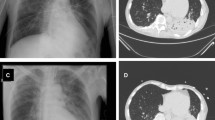
Abstract
Pneumonia is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in adults in the United States. While pneumonia classically presents with a fever, cough, and shortness of breath, the presentation can vary widely in adults. This review evaluates history and physical examination findings of pneumonia and several conditions that mimic pneumonia. Pneumonia is a potentially deadly disease. History and examination findings are variable in pneumonia, and many conditions mimic pneumonia. These conditions include pulmonary embolism, diffuse interstitial lung disease, endocarditis, vasculitis, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, acute decompensated heart failure, tuberculosis, lung cancer, and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Emergency clinicians should assess the patient while resuscitation occurs. Early antibiotics and the diagnosis of pneumonia can improve outcomes. Key historical and physical examination findings may lead the clinician to consider other conditions that require immediate management. Using clinical evaluation and adjunctive imaging, these conditions can be diagnosed and treated. Knowledge of pneumonia mimics is vital for the care of patients with respiratory complaints. Pneumonia is common and may be deadly, and emergency clinicians must differentiate conditions that mimic pneumonia. Rapid evaluation and management may alleviate morbidity and mortality for each of these conditions. The history and physical examination, in addition to utilizing imaging modalities such as ultrasound and computed tomography, are vital in diagnosis of pneumonia mimics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A et al (2007) Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis 44:S27
Johansson N, Kalin M, Tiveljung-Lindell A et al (2010) Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia: increased microbiological yield with new diagnostic methods. Clin Infect Dis 50:202
de Roux A, Marcos MA, Garcia E et al (2004) Viral community-acquired pneumonia in nonimmunocompromised adults. Chest 125:1343
Fine MJ, Stone RA, Singer DE et al (1999) Processes and outcomes of care for patients with community-acquired pneumonia: results from the Pneumonia Patient Outcomes Research Team (PORT) cohort study. Arch Intern Med 159(9):970–980
Metlay JP, Kapoor WN, Fine MJ (1997) Does this patient have community-acquired pneumonia? Diagnosing pneumonia by history and physical examination. JAMA 278(17):1440
Rosh AJ (2005) Diagnosing pneumonia by medical history and physical examination. Ann Emerg Med 46(5):465–467
Riquelme R, Torres A, el-Ebiary M et al (1996) Community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly: a multivariate analysis of risk and prognostic factors. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154(5):1450–1455
Metlay JP, Schulz R, Li YH, Singer DE et al (1997) Influence of age on symptoms at presentation in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Arch Intern Med 157(13):1453–1459
Fernandez-Sabe N, Carratala J, Roson B et al (2003) Community-acquired pneumonia in very elderly patients: causative organisms, clinical characteristics, and outcomes. Medicine (Baltimore) 82(3):159–169
Marrie TJ (1994) Community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis 18(4):501
Hu QJ, Shen YC, Jia LQ et al (2014) Diagnostic performance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of pneumonia: a bivariate meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med 7(1):115–121
Chavez MA, Shams N, Ellington LE et al (2014) Lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Res 23(15):50
Mikolasch T, Garthwaite H, Porter J (2016) Update in diagnosis and management of interstitial lung disease. Clin Med 16(Suppl 6):s71–s78
Raghu G, Nyberg F, Morgan G (2004) The epidemiology of interstitial lung disease and its association with lung cancer. Br J Cancer 91(Suppl2):S3–S10
Kim R, Meyer K (2008) Therapies for interstitial lung disease: past, present and future. Ther Adv Respir Dis 2(5):319–338
Churg A, Wright J, Tazelaar H (2011) Acute exacerbations of fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Histopathology 58(4):525–530
Meyer K (2014) Diagnosis and management of interstitial lung disease. Transl Respir Med 2:4
Disayabutr S, Calfee C, Collard H, Wolters P (2015) Interstitial lung diseases in the hospitalized patient. BMC Med 13:245
Collard H, Moore B, Flaherty K, Brown K, Kaner R et al (2007) Acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:636–643
Kim D, Park J, Park B, Lee J, Nicholson A et al (2006) Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: frequency and clinical features. Eur Respir J 27(1):143–150
