Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of rapid point pressure on clinical effect and pulmonary function of patients with chronic persistent bronchial asthma.
Methods
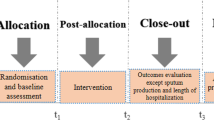
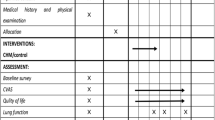
A total of 60 confirmed chronic persistent bronchial asthma cases were randomly allocated into two groups, 30 in each group. Cases in the treatment group were treated with rapid point pressure, 1 h for the initial treatment, and 40 min for the ensuing treatments. The treatment was done once a day for 40 d. Cases in the control group were treated with Compound Methoxyphenamine Hydrochloride Capsules, 2 capsules for each dose, 3 times a day. The treatment lasted for 7 consecutive days. A 1-year follow-up was made for both groups.
Results
After treatment, the scores of each symptom and total symptom scores for the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) symptoms in the treatment group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05); the total effective rates in the treatment group were higher than those in the control group in each time frame; and there was a between-group statistical significance in total effective rate after 7 d of treatment (P<0.01). After 40-day treatments, there were statistical significances in the forced expiratory volume in 1 s percentage of predicted value (FEV 1%) and inspiratory capacity (IC%) in the treatment group (P<0.05); however, there were no statistical significances (P>0.05) in forced expiratory volume in 1 second to forced vital capacity ratio (FEV1/FVC), peak expiratory flow rate (PEF%) and maximum midexpiratory flow rate (MMEF%); and there were no statistical significances in pulmonary function parameters in the control group. In addition, as for pulmonary function parameters, there were no intra-group statistical significances in differences before and after treatment (P>0.05).
Conclusion
Rapid point pressure can alleviate patients’ TCM symptoms and improve their FEV% and IC%.
摘要
目的
观察快速点穴治疗支气管哮喘慢性持续期的疗效及其对肺功能的影响。
方法
将60例支气管哮喘慢性持续期患者随机分为两组, 每组30例。 治疗组用快速点穴疗法, 首次点穴治疗1 h, 以后每次治疗40 min, 每日1次, 连续治疗40次。 对照组口服复方甲氧那明胶囊(Compound Methoxyphenamine Hydrochloride Capsules), 每次2粒, 每日3次。 连续治疗7 d。 两组均随访1年。
结果
治疗后, 治疗组各症状积分及症状总积分改善值均明显优于对照组(P<0.05); 两组各个时间点总有效率比较, 治疗组均高于对照组, 且在治疗7 d后的总有效率与对照组有统计学差异(P<0.01)。 治疗40 d后两组肺功能指标比较, 治疗组第一秒用力呼气容积占预计值比值(forced expiratory volume in 1 second percentage of predicted value, FEV1%)、 深吸气量(inspiratory capacity, IC%)均与治疗前有统计学差异(P<0.05), 第一秒用力呼气容积占用力肺活量的比值(forced expiratory volume in 1 second to forced vital capacity ratio, FEV1/FVC)、 呼吸峰流速(peak expiratory flow rate, PEF%)及最大呼气中段流率(maximum midexpiratory flow rate, MMEF%)差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05); 对照组肺功能各项指标与治疗前均无统计学差异(P>0.05); 两组肺功能指标治疗前后差值均无统计学差异(P>0.05)。
结论
快速点穴可改善患者中医证候, 对肺功能中的FEV1%、 IC%有改善。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asthma Working Group, Chinese Society of Respiratory Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Prevention and treatment guidelines for bronchial asthma (definition, treatment and management protocol of bronchial asthma). Zhonghua Jiehe He Huxi Zazhi, 2008, 31(3): 177–185.
State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1994: 77.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Guiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines. Beijing: China Medico-Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Publishing House, 2002: 56–58.
Geng LM, Yu XY. Mechanism of effect of collateral-pricking with ventouse on bronchial asthma at chronic persistent period. Zhonguo Quanke Yixue, 2011, 14(3A): 801–803.
Luo S, Li JX, Ling MH. Clinical effect observation on treating chronic persistent asthma by auricular point sticking. CJCM, 2013, 5(7): 43–45.
Li LP. Clinical observation on point application in preventing and treating bronchial asthma. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2013, 32(2): 96–98.
Xu J, Zheng S, Fang W. Role of combining spreading moxibustion and point injection in reducing ECP and LPO levels and improving lung function. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2014, 12(1): 12–16.
Ye Z, Chen LD. Research survey on needling the Governor Vessel for post-stroke cognitive dysfunction. Yatai Chuantong Yiyao, 2013, 9(4): 73–74.
Dai SQ, Yang QL. Differentiation and analysis of qi-regulating points in the Conception Vessel. Beijing Zhongyi, 2003, 22(3): 46–48.
Huang TJ, Luo XH. The progress of experimental researches on the acupuncture treatment of bronchial asthma. Chin J Nat Med, 2000, 2(4): 235–240.
Xie YL. Development of researches and clinical application on treatment of bronchial asthma with acupuncture. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2011, 13(1): 201–204.
He J, Bi WQ, Zhuang LX, Wang WH, Zhuang X, Huang LY. Clinical study on vesiculation moxibustion in preventing and treating asthma due to cold deficiency. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2014, 33(1): 34–37.
Hui P, Song TY, Fan FC, Li YJ, Wang XP, Chen ZN, Liang YS, Liu WZ, Peng JQ. Clinical study on Chuankezhi point injection in treatment of acute attack of bronchial asthma with cold syndrome and deficiency of kidney-yang and its effects on IFN-γ and IL-4. Hunan Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2013, 33(3): 78–80.
Chen LF, Fang JQ, Jia LH, Jin XQ, Jiang ZX. Effect of BCG-PSN acupoint injection on IgE content and asthma control test score of bronchial asthma. Zhongyi Zazhi, 2013, 54(14): 1207–1210.
Gu W, Zhou CX, Yan Y. Immune regulation of Th/Th2 imbalance in allergic asthma guinea pigs by acupoint application. CJTCMP, 2013, 28(6): 1689–1691.
Liu ZB, Niu XM. Study progress on tuina for bronchial asthma. Shaanxi Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao, 2008, 31(3): 67–69.
Wang TY. Shi CX. Clinical observation on acupoint massage for bronchial asthma. Jiaotong Yixue, 1997, 11(2): 251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, My., Shu, Zt., Zhang, W. et al. Effect of rapid point pressure on therapeutic efficacy and pulmonary function in patients with chronic persistent bronchial asthma. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 13, 36–43 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-015-0820-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-015-0820-3