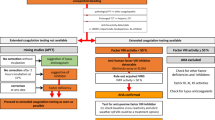
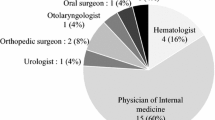
Abstract
Acquired hemophilia A (AHA) is a rare autoimmune disease, characterized by severe, often life-threatening hemorrhages in patients without a prior history of bleeding disorder. It most frequently occurs in the elderly, and may be associated with other clinical conditions, such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, pregnancy or without a relevant cause. Diagnosis and correct therapy are crucial for the patient’s outcome. Management of the disease consists of gaining immediate control of acute bleeding and the starting of an immunosuppressive therapy in order to eradicate the anti-factor VIII autoantibody. Factor VIII bypassing agents, such as prothrombin complex concentrates or recombinant activated factor VII, have proven effective in bleeding control, whereas the combined therapy of cyclophosphamide and corticosteroids seems to be, at present, the best immunosuppressive option. Other treatments including Rituximab, immunoadsorption or induction of immune tolerance are still experimental, and need to be validated through controlled clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delgado J, Jimenez-Yuste V, Hernandez-Navarro F, Villar A (2003) Acquired hemophilia: review and meta-analysis focused on the therapy and prognostic factors. Br J Haematol 121:21
Franchini M, Targher G, Montagnana M, Lippi G (2008) Laboratory, clinical and therapeutic aspects of acquired hemophilia A. Clin Chim Acta 395:14–18
Boggio LN, Green D (2001) Acquired hemophilia. Rev Clin Exp Hematol 5:389–404
Collins PW, Hirsch S, Baglin TP et al (2007) Acquired hemophilia A in the United Kingdom: a 2-year national surveillance study by the United Kingdom Haemophilia Centre Doctor’s Organization. Blood 109:1870–1877
Franchini M, Lippi G (2008) Acquired factor VIII inhibitors. Blood 112:250–255
Lévesque H, Collins P, Baudo F, Huth-Kuhne A, Knoebl P, Marco P, Nemes L, Tengborn L (2009) Acquired haemophilia: descriptive data of the European Acquired Haemophilia Registry (EACH2). J Thromb Haemost 7 (suppl 2): abstr 604
Vignes S, Le Moing V, Meekel P et al (1996) Acquired hemophilia A: a rare complication of Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 14:559–560
Green D, Lechner K (1981) A survey of 215 non-hemophilic patients with inhibitors to factor VIII. Thromb Haemost 45:200–203
Hauser I, Schneider B, Lechner K (1995) Post-partum factor VIII inhibitors: a review of the literature with special reference to the value of steroid and immunosuppressive treatment. Thromb Haemost 73:1–5
Italian Association of Hemophilia Centers (AICE) (2003) Acquired factor VIII inhibitors in pregnancy: data from the Italian Haemophilia Registry relevant to clinical practice. BJOG 110:311–314
Franchini M, Capra M, Nicolini N et al (2007) Drug-induced anti-factor VIII antibodies: a systematic review. Med Sci Monit 13:RA55–RA61
Franchini M, Targher G, Manzato F, Lippi G (2008) Acquired factor VIII inhibitors in onco-hematology: a systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 66:194–199
Huth-Kühne A, Baudo F, Collins P, Ingerslev J, Kessler CM, Lévesque H, Mingot Castellano ME, Shima M, St-Luis J (2009) International recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of patients with acquired hemophilia A. Haematologica 94:566–575
Verbruggen B, Novakova I, Wessel H, Boezeman J, van den Berg M, Mauser-Bunschoten E (1995) The Nijmegen modification of the Bethesda assay for factor VIII:C inhibitors: improve specificity and reliability. Thromb Hemost 73:247–251
Cohen AJ, Kessler CM (1996) Acquired inhibitors. Bailleres Clin Haematol 9:331–354
Kasper CK (1991) Laboratory tests for factor VIII inhibitor, their variation, significance and interpretation. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 2:7–10
Kessler CM (2000) Acquired factor VIII autoantibody inhibitors: current concept and potential therapeutic strategies for the future. Haematologica 85(Suppl):57–63
Collins PW (2007) Treatment of acquired hemophilia A. J Thromb Haemost 5:893–900
Hay CRM, Negrier C, Ludlam CA (1997) The treatment of bleeding in acquired hemophilia with recombinant factor VIIa: a multicenter study. Thromb Haemost 78:3–7
Baudo F, de Cataldo F, Gaidano G (2004) Treatment of acquired factor VIII inhibitor with recombinant activated factor VIIa: data from the Italian registry of acquired hemophilia. Haematologica 89:759–761
Baudo F, de Cataldo F (2004) Acquired hemophilia: a critical bleeding syndrome. Haematologica 89:96–100
Sumner MJ, Geldziler BD, Pedersen M, Seremetis S (2007) Treatment of acquired haemophilia with recombinant activated factor VIIa: a critical appraisal. Haemophilia 13:451–461
Yatuv R, Dayan I, Carmel-Goren L, Robinson M, Aviv I, Goldemberg-Furmanonv M, Baru M (2008) Enhancement of factor VIIa haemostatatic effect by formulation with PEGylated liposomes. Haemophilia 14:476–483
