Abstract
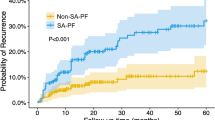
Hemoptysis is a life-threatening complication of Behcet’s disease that is likely related to pulmonary artery aneurysm (PAA). Vascular interventional radiology may offer effective emergency therapeutic option, but has not been thoroughly investigated in this setting. A case series of a French referral center for hemoptysis combined with a literature review of case reports was conducted. Between 1995 and 2016, 12 patients were referred to our center for hemoptysis revealing or complicating the course of Behcet’s disease. Pulmonary artery aneurysm (PAA) was the mechanism of hemoptysis in ten patients, nine of whom were treated by a transcatheter embolotherapy. Combining an additional 8 case reports from the literature, 17 patients treated by transcatheter embolotherapy for PAA were analyzed. The duration of the course of Behcet’s disease was 22 months [IQR 3–45] at the time of PAA diagnosis. Transcatheter embolotherapy of PAA was successful for immediately controlling hemoptysis in all patients, without major complication except for one. Hemoptysis recurred in seven patients (41%) within 5 months [IQR 1–12]. The use of coils for transcatheter embolotherapy was associated with hemoptysis recurrence. A bronchosystemic hypervascularization related to the previously occluded PAA was the main mechanism of bleeding recurrence, leading to bronchosystemic artery embolization in four patients and surgery in two patients. Behcet’s disease-related hemoptysis is mainly due to PAA. Transcatheter embolotherapy should be considered as the first-line emergency treatment for PAA-related hemoptysis, in association with the immunosuppressive regimen. Hemoptysis may recur in half of the cases, involving preferentially a bronchosystemic arterial mechanism.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAE:
-
Bronchial artery embolization
- BD:
-
Behcet’s disease
- BHV:
-
Bronchial hypervascularization
- F:
-
Female
- GS:
-
Gelfroam sponge
- HSS:
-
Hughes–Stovin syndrome
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- M:
-
Male
- NA:
-
Not available
- Nb:
-
Number
- NBCA:
-
n-Butyl-cyanoacrylate
- PAA:
-
Pulmonary artery aneurysm
- PE:
-
Pulmonary embolism
- TCE:
-
Transcatheter embolotherapy
References
Tunaci A, Berkmen YM, Gokmen E (1995) Thoracic involvement in Behcet’s disease: pathologic, clinical, and imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 164(1):51–56
Kural-Seyahi E, Fresko I, Seyahi N, Ozyazgan Y, Mat C, Hamuryudan V et al (2003) The long-term mortality and morbidity of Behcet syndrome: a 2-decade outcome survey of 387 patients followed at a dedicated center. Medicine (Baltim) 82(1):60–76
Ideguchi H, Suda A, Takeno M, Ueda A, Ohno S, Ishigatsubo Y (2011) Behcet disease: evolution of clinical manifestations. Medicine (Baltim) 90(2):125–132
Sarica-Kucukoglu R, Akdag-Kose A, KayabalI M, Yazganoglu KD, Disci R, Erzengin D, Azizlerli G (2006) Vascular involvement in Behçet’s disease: a retrospective analysis of 2319 cases. Int J Dermatol 45(8):919–921
Emmi G, Silvestri E, Squatrito D, Amedei A, Niccolai E, D’Elios MM, Della Bella C, Grassi A, Becatti M, Fiorillo C, Emmi L, Vaglio A, Prisco D (2015) Thrombosis in vasculitis: from pathogenesis to treatment. Thromb J 13:15
Hamza M (1987) Large artery involvement in Behcet’s disease. J Rheumatol 14(3):554–559
Calamia KT, Schirmer M, Melikoglu M (2005) Major vessel involvement in Behcet disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17(1):1–8
Houman MH, Neffati H, Braham A, Harzallah O, Khanfir M, Miled M et al (2007) Behcet’s disease in Tunisia. Demographic, clinical and genetic aspects in 260 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25(4 Suppl 45):S58–S64
Saadoun D, Asli B, Wechsler B, Houman H, Geri G, Desseaux K et al (2012) Long-term outcome of arterial lesions in Behcet disease: a series of 101 patients. Medicine (Baltim) 91(1):18–24
Lakhanpal S, Tani K, Lie JT, Katoh K, Ishigatsubo Y, Ohokubo T (1985) Pathologic features of Behcet’s syndrome: a review of Japanese autopsy registry data. Hum Pathol 16(8):790–795
Hamuryudan V, Yurdakul S, Moral F, Numan F, Tüzün H, Tüzüner N et al (1994) Pulmonary arterial aneurysms in Behcet’s syndrome: a report of 24 cases. Br J Rheumatol 33(1):48–51
