wade WH, Weerasooriya V, Yapa A (1994) Microemulsion formation with mixed chlorinated hydrocarbon liquids. J Colloid Inter Sci 168:67–72
Baran JR, Pope GA, Wade WH, Weerasooriya V (1996) Water/chlorocarbon Winsor I⇔ III⇔ II microemulsion phase behavior with alkyl glucamide surfactants. Environ Sci Technol 30:2143–2147
Castellino V, Cheng Y-L, Acosta E (2011) The hydrophobicity of silicone-based oils and surfactants and their use in reactive microemulsions. J Colloid Inter Sci 353:196–205
Salager J, Bullón J, Pizzino A, Rondón-González M, Tolosa L, Somasundaran P (2010) Emulsion formulation engineering for the practitioner. Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science 1:1–6
Jv Boyd, Parkinson C, Sherman P (1972) Factors affecting emulsion stability, and the HLB concept. J Colloid Inter Sci 41:359–370
Bourrel M, Graciaa A, Schechter RS, Wade WH (1979) The relation of emulsion stability to phase behavior and interfacial tension of surfactant systems. J Colloid Inter Sci 72:161–163
Salager JL, Quintero L, Ramos E, Anderez J (1980) Properties of surfactant/oil/water emulsified systems in the neighborhood of the three-phase transition. J Colloid Inter Sci 77:288–289
Vinatieri JE (1980) Correlation of emulsion stability with phase behavior in surfactant systems for tertiary oil recovery. Soc Petrol Eng J 20:402–406
Milos F, Wasan D (1982) Emulsion stability of surfactant systems near the three phase region. Colloids Surf 4:91–96
Salager J, Loaiza-Maldonado I, Minana-Perez M, Silva F (1982) Surfactant–oil–water systems near the affinity inversion part I: relationship between equilibrium phase behavior and emulsion type and stability. J Disper Sci Technol 3:279–292
Antón RE, Salager J-L (1986) Emulsion instability in the three-phase behavior region of surfactant-alcohol-oil-brine systems. J Colloid Inter Sci 111:54–59
Acosta E, Szekeres E, Sabatini DA, Harwell JH (2003) Net-average curvature model for solubilization and super solubilization in surfactant microemulsions. Langmuir 19:186–195
Tolosa L-I, Forgiarini A, Moreno P, Salager J-L (2006) Combined effects of formulation and stirring on emulsion drop size in the vicinity of three-phase behavior of surfactant-oil water systems. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:3810–3814
Graciaa A, Barakat Y, El-Emary M, Fortney L, Schechter R, Yiv S, Wade W (1982) HLB, CMC, and phase behavior as related to hydrophobe branching. J Colloid Inter Sci 89:209–216
Barakat Y, Fortney LN, Schechter RS, Wade WH, Yiv SH, Graciaa A (1983) Criteria for structuring surfactants to maximize solubilization of oil and water: II. Alkyl benzene sodium sulfonates. J Colloid Inter Sci 92:561–574
Salager J-L, Forgiarini AM, Márquez L, Manchego L, Bullón J (2013) How to attain an ultralow interfacial tension and a three-phase behavior with a surfactant formulation for enhanced oil recovery: a review. Part 2. Performance improvement trends from Winsor’s premise to currently proposed inter-and intra-molecular mixtures. J Surfactants Deterg 16:631–663
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the U.S. Department of Agriculture under the Biomass Research and Development Initiative (award # 2009-10001-05112) and the US Department of Transportation, Office of the Secretary (Grant # DTOS59-07-G-00050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, S., Callow, N., Soltani Dashtbozorg, S. et al. Ethylation of Di-rhamnolipids: A Green Route to Produce Novel Sugar Fatty Acid Nonionic Surfactants. J Surfact Deterg 17, 1069–1080 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-014-1641-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-014-1641-y