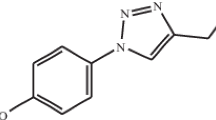
Abstract
The corrosion-inhibiting behavior and adsorption of Venlafaxine on mild steel has been examined using 1 M HCl at 298 K. Techniques used include weight loss studies, potentiodynamic polarization studies, electron impedance spectroscopy, computational studies (Monte Carlo simulation studies) and AFM studies. The polarization data revealed that Venlafaxine mostly behaves as mixed type of inhibitor. The data from weight loss results suggested that inhibition efficiency varied directly with concentration and inversely with temperature. A quantum chemical calculation and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation studies were used to further validate inhibition mechanism.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adejoro IA, Ojo FK, Obafemi SK (2015) Corrosion inhibition potentials of ampicillin for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. J Taibah Univ Sci 9:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2014.10.002
Bashir S, Singh G, Kumar A (2017) Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus) as green corrosion inhibitor of aluminium in acidic medium. J Mater Environ Sci 8:4284. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205118010185
Bashir S, Sharma V, Lgaz H, Chung IM, Singh A, Kumar A (2018a) The inhibition action of analgin on the corrosion of mild steel in acidic medium: a combined theoretical and experimental approach. J Mol Liq 263:454–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.143
Bashir S, Singh G, Kumar A (2018b) An investigation on mitigation of corrosion of aluminium by Origanum vulgare in acidic medium. Protect Metals Phys Chem Surf 54:148–152. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205118010185
Benabdellah M, Aouniti A, Dafali A, Hammouti B, Benkaddour M, Yahyi A, Ettouhami A (2006) Investigation of the inhibitive effect of triphenyltin 2-thiophene carboxylate on corrosion of steel in 2 M H3PO4 solutions. Appl Surf Sci 252:8341–8347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.11.037
Bentiss F, Traisnel M, Lagrenee M (2000) The substituted 1, 3, 4-oxadiazoles: a new class of corrosion inhibitors of mild steel in acidic media. Corros Sci 42:127–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(99)00049-9
Bentiss F, Lebrini M, Lagrenee M (2005a) Thermodynamic characterization of metal dissolution and inhibitor adsorption processes in mild steel/2, 5-bis (n-thienyl)-1, 3, 4-thiadiazoles/hydrochloric acid system. Corros Sci 47:2915–2931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.05.034
Bentiss F, Lebrini M, Lagrenée M (2005b) Thermodynamic characterization of metal dissolution and inhibitor adsorption processes in mild steel/2, 5-bis (n-thienyl)-1, 3, 4-thiadiazoles/hydrochloric acid system. Corros Sci 47:2915–2931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.05.034
Bentiss F, Lebrini M, Lagrenee M (2005c) Thermodynamic characterization of metal dissolution and inhibitor adsorption processes in mild steel/2, 5-bis (n-thienyl)-1, 3, 4-thiadiazoles/hydrochloric acid system. Corros Sci 47:2915–2931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.05.034
Bockris JOM, Reddy AKN, Gamboa-Aldeco M, Gamboa-Aldeco M (2000) Modern electrochemistry 2A. Fundamentals of Electrodics
Bouklah M, Hammouti B, Lagrenee M, Bentiss F (2006) Thermodynamic properties of 2, 5-bis (4-methoxyphenyl)-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in normal sulfuric acid medium. Corros Sci 48:2831–2842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.08.019
da Conceicao TF, Scharnagl N, Dietzel W, Hoeche D, Kainer KU (2011) Study on the interface of PVDF coatings and HF-treated AZ31 magnesium alloy: determination of interfacial interactions and reactions with self-healing properties. Corros Sci 53:712–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.11.001
Delley B (2000) From molecules to solids with the DMol 3 approach. J Chem Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1316015
Delley B (2006) Ground-state enthalpies: evaluation of electronic structure approaches with emphasis on the density functional method. J Phys Chem A 110:13632–13639. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0653611
Eddy NO, Odoemelam SA, Ekwumemgbo P (2009) Inhibition of the corrosion of mild steel in H2SO4 by penicillin G. Sci Res Essays 4:033–038
Elachouri M, Hajji MS, Salem M, Kertit S, Aride J, Coudert R, Essassi E (1996) Some nonionic surfactants as inhibitors of the corrosion of iron in acid chloride solutions. Corrosion 52:103–108. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3292100
Elkadi L, Mernari B, Traisnel M, Bentiss F, Lagrenee M (2000) The inhibition action of 3, 6-bis (2-methoxyphenyl)-1, 2-dihydro-1, 2, 4, 5-tetrazine on the corrosion of mild steel in acidic media. Corros Sci 42:703–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(99)00101-8
El-Mahdy GA, Mahmoud SS (1995) Inhibition of acid corrosion of pure aluminum with 5-benzylidine-1-methyl-2-methylthio-imidazole-4-one. Corrosion 51:436–440. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3293609
El-Sherbini EF, Wahaab SA, Deyab M (2005) Ethoxylated fatty acids as inhibitors for the corrosion of zinc in acid media. Mater Chem Phys 89:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2003.09.055
Emregul KC, Hayvali M (2004) Studies on the effect of vanillin and protocatechualdehyde on the corrosion of steel in hydrochloric acid. Mater Chem Phys 83:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2003.08.030
Flis J, Zakroczymski T (1996) Impedance study of reinforcing steel in simulated pore solution with tannin. J Electrochem Soc 143:2458–2464. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1837031
Gece G (2011) Drugs: a review of promising novel corrosion inhibitors. Corros Sci 53:3873–3898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.08.006