Seyahi E, Melikoglu M, Akman C, Hamuryudan V, Ozer H, Hatemi G et al (2012) Pulmonary artery involvement and associated lung disease in Behcet disease: a series of 47 patients. Medicine (Baltim) 91(1):35–48
Uzun O, Akpolat T, Erkan L (2005) Pulmonary vasculitis in Behcet disease: a cumulative analysis. Chest 127(6):2243–2253
Hamuryudan V, Er T, Seyahi E, Akman C, Tüzün H, Fresko I et al (2004) Pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behcet syndrome. Am J Med 117(11):867–870
Gebitekin C, Yilmaz M, Senkaya I, Saba D, Sağdiç K, Ozer G (1997) Fatal haemoptysis due to pulmonary artery aneurysm in Behçet’s disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 13(2):233–236
Uzun O, Erkan L, Akpolat I, Findik S, Atici AG, Akpolat T (2008) Pulmonary involvement in Behcet’s disease. Respiration 75(3):310–321
Raz I, Okon E, Chajek-Shaul T (1989) Pulmonary manifestations in Behcet’s syndrome. Chest 95(3):585–589
Andréjak C, Parrot A, Bazelly B, Ancel PY, Djibré M, Khalil A et al (2009) Surgical lung resection for severe hemoptysis. Ann Thorac Surg 88(5):1556–1565
Tuzun H, Hamuryudan V, Yildirim S, Beşirli K, Yörük Y, Yurdakul S et al (1996) Surgical therapy of pulmonary arterial aneurysms in Behcet’s syndrome. Ann Thorac Surg 61(2):733–735
International Team for the Revision of the International (2014) Criteria for Behçet’s Disease (ITR-ICBD). The International Criteria for Behçet’s Disease (ICBD): a collaborative study of 27 countries on the sensitivity and specificity of the new criteria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 28(3):338–347
Erkan D, Yazici Y, Sanders A, Trost D, Yazici H (2004) Is Hughes–Stovin syndrome Behcet’s disease? Clin Exp Rheumatol 22(4 Suppl 34):S64–S68
Khalid U, Saleem T (2011) Hughes–Stovin syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 6:15
Kim JT, Oh TY, Chang WH (2007) Rare case of multiple pulmonary artery aneurysms with caval thrombosis–Hughes–Stovin syndrome. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 31(3):561–562
Tzilalis VD, Vourliotakis G, Tsironis IA, Tsiligiris VD, Brountzos EN (2011) Use of an Amplatzer vascular plug in embolization of a pulmonary artery aneurysm in a case of Hughes–Stovin syndrome: a case report. J Med Case Rep 5:425
Cil BE, Geyik S, Akmangit I, Cekirge S, Besbas N, Balkanci F (2005) Embolization of a giant pulmonary artery aneurysm from Behcet disease with use of cyanoacrylate and the “bubble technique”. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16(11):1545–1549
Cil BE, Turkbey B, Canyigit M, Kumbasar OO, Celik G, Demirkasik FB (2006) Transformation of a ruptured giant pulmonary artery aneurysm into an air cavity after transcatheter embolization in a Behcet’s patient. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 29(1):151–154
Cantasdemir M, Kantarci F, Mihmanli I, Akman C, Numan F, Islak C et al (2002) Emergency endovascular management of pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behcet’s disease: report of two cases and a review of the literature. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 25(6):533–537
Lacombe P, Frija G, Parlier H, Lang F, Hamza M, Hamza R et al (1985) Transcatheter embolization of multiple pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behcet’s syndrome. Report of a case. Acta Radiol Diagn 26(3):251–253
Lacombe P, Qanadli SD, Jondeau G, Barré O, Mesurolle B, Mouas H et al (1997) Treatment of hemoptysis in Behcet syndrome with pulmonary and bronchial embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol 8(6):1043–1047
Durieux P, Bletry O, Huchon G, Wechsler B, Chretien J, Godeau P (1981) Multiple pulmonary arterial aneurysms in Behcet’s disease and Hughes–Stovin syndrome. Am J Med 71(4):736–741
Bennji SM, du Preez L, Griffith-Richards S, Smit DP, Rigby J, Koegelenberg CFN, Irusen EM, Allwood BW (2017) Recurrent pulmonary aneurysms: Hughes–Stovin syndrome on the spectrum of Behçet disease. Chest 152(5):e99–e103
Kably IM, Reveron C (2015) Multimodal endovascular management of a Jehovah’s Witness patient with Hughes–Stovin syndrome presenting with ruptured pulmonary artery aneurysm and cardiopulmonary thromboembolism. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 47(4):e158–e161
