Abstract
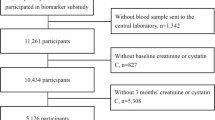
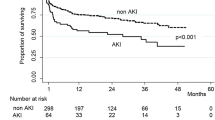
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is proven to be an independent risk factor for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with stroke, but data about the epidemiology of AKI in these patients are not well characterized. Therefore, we investigated the incidence, risk factors, and the impact of AKI on the clinical outcomes in a group of Chinese patients with stroke. We retrospectively recruited 647 stroke patients from the neurology ICU between 2012 and 2013. AKI was identified according to the 2012 KDIGO criteria. Baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using modified Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation for Chinese patients. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score was assessed for the stroke severity. A total of 135 (20.9%) patients developed AKI. Patients with AKI stages from 1 to 3 were 84 (62.2%), 26 (19.3%), and 25 (18.5%), respectively. Logistic regression analysis showed that independent risk factors for AKI were higher NIHSS score (OR, 1.027; 95% CI 1.003–1.051), lower baseline eGFR (OR, 0.985; 95% CI 0.977–0.993), the presence of hypertension (OR, 1.592; 95% CI 1.003–2.529), and infectious complications (OR, 3.387; 95% CI 1.997–5.803) (P < 0.05 for all). AKI patients were also significantly associated with all-cause mortality in the neurology ICU [OR and 95% CI of AKI-stage 1, AKI-stage 2, and AKI-stage 3 were 4.961 (2.191–11.232), 19.722 (6.354–61.217), and 48.625 (17.616–134.222), respectively (P < 0.001 for all)]. AKI is common among patients with stroke and is associated with worse clinical outcomes after stroke. Prevention of AKI seems to be very important among these patients, because they are exposed to many risk factors for developing AKI.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
Acute kidney injury
- KDIGO:
-
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes
- NICU:
-
Neurological intensive care unit
- Scr:
-
Serum creatinine
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial blood pressure
- NIHSS:
-
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
- mRS:
-
Modified Rankin Scale
- ACEIs:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- ARBs:
-
Angiotensin receptor blockers
- NSAIDs:
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- WBC:
-
White blood cell count
- PLT:
-
Platelet
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- CO2CP:
-
Carbon dioxide combining power
- BUN:
-
Blood urea nitrogen
- CKD-EPI:
-
Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration
- OR:
-
Odds ratios
- CI:
-
Confidence intervals
References
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S et al (2005) Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294:813–818
Nash K, Hafeez A, Hou S (2002) Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis 39:930–936
Ali T, Khan I, Simpson W, Prescott G, Townend J, Smith W et al (2007) Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury: a comprehensive population-based study. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1292–1298
Lafrance JP, Miller DR (2010) Acute kidney injury associates with increased long-term mortality. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:345–352
Challiner R, Ritchie JP, Fullwood C, Loughnan P, Hutchison AJ (2014) Incidence and consequence of acute kidney injury in unselected emergency admissions to a large acute UK hospital trust. BMC Nephrol 15:1
Fang Y, Ding X, Zhong Y, Zou J, Teng J, Tang Y et al (2010) Acute kidney injury in a Chinese hospitalized population. Blood Purif 30:120–126
Johnston SC, Mendis S (2009) MathersCD. Global variation in stroke burden and mortality: estimates from monitoring, surveillance, and modelling. Lancet Neurol 8:345–354
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM (2008) Stroke. Lancet 371:1612–1623
Pisoni R, Wille KM, Tolwani AJ (2008) The epidemiology of severe acute kidney injury: from BEST to PICARD, in acute kidney injury: new concepts. Nephron Clin Pract 109:c188–c191
Liu M, Wu B, Wang WZ, Lee LM, Zhang SH, Kong LZ (2007) Stroke in China: epidemiology, prevention, and management strategies. Lancet Neuro. 6:456–464
Tsagalis G, Akrivos T, Alevizaki M, Manios E, Theodorakis M, Laggouranis A et al (2009) Long-term prognosis of acute kidney injury after first acute stroke. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:616–622