Ghanbari A, Attar MM, Mahdavian M (2010) Corrosion inhibition performance of three imidazole derivatives on mild steel in 1 M phosphoric acid. Mater Chem Phys 124:1205–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.08.058
Goel R, Siddiqi WA, Ahmed B, Hussan J (2010) Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in HCl by isolated compounds of Riccinus communis (L.). Journal of Chemistry 7:S319–S329. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/308057
Hameed RA, Al-Shafey HI, Abu-Nawwas AH (2014) 2-(2, 6-dichloranilino) phenyl acetic acid drugs as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M HCl. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:6006–6019
Hoai NS, Hien PV, Mathesh M, Hanh VT (2019) Improved corrosion resistance of steel in ethanol fuel blend by titania nanoparticles and Aganonerion polymorphum leaf extract. ACS Omega. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02084
James AO, Oforka NC, Abiola OK (2007) Inhibition of acid corrosion of mild steel by pyridoxal and pyridoxol hydrochlorides. Int J Electrochem Sci 2:278–284
Kokalj A (2012) On the HSAB based estimate of charge transfer between adsorbates and metal surfaces. Chem Phys 393:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2011.10.021
Kumar A, Bashir S (2016) Ethambutol: a new and effective corrosion inhibitor of mildsteel in acidic medium. Russ J Appl Chem 89:1158–1163. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427216070168
Kumar SH, Karthikeyan S (2013) Amoxicillin as an efficient green corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M sulphuric acid. J Mater Environ Sci 4:675–984
Lgaz H, Salghi R, Larouj M, Elfaydy M, Jodeh S, Rouifi Z, Oudda H (2016) Experimental, theoretical and Monte Carlo simulation of quinoline derivative as effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M HCl. J Mater Environ Sci 7:4471–4488. https://doi.org/10.4172/2472-0437.1000111
Lgaz H, Salghi R, Jodeh S, Hammouti B (2017) Effect of clozapine on inhibition of mild steel corrosion in 1.0 M HCl medium. J Mol Liq 225:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.11.039
Li X, Tang L, Li L, Mu G, Liu G (2006) Synergistic inhibition between o-phenanthroline and chloride ion for steel corrosion in sulphuric acid. Corros Sci 48:308–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2004.11.029
Loto RT, Loto CA, Ranyaoa M (2012) Pyrimidine derivatives as environmentally-friendly corrosion inhibitors: a review. Int J Phys Sci 7:2697–2705. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJPS11.1579
Magaji L, Ameh PO, Eddy NO, Uzairu A, Siaka AA, Habib S, Gumel SM (2012) Ciprofloxacin as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel-effects of concentration and temperature. Int J Modern Chem 2:64–73
Megalai MS, Ramesh R, Maniula P (2013) Inhibition of corrosion mild steel in acid media by trazodone drug. Res Desk 2:326–333
Oguzie EE (2007) Corrosion inhibition of aluminium in acidic and alkaline media by Sansevieria trifasciata extract. Corros Sci 49:1527–1539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2006.08.009
Materials Studio, Revision 6.0, Accelrys Inc., San Diego, USA, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce26487k
Sharma V, Kumar S, Bashir S, Ghelichkhah Z, Obot IB, Kumar A (2018) Use of Sapindus (reetha) as corrosion inhibitor of aluminium in acidic medium. Mater Res Express 5:076510. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aacf76
Shriver DF, Atkins PW, Langford CH (1994) Inorganic Chemistry. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Sigirik G, Tuken T, Erbil M (2015) Inhibition efficiency of aminobenzonitrile compounds on steel surface. Appl Surf Sci 324:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.206
Singh A, Singh AK, Quraishi MA (2010) Dapsone: a novel corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acid media. Open Electrochem J 2:43–51
Singh A, Pramanik T, Kumar A, Gupta M (2013) Phenobarbital: a new and effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution. Asian J Chem 25:17. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2013.15414
Solmaz R, Kardaş G, Culha M, Yazıcı B, Erbil M (2008) Investigation of adsorption and inhibitive effect of 2-mercaptothiazoline on corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid media. Electrochim Acta 53:5941–5952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2008.03.055
Trabanelli G (1991) Whitney award lecture: inhibitors—an old remedy for a new challenge. Corrosion 47:410–419. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3585271
Tsuru T, Haruyama S, Gijutsu B (1978) Corrosion inhibition of iron by amphoteric surfactants in 2 M HCl. J Jpn Soc Corros Eng 27:573–581. https://doi.org/10.3323/jcorr1974.27.11_573
Vracar LM, Drazic DM (2002) Adsorption and corrosion inhibitive properties of some organic molecules on iron electrode in sulfuric acid. Corros Sci 44:1669–1680. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(01)00166-4
Wahdan MH, Hermas AA, Morad MS (2002) Corrosion inhibition of carbon-steels by propargyltriphenylphosphonium bromide in H2SO4 solution. Mater Chem Phys 76:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(01)00526-0
Zhang Q, Hua Y (2010) Corrosion inhibition of aluminum in hydrochloric acid solution by alkylimidazolium ionic liquids. Mater Chem Phys 119:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.07.035
Zhao T, Mu G (1999) The adsorption and corrosion inhibition of anion surfactants on aluminium surface in hydrochloric acid. Corros Sci 41:1937–1944. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(99)00029-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, S., Lgaz, H., Chung, IM. et al. Potential of Venlafaxine in the inhibition of mild steel corrosion in HCl: insights from experimental and computational studies. Chem. Pap. 73, 2255–2264 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00775-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00775-0