Khalil A, Parrot A, Fartoukh M, Marsault C, Carette MF (2006) Images in cardiovascular medicine. Large pulmonary artery aneurysm rupture in Hughes–Stovin syndrome: multidetector computed tomography pattern and endovascular treatment. Circulation 114(10):e380–e381
Emmi G, Silvestri E, Squatrito D, D’Elios MM, Ciucciarelli L, Prisco D, Emmi L (2014) Behçet’s syndrome pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets. Intern Emerg Med 9(3):257–265
De Prost N, Parrot A, Picard C, Ancel PY, Mayaud C, Fartoukh M et al (2010) Diffuse alveolar haemorrhage: factors associated with in-hospital and long-term mortality. Eur Respir J 35(6):1303–1311
Khalil A, Parrot A, Nedelcu C, Fartoukh M, Marsault C, Carette MF (2008) Severe hemoptysis of pulmonary arterial origin: signs and role of multidetector row CT angiography. Chest 133(1):212–219
Erkan F, Gul A, Tasali E (2001) Pulmonary manifestations of Behcet’s disease. Thorax 56(7):572–578
Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Chamberlain AM, Gul A et al (2008) EULAR recommendations for the management of Behcet disease. Ann Rheum Dis 67(12):1656–1662
Tunaci M, Ozkorkmaz B, Tunaci A, Gül A, Engin G, Acunas B (1999) CT findings of pulmonary artery aneurysms during treatment for Behcet’s disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172(3):729–733
de Montpreville VT, Macchiarini P, Dartevelle PG, Dulmet EM (1996) Large bilateral pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behcet’s disease: rupture of the contralateral lesion after aneurysmorrhaphy. Respiration 63(1):49–51
Tuzun H, Besirli K, Sayin A, Vural FS, Hamuryudan V, Hizli N et al (1997) Management of aneurysms in Behcet’s syndrome: an analysis of 24 patients. Surgery 121(2):150–156
Hirohata S, Kikuchi H (2009) Histopathology of the ruptured pulmonary artery aneurysm in a patient with Behcet’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27(2 Suppl 53):S91–S95
Emad Y, Ragab Y, Shawki A-H, Gheita T, El-Marakbi A, Salama MH (2007) Hughes–Stovin syndrome: is it incomplete Behçet’s? Report of two cases and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 26(11):1993–1996
Slavin RE, de Groot WJ (1981) Pathology of the lung in Behçet’s disease. Case report and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol 5(8):779–788
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GV had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis, including and especially any adverse effects. GV participated in the conception and the design of the study, participated in the data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, and the statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. AP participated in the conception and the design of the study, participated in the data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, and helped to revise the manuscript critically for intellectual content. MA participated in the conception and the design of the study, performed the histological analysis, participated in the data acquisition and analysis, and helped to revise the manuscript critically for intellectual content. AG participated in the data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, and helped to revise the manuscript critically for intellectual content. SH participated in the data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, and helped to revise the manuscript critically for intellectual content. MFC participated in the conception and the design of the study, performed the interventional radiology procedures and helped to revise the manuscript critically for intellectual content. MF participated in the conception and design of the study, the data analysis and interpretation, and the statistical analysis, and revised the manuscript critically for intellectual content. AK designed the study, performed the interventional radiology procedures, participated in the data analysis and interpretation, and revised the manuscript critically for intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final version to be submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Availability of supporting data
Data and materials supporting the findings of this study can be entirely shared on asking.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the French law, which does not require approval of an institutional review board.
