Abstract
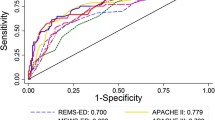
The Objective of this prospective observational study was to evaluate the applicability of the simplified acute physiology score (SAPS II) in patients admitted to an Emergency Medicine Ward in the Emergency Medicine Ward of a tertiary university hospital. We studied consecutive patients admitted to an Emergency Medicine Ward from the emergency department. The SAPS II was assessed in predicting overall in-hospital mortality in terms of sensitivity, specificity and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. A total of 211 consecutive patients were admitted over a period of 2 months. Median SAPS II score was 28 (range 6–93), with a mean risk of in-hospital mortality of 0.17 (range 0.01–0.97) for the whole population, and an observed mortality of 15%. The area under the receiver operator curve (ROC) was 0.84 (0.77–0.91). Considering a cut-off value of SAPS II of 49, the sensitivity was 0.50 (95% CI 0.42–0.56), the specificity was 0.95 (0.92–0.98), the positive predictive value (PPV) was 0.64 (0.58–0.71), and the negative predictive value (NPV) was 0.91 (0.87–0.95), the positive likelihood ratio (pLH) was 9.9, and the negative likelihood ratio (nLH) was 0.5. If contrarily a cut-off value of SAPS II of 22 were used, the sensitivity would be 1.0, the specificity would be 0.21 (0.16–0.26), the PPV would be 0.18 (0.13–0.23), the NPV would be 1.0, the pLH would be 1.3, and the nLH would be 0.0. In this preliminary study, SAPS II predicted in-hospital mortality in patients admitted to an Emergency Ward.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F (1993) A new simplified acute physiology score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA 270:2957–2963
Hargrove J, Nguyen HB (2005) Bench-to-bedside review: outcome predictions for critically ill patients in the emergency department. Crit Care 9:376–383
Nguyen HB, Rivers EP, Havstad S et al (2000) Critical care in the emergency department: a physiologic assessment and outcome evaluation. Acad Emerg Med 7:1354–1361
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and the use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Rhee K, Fisher C, Willitis N (1987) The rapid acute physiology score. Am J Emerg Med 5:278–286
Olsson T, Terent A, Lind L (2004) Rapid emergency medicine score: a new prognostic tool for in-hospital mortality in nonsurgical emergency department patients. J Int Med 255:579–587
Blot F, Cordonnier C, Buzin A, Nitenberg G, Sclemmer B, Batuji-Garin S (2001) Severity of illness scores: are they useful in febrile neutropenic adult patients in hematology wards? A prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med 29:2125–2131
Carson SS, Bach PB (2001) Predicting mortality in patients suffering from prolonged critical illness. An assessment of four severity-of-illness measures. Chest 120:928–933
Jones AE, Fitch MT, Kline JA (2005) Operational performance of validated physiologic scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality among critically ill emergency department patients. Crit Care Med 33:974–978
Auriant I, Vinatier I, Thaler F, Tourneur M, Loirat P (1998) Simplified acute physiology score II for measuring severity of illness in intermediate care units. Crit Care Med 26:1368–1371
Schuster HP, Wilts S, Ritschel P (1996) Analysis of outcome quality control in intensive care medicine using the simplified acute physiology score II. Med Klin (Munich) 15(91):343–348
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to F. Calamida, MD, for helping to prepare the data base.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cosentini, R., Folli, C., Cazzaniga, M. et al. Usefulness of simplified acute physiology score II in predicting mortality in patients admitted to an emergency medicine ward. Intern Emerg Med 4, 241–247 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-009-0250-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-009-0250-7