Abshire T, Kenet G (2008) Safety update on the use of recombinant factor VIIa and the treatment of congenital and acquired deficiency of factor VIII or IX with inhibitors. Haemophilia 14:898–902
Grünewald M, Beneke H, Güthner C, Germowitz A, Brommer A (2001) Acquired haemophilia: experiences with a standardized approach. Haemophilia 7:164–169
Goudemand J (2004) Treatment of bleeding episodes occurring in patients with acquired haemophilia with FEIBA: the French experience. Haemophilia 10:14
Sallah S (2004) Treatment of acquired haemophilia with factor eight inhibitor bypassing activity. Haemophilia 10:169–173
Holme PA, Brosstad F, Tjonnfjord GE (2005) Acquired hemophilia: management of bleeds and immune therapy to eradicate autoantibodies. Haemophilia 11:510–515
Baudo F, Collins P, Huth-Kühne A, Knoebl P, Lévesque H, Pascual M, Nemes L, Peerlinck K, Tengborn L (2009) Hemostatic therapy in acquired hemophilia: data from the European Acquired Hemophilia (EACH2) Registry. J Thromb Haemost 7 (suppl 2): abstr 058
Hay CR, Lozier JN, Lee CA et al (1996) Safety profile of porcine factor VIII and its use as hospital and home-therapy for patients with haemophilia-A and inhibitors: the results of an international survey. Thromb Haemost 75:25–29
Mudad R, Kane WH (1993) DDAVP in acquired haemophilia A: case report and review of the literature. Am J Haematol 43:295–299
Franchini M, Girelli D, Olivieri O et al (2005) Clinical heterogeneity of acquired hemophilia A: a description of 4 cases. Haematologica 90:e46–e49
Green D, Rademaker AW, Briet E (1993) A prospective, randomized trial of prednisone and cyclophosphamide in the treatment of patients with factor VIII autoantibodies. Thromb Haemost 70:753–757
Shaffer LG, Phillips MD (1997) Successful treatment of acquired hemophilia with oral immunosuppressive therapy. Ann Intern Med 127:206–209
Collins P, Baudo F, Huth-Kuhne A, Knoebl P, Levesque H, Marco P, Nemes L, Peerlinck K, Tengborn L (2009) First line immunosuppressive treatment for acquired factor VIII antibodies: results of the European Acquired Haemophilia Registry (EACH2). J Thromb Haemost 7 (suppl 2): abstr 609
Söhngen D, Specker C, Bach D et al (1997) Acquired factor VIII inhibitors in non hemophilic patients. Ann Hematol 74:89–93
Lian EC, Larcada AF, Chiu AY (1989) Combination immunosuppressive therapy after factor VIII infusion for acquired factor VIII inhibitor. Ann Intern Med 110:774–778
Borg JY, Levesque H, for the SACHA study group (2007) Epidemiology and one-year outcomes in patients with acquired hemophilia in France. J Thromb Haemost 5(suppl 1): O-M-062
Petrovic M, Derom E, Baele G (2000) Cyclosporine treatment of acquired hemophilia due to factor VIII antibodies. Haematologica 85:895–896
Eisert S, Mosler K, Laws HJ, Gobel U (2005) Successful use of mycophenolate mofetil and prednisone in a 14-year-old girl with acquired hemophilia A. Thromb Haemost 93:792–793
Schwartz RS, Gabriel DA, Aledort LM, Green D, Kessler CM (1995) A prospective study of treatment of acquired (autoimmune) factor VIII inhibitors with high-dose intravenous gamma globulin. Blood 86:797–804
Dykes AC, Walker ID, Lowe GD, Tait RC (2001) Combined prednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for acquired factor VIII inhibitor: a 2-years review. Haemophilia 7:160–163
Crenier L, Ducobu J, des Grottes JM, Cerni J, Delaunoit C, Capel P (1996) Low response to high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of acquired factor VIII inhibitor. Br J Haematol 95:750–753
Jansen M, Schrnaldienst S, Banyai S, Quehenberger P, Pabinger I, Derfler K (2001) Treatment of coagulation inhibitors with extracorporeal immunoadsorption (Ig-Therasorb). Br J Haematol 112:91–97
Nemes L, Pitlik E (2000) New protocol for immune tolerance induction in acquired hemophilia. Haematologica 85:64–68
Zeitler H, Ulrich-Merzenich G, Hess L et al (2005) Treatment of acquired hemophilia by the Bonn–Malmo protocol:documentation of an in vivo immunomodulating concept. Blood 105:2287–2293
Stasi R, Brunetti M, Stipa E, Amadori S (2004) Selective B-cell depletion with rituximab for the treatment of patients with acquired hemophilia. Blood 103:4424–4428
Adedayo AA, Skorupa A, Lal A, Ronsih E, Mercier RJ, Islam R (2006) Rituximab in the treatment of acquired factor VIII inhibitors. Thromb Haemost 96:87
Franchini M, Veneri D, Lippi G, Stenner R (2006) The efficacy of rituximab in the treatment of inhibitor-associated hemostatic disorder. Thromb Haemost 96:119–125
Conflict of interest
Dr. Vincenzo Toschi has received honoraria for consulting or lecturing from Bayer HealthCare and GSK-GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Francesco Baudo has received honoraria for consulting or lecturing from Bayer HealthCare and Novo Nordisk.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toschi, V., Baudo, F. Diagnosis, laboratory aspects and management of acquired hemophilia A. Intern Emerg Med 5, 325–333 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-010-0380-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-010-0380-y