Informed consent
None.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1.
Pathological findings: pulmonary artery thrombosis. A 27-year-old patient was admitted to our department for massive hemoptysis (see legend of Figure 3). Seven years earlier, he was diagnosed a Behçet’s disease. A pulmonary artery angiography revealed a pulmonary artery aneurysm, which was occluded with coils. Nineteen months later, hemoptysis recurred and was related to a systemic hypervascularization. Two procedures of bronchial artery embolization did not allow to control the bleeding, leading to perform a right lower lobectomy. The removed lobe underwent staining with hematein-safran-eosin, and examination under a light microscope. The pulmonary artery (Pa) was thrombosed and repermeabilized. The material of embolization (arrow) was observed close to the pulmonary artery parietal wall, which displayed a marked fibrosis. Magnification X2.5. (TIFF 612 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2.
Pathological findings: systemic hypervascularization and inflammatory process. A 42-year-old patient with a history of recurrent pulmonary embolism was admitted to our department for massive hemoptysis. Hughes–Stovin syndrome (HSS) was diagnosed on the basis of the association of multiple pulmonary arteries aneurysms, pulmonary embolism, and thrombus into the right atrium. Only one pulmonary artery aneurysm (located in the right middle lobe) displayed signs of recent bleeding (air bubble and ground-glass opacities around the pulmonary artery aneurysm). The sac of this pulmonary artery aneurysm was occluded using a total of 2.07 meters of coils. The bleeding stopped. Immunosuppressive therapy was started. One month later, hemoptysis recurred and was related to a systemic hypervascularization. A bronchial artery embolization allowed to control the bleeding transiently, but the bleeding recurred 4 months later. Two additional procedures of systemic artery embolization failed to control the bleeding, leading to perform a right middle lobectomy. The removed lobe underwent staining with hematein-safran-eosin, and examination under a light microscope. (A, B) The pulmonary artery (Pa) was thrombosed; materials of bronchosystemic artery embolization (arrows) were observed in lumens of both the pulmonary artery and the adjacent systemic arteries (Sv). (C, D) A marked systemic hypervascularization (Sv) was observed around the thrombosed pulmonary artery (Pa) and its satellite bronchus (Br). (E, F) Macrophage (Mp) infiltrates were observed within the pulmonary artery thrombus; lymphocytes (Ly) and macrophage infiltrates were observed within the pulmonary artery parietal wall. Magnification X2.5 (A, C, E) and X10 (B, D, F). (TIFF 5090 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voiriot, G., Parrot, A., Antoine, M. et al. Transcatheter embolotherapy of pulmonary artery aneurysms as emergency treatment of hemoptysis in Behcet patients: experience of a referral center and a review of the literature. Intern Emerg Med 13, 491–500 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-018-1817-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-018-1817-y