Abstract
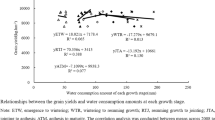
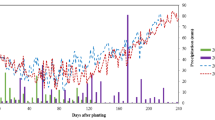
This paper studied the variation characters on wheat and corn water consumption and irrigation watersaving amount under different water conditions (ample irrigation level, farmers conventional irrigation level and optimizing irrigation level). The water use efficiency and water saving potential of optimizing treatment and farmers’ conventional irrigation treatment were analyzed respectively. The objective of this study was to provide theoretical supporting for popularization and application of optimizing irrigation measures. Crop water requirement under sufficient water supply was calculated by Penman equation. We obtained crop water consumption under conventional treatment and optimizing treatment by field experiment. The main results showed that the irrigation amount of wheat and corn was too much under farmers’ conventional irrigation level and basically satisfied their water requirement, therefore, the water-saving amount was smaller while water-saving potential was bigger compared with the optimizing irrigation treatment. The grain yield under optimizing irrigation treatment was improved or appreciably reduced compared with that under conventional irrigation treatment, while the water consumption and irrigation amount of optimizing irrigation treatment was lower, with a higher water use efficiency. Therefore, the optimizing irrigation treatment could achieve a stable yield and high water efficiency at the same time. Moreover, when the optimizing irrigation measure was adopted, the grain yield reached 5940 kg/hm2, water-saving amount reached 91mm for winter wheat, and the grain yield reached 7743 kg/hm2, with water-saving amount of 49mm for summer corn in the piedmont region of Taihang Mount. The grain yield got 7710 kg/hm2, with water-saving amount of 20mm for winter wheat in Heilonggang Plain. Therefore, the water-saving amount in the piedmont region of Taihang Mountain was obviously higher than that in Heilonggang Plain. Thus, the piedmont region of Taihang Mountain in the North China Plain is viewed as the key district for water-saving.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen R G, Pereira L S and Raes D S (1998). Crop Evapotranspiration Guidelines for Estimating Crop Water Requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper, No.56, FAO Rome.300
Chen S Y, Zhang X Y, Pei D, Sun H Y, Chen S L (2007). Effects of straw mulching on soil temperature, evaporation and yield of winter wheat: field experiments on the North China Plain. Annals of Applied Biology, 150(3): 261–268
Chen YM Guo G S Wang G X Kang S Z Luo H B Zhang D Z (1995). Water Requirement and Irrigation for Main Crops in China. Beijing: Water Resource and Hydropower Press, 77, 87 (in Chinese)
Hu C S Zhang X Y Cheng Y S Pei D (2005). An analysis on dynamics of water table and overdraft of groundwater in the piedmont of Mt. Taihang. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 18(2): 89–91 (in Chinese)
Huang R H, Xu Y H, Zhou LT (1999). Fluctuation of summer rainfall in China and the tendency of drought in North-China. Plateau Meteorology, 18(4): 465–476 (in Chinese)
Li J M, Wang P, Zhou D X, Lan LW (1999). Effects of irrigation system on the water consumption and the yield of winter wheat. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 7(4): 23–26 (in Chinese)
Liu C M, Wei Z Y (1989). Agricultural Hydrology and Water Resources in the North China Plain. Beijing: Chinese Scientific Press, 108 (in Chinese)
Liu C M, Zhang X Y, Zhang Y Q (2002). Determination of daily evaporation and evapotranspiration of winter wheat and maize by large-scale weighing lysimeter and micro-lysimeter. Agric Meteorol, 111(2): 109–120
Liu C S, Chen X, Qiao J H (2004). Investigation of farms water use condition in well irrigation area of north China. Water Resources Development Research, 10: 38–40 (in Chinese)
Mao R H, Yan J F (1995). Soil moisture dynamics in winter wheat fields and soil moisture balance in farmlands in the rainfed area on Weibei rainfed highland. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 13(4): 52–57 (in Chinese)
Wang H J (2010). Research of Grains Comprehensive Productivity in Hebei Province. Shijiazhuang: Science And Technology Press of Hebei, 110 (in Chinese)
Wu K, Xie X Q, Liu E M (1998). Schedules and managements of irrigation in the high yielding cultivation of winter wheat and summer maize in Yucheng City of Shandong Province. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 14(2): 150–154 (in Chinese)
Zhang X Y, Chen S Y, Sun H Y, Pei D, Wang Y M (2008). Dry matter, harvest index, grain yield and water use efficiency as affected by water supply in winter wheat. Irrig Sci, 27(1): 1–10
Zhang X Y, Pei D, Chen S Y, Sun H Y, Yang Y H (2006). Performance of double-cropped winter wheat-summer maize under minimum irrigation in the North China Plain. Agron J, 98(6): 1620–1626
Zhang X Y, Pei D, Hu C S (2003a). Conserving groundwater for irrigation in the North China Plain. Irrig Sci, 21: 159–166
Zhang Z B, Cui Y T, Chen Z B, Xu P, Huang L, Liu MY, Liu J (2003b). Discussions on water balance of North-China and development of water-saving agriculture. Journal of Chinese Agriculture Science and Technology, 5(4): 42–47 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, L., Wang, H., Jia, X. et al. Analysis on water requirement and water-saving amount of wheat and corn in typical regions of the North China Plain. Front. Agric. China 5, 556–562 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-011-1149-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-011-1149-4