Wilcox S, Kabrhel C, Channick R (2015) Pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure in emergency medicine. Ann Emerg Med 66(6):619–628
Vianello A, Arcaro G, Battistella L, Pipitone E, Vio S et al (2014) Noninvasive ventilation in the event of acute respiratory failure in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Crit Care 29(4):562–567
Yokoyama T, Kondoh Y, Taniguichi H, Kataoka K, Kato K et al (2010) Noninvasive ventilation in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Intern Med 49(15):1509–1514
Murdoch DR, Corey GR, Hoen B et al (2009) Clinical presentation, etiology and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century: the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch Intern Med 169(5):463–473
Cahill TJ, Prendergast BD (2016) Infective endocarditis. Lancet 387(10021):882–893
Hill EE, Herijgers P, Claus P et al (2007) Infective endocarditis: changing epidemiology and predictors of 6-month mortality: a prospective cohort study. Eur Heart J 28(2):196–203
Cantrell M, Yoshikawa TT (1984) Infective endocarditis in the aging patient. Gerontology 30(5):316–326
Castillo FJ, Anguita M, Castillo JC et al (2015) Changes in the clinical profile, epidemiology and prognosis of left-sided native-valve infective endocarditis without predisposing heart conditions. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 68(5):445–448 Epub 2015 Mar 16
Steckelberg JM, Murphy JG, Ballard D et al (1991) Emboli in infective endocarditis: the prognostic value of echocardiography. Ann Intern Med 114(8):635–640
Falk RJ, Gross WL, Guillevin L et al (2011) Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): an alternative name for Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum 63:863
Jennette JC, Falk RJ (1997) Small-vessel vasculitis. N Engl J Med 337:1512
Seo P, Stone JH (2004) The antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides. Am J Med 117:39
Falk RJ, Hogan S, Carey TS, Jennette JC (1990) Clinical course of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis and systemic vasculitis. The Glomerular Disease Collaborative Network. Ann Intern Med 113:656
Hoffman GS, Kerr GS, Leavitt RY et al (1992) Wegener granulomatosis: an analysis of 158 patients. Ann Intern Med 116:488
Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, Bloch DA et al (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum 33:1101
Sinico RA, Bottero P (2009) Churg-Strauss angiitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 23:355
Pagnoux C, Guilpain P, Guillevin L (2007) Churg-Strauss syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol 19:25
Katzenstein AL (2000) Diagnostic features and differential diagnosis of Churg-Strauss syndrome in the lung. A review. Am J Clin Pathol 114:767
Lazor R, Bigay-Gamé L, Cottin V et al (2007) Alveolar hemorrhage in anti-basement membrane antibody disease: a series of 28 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 86:181
Pusey CD (2003) Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. Kidney Int 64:1535
Bolton WK (1996) Goodpasture’s syndrome. Kidney Int 50:1753
King TE Jr, Kim EJ, Kinder BW (2011) Connective tissue diseases. In: Schwartz MI, King TE Jr (eds) Interstitial lung disease, 5th edn. People’s Medical Publishing House, Shelton, p 689
Petri M, Orbai A-M, Alarcón GS et al (2012) Derivation and validation of systemic lupus international collaborating clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2677–2686
Matthay RA, Schwarz MI, Petty TL et al (1975) Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus: review of twelve cases of acute lupus pneumonitis. Medicine (Baltimore) 54(5):397–409
Wiedemann HP, Matthay RA (1992) Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Thorac Imaging 7(2):1–18
Orens JB, Martinez FJ, Lynch JP III (1994) Pleuropulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 20:159–193
Fishback N, Koss MN (1995) Pulmonary involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Pulm Med 1(5):368–375
Zamora MR, Warner ML, Tuder R et al (1997) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical presentation, histology, survival, and outcome. Medicine (Baltimore) 76(3):192–202
Andrade C, Mendonca T, Farinha F et al (2016) Alveolar hemorrhage in systemic lupus erythematosus: a cohort review. Lupus 25(1):75–80 (epub 2015 Sep 18)
Collard HR, Schwarz MI (2004) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Clin Chest Med 25:583–592 (vii)
Lara AR, Schwarz MI (2010) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Chest 137:1164–1171
Ioachimescu OC, Stoller JK (2008) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: diagnosing it and finding the cause. Cleve Clin J Med. 75:258–280
