Abstract
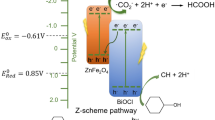
ZnFe2O4-BiOCl composites were prepared by both hydrothermal and direct precipitation processes and the structures and properties of the samples were characterized by various instrumental techniques. The samples were then used as catalysts for the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in cyclohexanol under ultraviolet irradiation to give cyclohexanone (CH) and cyclohexyl formate (CF). The photocatalytic CO2 reduction activities over the hydrothermally prepared ZnFe2O4-BiOCl composites were higher than those over the directly-precipitated composites. This is because compared to the directprecipitation sample, the ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles in the hydrothermal sample were smaller and more uniformly distributed on the surface of BiOCl and so more heterojunctions were formed. Higher CF and CH yields were obtained for the pure BiOCl and BiOCl composite samples with more exposed (001) facets than for the samples with more exposed (010) facets. This is due to the higher density of oxygen atoms in the exposed (001) facets, which creates more oxygen vacancies, and thereby improves the separation efficiency of the electron-hole pairs. More importantly, irradiation of the (001) facets with ultraviolet light produces photo-generated electrons which is helpful for the reduction of CO2 to ∙CO -2 . The mechanism for the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in cyclohexanol over ZnFe2O4-BiOCl composites with exposed (001) facets involves electron transfer and carbon radical formation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
He Y, Wang Y, Zhang L, Teng B, Fan M. High-efficiency conversion of CO2 to fuel over ZnO/g-C3N4 photocatalyst. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 168: 1–8
Ehsan M F, He T. In situ synthesis of ZnO/ZnTe common cation heterostructure and its visible-light photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into CH4. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 166: 345–352
Habisreutinger S N, Schmidt-Mende L, Stolarczyk J K. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on TiO2 and other semiconductors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(29): 7372–7408
Liu Y, Zhou S, Li J, Wang Y, Jiang G, Zhao Z, Liu B, Gong X, Duan A, Liu J, Wei Y, Zhang L. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 with water vapor on surface La-modified TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced CH4 selectivity. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 168: 125–131
Liu Q, Zhou Y, Kou J, Chen X, Tian Z, Gao J, Yan S, Zou Z. Highyield synthesis of ultralong and ultrathin Zn2GeO4 nanoribbons toward improved photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuel. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(41): 14385–14387
Fan W, Zhang Q, Wang Y. Semiconductor-based nanocomposites for photocatalytic H2 production and CO2 conversion. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(8): 2632–2649
Richardson P L, Perdigoto M L N, Wang W, Lopes R J G. RETRACTED: Heterogeneous photo-enhanced conversion of carbon dioxide to formic acid with copper-and gallium-doped titania nanocomposites. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 132: 408–415
Asi MA, He C, Su M, Xia D, Lin L, Deng H, Xiong Y, Qiu R, Li X. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to hydrocarbons using AgBr/TiO2 nanocomposites under visible light. Catalysis Today, 2011, 175(1): 256–263
He Z, Wen L, Wang D, Xue Y, Lu Q, Wu C, Chen J, Song S. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in aqueous solution on surfacefluorinated anatase TiO2 nanosheets with exposed {001} facets. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(6): 3982–3993
Xu H, Ouyang S, Li P, Kako T, Ye J. High-active anatase TiO2 nanosheets exposed with 95% {100} facets toward efficient H2 evolution and CO2 photoreduction. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(4): 1348–1354
Wang W N, Wu F, Myung Y, Niedzwiedzki D M, Im H S, Park J, Banerjee P, Biswas P. Surface engineered CuO nanowires with ZnO islands for CO2 photoreduction. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(10): 5685–5692
Zhou Y, Tian Z, Zhao Z, Liu Q, Kou J, Chen X, Gao J, Yan S, Zou Z. High-yield synthesis of ultrathin and uniform Bi2WO6 square nanoplates benefitting from photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuel under visible light. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2011, 3(9): 3594–3601
Liu Q, Zhou Y, Kou J, Chen X, Tian Z, Gao J, Yan S, Zou Z. Highyield synthesis of ultralong and ultrathin Zn2GeO4 nanoribbons toward improved photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuel. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(41): 14385–14387
Chen X, Zhou Y, Liu Q, Li Z, Liu J, Zou Z. Ultrathin, single-crystal WO3 nanosheets by two-dimensional oriented attachment toward enhanced photocatalystic reduction of CO2 into hydrocarbon fuels under visible light. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012, 4(7): 3372–3377
