Abstract
Objective
To observe the therapeutic effect of electroacupuncture (EA) at Zusanli (ST 36), Guanyuan (CV 4) and Ashi points on adjuvant arthritis rats, and explore the mechanism of EA treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
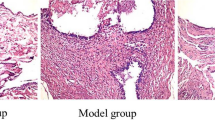
Sixty male rats were randomly divided into a normal group, a model group, a methotrexate group and an EA group, with 15 rats in each group. Rats in the normal group and the model group were routinely raised and did not receive treatment; rats in the methotrexate group received methotrexate at a dose of 0.35 mg/(kg·bw), twice a week for 3 weeks; rats in the EA group received acupuncture at Zusanli (ST 36), Guanyuan (CV 4) and Ashi points, and the bilateral Zusanli (ST 36) and Ashi points were connected to EA apparatus, once a day for 3 weeks. The general status, the swelling degree of the toe, the arthritis index (AI) score, the pathological morphology of the ankle joint, and the mRNA expressions of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein (c-IAP) 1 and c-IAP2 in joint synovial tissue cells of the rats in each group were observed.
Results
The swelling degree of the toe, AI score and mRNA expressions of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 in the model group were significantly higher than those in the normal group (all P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the swelling degree of the toe, AI score and mRNA expressions of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 in the methotrexate group and the EA group improved (P<0.01 or P<0.05); the expressions of c-IAP1 mRNA and c-IAP2 mRNA in rat synovial tissues in the EA group were significantly higher than those in the methotrexate group (P<0.01).
Conclusion
EA alleviates joint swelling in rats with adjuvant arthritis. The mechanism may be related to suppressing mRNA expressions of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2, thus to induce apoptosis of synoviocytes.
概要
目的
观察电针刺激足三里、关元和阿是穴对佐剂性关节炎大鼠的治疗作用, 探讨电针治疗类风湿性关 节炎(RA)的作用机理。
结果
将60 只雄性大鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、甲氨蝶呤组和电针组, 每组15 只。空 白组、模型组不予治疗, 常规饲养; 甲氨蝶呤组按0.35 mg/(kg·bw)进行甲氨蝶呤灌胃, 每周2 次, 连续给药3 周; 电针组针刺足三里、关元及阿是穴, 双侧足三里和阿是穴接电针, 每日1 次, 连续治疗3 周。观察并检测各组大 鼠的一般状态、足跖肿胀度、关节炎指数(AI)评分、踝关节病理形态学及关节滑膜组织细胞凋亡抑制蛋白(c-IAP) 1 mRNA 和c-IAP2 mRNA 的表达情况。
结果
模型组大鼠足跖肿胀度、AI 评分及c-IAP1 mRNA 和c-IAP2 mRNA 表达 均较空白组显著升高(均P<0.05)。与模型组比较, 甲氨蝶呤组和电针组大鼠足跖肿胀度、AI 评分及c-IAP1 mRNA 和c-IAP2 mRNA 表达均有改善(P<0.01 或P<0.05); 电针组大鼠滑膜组织细胞c-IAP1 mRNA 和c-IAP2 mRNA 表达 较甲氨蝶呤组显著增高(P<0.01)。
结论
电针疗法能够减轻佐剂性关节炎大鼠关节肿胀度, 其作用机理可能与抑 制凋亡抑制蛋白c-IAP1 mRNA 和c-IAP2 mRNA 表达, 从而诱导滑膜细胞凋亡有关。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvikar SL, Crowley JT, Sulka KB, Steere AC. Autoimmune arthritides, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or peripheral spondyloarthritis following lyme disease. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2017, 69(1): 194–202.
Li H, Wan A. Apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblastlike synoviocytes: possible roles of nitric oxide and the thioredoxin 1. Mediators Inflamm, 2013, 2013: 953462.
Shi DL, Shi GR, Xie J, Du XZ, Yang H. MicroRNA–27a inhibits cell migration and invasion of fibroblast–like synoviocytes by targeting follistatin–like protein 1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Cells, 2016, 39(8): 611–618.
Liu XZ, Fan J, Qi K, Liu SP, Xu WD, Gao Y, Gu XD, Li J, Bai CG, Shi YQ, Zhang LL, Zhao DB. Dishevelled2 promotes apoptosis and inhibits inflammatory cytokine secretion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast–like synoviocytes through crosstalk with the NF–?B pathway. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(8): 12649–12663.