Colby TV, Fukuoka J, Ewaskow SP, Helmers R, Leslie KO (2001) Pathologic approach to pulmonary hemorrhage. Ann Diagn Pathol. 5:309–319
Cordier JF, Cottin V (2011) Alveolar hemorrhage in vasculitis: primary and secondary. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 32:310–321
Schnabel A, Holl-Ulrich K, Dalhoff K et al (1997) Efficacy of transbronchial biopsy in pulmonary vasculitides. Eur Respir J 10:2738–2743
Papiris SA, Manali ED, Kalomenidis I et al (2007) Bench-to-bedside review: pulmonary-renal syndromes—an update for the intensivist. Crit Care 11:213
Gallagher H, Kwan J, Jayne RW (2002) Pulmonary renal syndrome: a 4-year, single center experience. Am J Kidney Dis 38:42–47
Stanton MC, Tange JD (1958) Goodpasture’s syndrome (pulmonary haemorrhage associated with glomerulonephritis). Australas Ann Med 7:132–144
Rodriguez W, Hanania N, Guy E, Guntupalli J (2002) Pulmonary-renal syndromes in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Clin 18:881–895
Tesar V, Rihova Z, Jancova E et al (2003) European randomized trials: current treatment strategies in ANCA-positive renal vasculitis-lessons from European randomized trials. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:v2–v4
Hogan S, Falk RJ, Chin H, Cai J et al (2005) Predictors of relapse and treatment resistance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated small vessel vasculitis. Ann Intern Med 143:621–631
Friedman T, Sterline T, Munsif SS et al (2003) Tuberculosis. Lancet 362(9387):887–899
Barnes PF, Verdegem TD, Vachon LA et al (1988) Chest roentgenogram in pulmonary tuberculosis. New data on an old test. Chest 94(2):316–320
Oeltmann JE, Kammerer JS, Pevzner ES et al (2009) Tuberculosis and substance abuse in the United States, 1997–2006. Arch Intern Med 169(2):189–197
Figueroa-Munoz JI, Ramon-Parko P (2008) Tuberculosis control in vulnerable groups. Bull World Health Org 86(9):733–735
World Health Organization (2014) Global tuberculosis report 2014. http://www.who.int.proxy.library.vanderbilt.edu/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed 2 Feb 2017
Guideline (2009) Updated guidelines for the use of nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 58(1):7–10
Marks SM, Cronin W, Venkatappa T et al (2013) The health-system benefits and cost-effectiveness of using mycobacterium tuberculosis direct nucleic acid amplification testing to diagnose tuberculosis disease in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 57(4):532–542
World Cancer Research Fund International (2016) Worldwide data. http://www.wcrf.org/int/cancer-facts-figures/worldwide-data. Accessed June 2016
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66(1):7–30
Hyde L, Hyde CI (1974) Clinical manifestations of lung cancer. Chest 65(3):299–306
Chute CG, Greenberg ER, Baron J et al (1985) Cancer 56(8):2107–2111
Establishing the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer (2013) Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd edn: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 143(5 Suppl):e142S
MacCallum NS, Evans TW (2005) Epidemiology of acute lung injury. Curr Opin Crit Care 11(1):43–49
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E et al (2005) Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med 353(16):1685–1693
Definition Task Force ARDS, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT et al (2012) Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA 307(23):2526–2533
Ashbaugh DG, Bigelow DB, Petty TL et al (1967) Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet 2(7511):319–323
Pepe PE, Potkin RT, Reus DH et al (1982) Clinical predictors of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Surg 144(1):124–130
Miyashita N, Kawai Y, Tanaka T et al (2015) Detection failure of chest radiography for the identification of nursing and healthcare-associated pneumonia. J Infect Chemother 21(7):492–496
Shiley KT, Van Deerlin VM, Miller WT Jr (2010) Chest CT features of community-acquired respiratory viral infections in adult inpatients with lower respiratory tract infections. J Thorac Imaging 25(1):68–75
Acknowledgements
This manuscript did not utilize any grants, and it has not been presented in abstract form. It does not reflect the views or opinions of the U.S. Government, U.S. Army, U.S. Air Force, Department of Defense, or SAUSHEC residency program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, D.A., Long, B. & Koyfman, A. Clinical mimics: an emergency medicine focused review of pneumonia mimics. Intern Emerg Med 13, 539–547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-018-1840-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-018-1840-z