Covic A, Schiller A, Mardare NG, Petrica L, Petrica M, Mihaescu A et al (2008) The impact of acute kidney injury on short-term survival in an Eastern European population with stroke. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:2228–2234
Khatri M, Himmelfarb J, Adams D, Becker K, Longstreth WT, Tirschwell DL (2014) Acute kidney injury is associated with increased hospital mortality after stroke. Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23:25–30
Zacharia BE, Ducruet AF, Hickman ZL, Grobelny BT, Fernandez L, Schmidt JM et al (2009) Renal dysfunction as an independent predictor of outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a single-center cohort study. Stroke 40:2375–2381
Qureshi AI, Palesch YY, Martin R, Novitzke J, Flores SC, Ehtisham A et al (2012) Systolic blood pressure reduction and risk of acute renal injury in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Am J Med 125:7181–7186
Kamouchi M, Sakai H, Kiyohara Y, Minematsu K, Hayashi K, Kitazono T (2013) Acute kidney injury and edaravone in acute ischemic stroke: the Fukuoka Stroke Registry. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 22:e470–e476
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO), (2012) Clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl 2:6
Wang X, Luo Y, Wang Y, Wang C, Zhao X, Wang D et al (2014) China National Stroke Registry Investigators. Comparison of associations of outcomes after stroke with estimated GFR using Chinese modifications of the MDRD study and CKD-EPI creatinine equations: results from the China National Stroke Registry. Am J Kidney Dis 63:59–67
Bagshaw SM, George C, Bellomo R (2008) Early acute kidney injury and sepsis: a multicentre evaluation. Crit Care 12:1
Otto GP, Sossdorf M, Breuel H, Schlattmann P, Bayer O, Claus RA et al (2014) Renal outcome after vancomycin treatment and renal replacement therapy in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: a retrospective study. J Crit Care 29:656–661
Levi TM, Souza SP, Magalhães JG, Carvalho MS, Cunha AL, Dantas JG et al (2013) Comparison of the RIFLE, AKIN and KDIGO criteria to predict mortality in critically ill patients. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 25:290–296
Rodrigues FB, Bruetto RG, Torres US, Otaviano AP, Zanetta DM, Burdmann EA (2013) Incidence and mortality of acute kidney injury after myocardial infarction: a comparison between KDIGO and RIFLE criteria. PLoS ONE 8:e69998
Hsu RK, Hsu CY (2011) Proteinuria and reduced glomerular filtration rate as risk factors for acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20:211–217
Goldfarb S, McCullough PA, McDermott J, Gay SB (2009) Contrast-induced acute kidney injury: specialty-specific protocols for interventional radiology, diagnostic computed tomography radiology, and interventional cardiology. Mayo Clin Proc 84:170–179
Jacka MJ, Ivancinova X, Gibney RTN (2005) Continuous renal replacement therapy improves renal recovery from acute renal failure. Can J Anesth 52:327–332
Zarbock A, Kellum JA, Schmidt C, Van Aken H, Wempe C, Pavenstädt H, Boanta A, Gerß J, Meersch M (2016) Effect of early vs delayed initiation of renal replacement therapy on mortality in critically Ill patients with acute kidney injury: The ELAIN randomized clinical trial. JAMA 315:2190–2199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Statement of human and animal rights
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Beijing Tiantan Hospital.
Informed consent
The exemption of the informed consent in our study was also given by the ethical committee in the hospital because our study was a retrospective study and no any other intervence was performed towards the patients in our study.
Sources of funding
This study was supported by the Foundation of Clinical Characteristics of the Capital Project from Beijing Municipal Commission of Science and Technology (Grant Number Z141107002514150).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Guo, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in patients with stroke: a retrospective analysis from the neurology ICU. Intern Emerg Med 13, 17–25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-017-1703-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-017-1703-z