Stanford SM, Maestre MF, Campbell AM, Bartok B, Kiosses WB, Boyle DL, Arnett HA, Mustelin T, Firestein GS, Bottini N. Protein tyrosine phosphatase expression profile of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast–like synoviocytes: a novel role of SH2 domain–containing phosphatase 2 as a modulator of invasion and survival. Arthritis Rheum, 2013, 65(5): 1171–1180.
Tokunaga F, Sakata S, Saeki Y, Satomi Y, Kirisako T, Kamei K, Nakagawa T, Kato M, Murata S, Yamaoka S, Yamamoto M, Akira S, Takao T, Tanaka K, Iwai K. Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF–kappaB activation. Nat Cell Biol, 2009, 11(2): 123–132.
Su HY, Du YH. Metaanalysis of the clinical efficacy of moxibustion and acupuncture in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Fengshibing Yu Guanjieyan, 2016, 5(3): 27–30.
Zhang XH, Zhu BW, Zhao BY, Qin XG, Du XZ. Meta–analysis on randomized controlled clinical trials of acupuncture and moxibustion for rheumatoid arthritis. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Xinxi Zazhi, 2015, 22(2): 42–46.
Qi F, Li YL, Ai K, Cai X, Li X, Liu L, Zhang H, Yang QY. The establishment and evaluation of adjuvant–induced arthritis in SD rats. Hunan Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2016, 36(1): 23–26.
Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2003: 425–431.
Lu Y. Progress in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Guowai Yixue Mianyixue Fence, 2001, 24(5): 256–258.
Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast–like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev, 2010, 233(1): 233–255.
Schurigt U, Pfirschke C, Irmler IM, Hückel M, Gajda M, Janik T, Baumgrass R, Bernhagen J, Bräuer R. Interactions of T helper cells with fibroblast–like synoviocytes: up–regulation of matrix metalloproteinases by macrophage migration inhibitory factor from both Th1 and Th2 cells. Arthritis Rheum, 2008, 58(10): 3030–3040.
LeBlanc AC. Natural cellular inhibitors of caspases. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 2003, 27(2): 215–229.
Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH, Mrad RL, Plenchette S, Simard C, Enwere E, Arora V, Mak TW, Lacasse EC, Waring J, Korneluk RG. Both c–IAP1 and c–IAP2 regulate TNFa–mediated NF–?B activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(33): 11778–11783.
Ai K, Wu D, Chang XR, Liu M, Liu L, Liu MR. Effects of electrical acupuncture on swelling of voix pedis and proinflammatory cytokines in adjuvant arthritis rats. Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun Yu Shijian, 2011, 17(7): 622–624.
Li YW, Zhao DD, Yuan T. Therapeutic observation of warm needling plus Chinese medicinal fumigation for rheumatoid arthritis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2016, 35(7): 853–856.
Wu XY, Wang Y, Sun ZL, Qin X, Zhao J, Xu X, Zhang YY, Xue L. Experimental study on the effect of different moxibustion durations on rats with rheumatoid arthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(3): 177–183.
Zhang Y. The main treatment principles of Chinese medicine for rheumatoid arthritis. Heilongjiang Zhongyiyao, 2011, 40(2): 6–7.
Chi DQ. Three principles of TCM treatment of arthromyodynia. Zhongguo Yixue Chuangxin, 2008, 5(31): 122.
Zhang H, Ma XP, Wu HG, Wu SB, Su SS, Hu YC, Li ZF, Zhang L, Xie MY. Effect of moxibustion on tumor necrosis factor–a and nuclear transcription factor kappa B in ankle joints of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(3): 171–176.
Cai GW, Peng R, Li J, Li J. Effect of warm needling moxibustion on articular cartilage vimentin in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2017, 36(11): 1361–1366.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Youth Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (国家自然科学基金 青年基金项目, No. 81303048, No. 81804204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ai, K., Li, Yl., Qi, F. et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on c-IAP1 mRNA and c-IAP2 mRNA in synovial tissues of rats with adjuvant arthritis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 16–23 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1088-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1088-9
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Arthritis, Rheumatoid
- Arthritis, Experimental
- Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins
- Rats