Li X, Liu H, Luo D, Li J, Huang Y, Li H, Fang Y, Xu Y, Zhu L. Adsorption of CO2 on heterostructure CdS (Bi2S3)/TiO2 nanotube photocatalysts and their photocatalytic activities in the reduction of CO2 to methanol under visible light irradiation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 180: 151–158
Li X, Zhuang Z, Li W, Pan H. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 over noble metal-loaded and nitrogen-doped mesoporous TiO2. Applied Catalysis A, General, 2012, 429: 31–38
Xia J, Xu L, Zhang J, Yin S, Li H, Xu H, Di J. Improved visible light photocatalytic properties of Fe/BiOCl microspheres synthesized via self-doped reactable ionic liquids. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(46): 10132–10141
Zhang K, Liang J, Wang S, Liu J, Ren K, Zheng X, Luo H, Peng Y, Zou X, Bo X, Li J, Yu X. BiOCl sub-microcrystals induced by citric acid and their high photocatalytic activities. Crystal Growth & Design, 2012, 12(2): 793–803
Zhu L P, Liao G H, Bing N C, Wang L L, Yang Y, Xie H Y. Selfassembled 3D BiOCl hierarchitectures: Tunable synthesis and characterization. CrystEngComm, 2010, 12(11): 3791–3796
Jiang J, Zhao K, Xiao X, Zhang L. Synthesis and facet-dependent photoreactivity of BiOCl single-crystalline nanosheets. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(10): 4473–4476
Li H, Zhang L. Oxygen vacancy induced selective silver deposition on the {001} facets of BiOCl single-crystalline nanosheets for enhanced Cr (VI) and sodium pentachlorophenate removal under visible light. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(14): 7805–7810
Lin H, Ding L, Pei Z, Zhou Y, Long J, Deng W, Wang X. Au deposited BiOCl with different facets: On determination of the facetinduced transfer preference of charge carriers and the different plasmonic activity. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 160: 98–105
Fu Y, Wang X. Magnetically separable ZnFe2O4-graphene catalyst and its high photocatalytic performance under visible light irradiation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(12): 7210–7218
Kong L, Jiang Z, Xiao T, Lu L, Jonesac M O, Edwards Peter P. Exceptional visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity over BiOBr-ZnFe2O4 heterojunctions. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(19): 5512–5514
Song G, Xin F, Yin X. Photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide over ZnFe2O4/TiO2 nanobeltsheterostructure in cyclohexanol. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 442: 60–66
Yu T H, Cheng W Y, Chao K J, Lu S Y. ZnFe2O4 decorated CdS nanorods as a highly efficient, visible light responsive, photochemically stable, magnetically recyclable photocatalyst for hydrogen generation. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(16): 7356–7360
Wang M, Sun L, Cai J, Huang P, Su Y, Lin C. A facile hydrothermal deposition of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles on TiO2 nanotube arrays for enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2013, 1(39): 12082–12087
Guan M, Xiao C, Zhang J, Fan S, An R, Cheng Q, Xie J, Zhou M, Ye B, Xie Y. Vacancy associates promoting solar-driven photocatalytic activity of ultrathin bismuth oxychloride nanosheets. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(28): 10411–10417
Zhang X, Wang X B, Wang L W, Wang WK. Long L L, Li WW, Yu H Q. Synthesis of a highly efficient BiOCl single-crystal nanodisk photocatalyst with exposing {001} facets. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(10): 7766–7772
Zhang N, Yang M Q, Tang Z R, Xu Y J. CdS-graphene nanocomposites as visible light photocatalyst for redox reactions in water: A green route for selective transformation and environmental remediation. Journal of Catalysis, 2013, 303: 60–69
Song G, Xin F, Chen J, Yin X. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in cyclohexanol on CdS-TiO2 heterostructuredphotocatalyst. Applied Catalysis A, General, 2014, 473: 90–95
Ye L, Zan L, Tian L, Peng T, Zhang J. The {001} facets-dependent high photoactivity of BiOCl nanosheets. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(24): 6951–6953
Ye L, Deng K, Xu F, Tian L, Peng T, Zan L. Increasing visible-light absorption for photocatalysis with black BiOCl. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2012, 14(1): 82–85
Zhang S, Li J, Zeng M, Zhao G, Xu J, Hu W, Wang X. In situ synthesis of water-soluble magnetic graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst and its synergistic catalytic performance. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(23): 12735–12743
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21176192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, G., Wu, X., Xin, F. et al. ZnFe2O4 deposited on BiOCl with exposed (001) and (010) facets for photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in cyclohexanol. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 11, 197–204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-016-1606-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-016-1606-y