Abstract
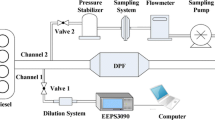
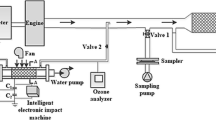
The emission tests were performed on a light-duty direct injection diesel engine. A polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE) mixture was blended with diesel at a volume ratio of 0, 10, 20 and 30%, denoted as P0, P10, P20 and P30, respectively. The particle size distribution before and after the diesel particulate filter (DPF) was measured to evaluate the DPF filtering efficiency of various modal particles. The oxidation activity of the particles on the DPF intake end plane was analyzed by the Arrhenius method. The regeneration of the DPF was conducted using a non-thermal plasma (NTP) injection system. The results showed that blending PODE with diesel contributed to reducing the particle number concentrations. PODE adversely affected the improvement of the DPF filtering efficiency, especially that of P30. However, the DPF filtering efficiency of all fuels was still higher than 94%. Blending PODE with diesel increased the mass fraction of volatile substances (VS) and decreased the mass fraction of dry soot. Particles of P20 showed a better oxidation activity with lower apparent activation energy. In addition, PODE increased the DPF regeneration effect by NTP technology. The deposit removal mass of the DPF rose to the peak level and then decreased as the PODE blending ratio increased. The better DPF regeneration effect was observed when P20 was employed.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PODE:
-
Polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers
- DPF:
-
Diesel particulate filter
- NTP:
-
Non-thermal plasma
- VS:
-
Volatile substances
- DS:
-
Dry soot
- PM:
-
Particulate matter
- SOF:
-
Soluble organic fraction
- ULSD:
-
Ultra-low sulfur diesel
- B100:
-
Biodiesel fuel
- B20:
-
20% biodiesel/diesel blends
- FT:
-
Fischer–Tropsch fuel
- CO:
-
Carbon monoxide
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- NOx :
-
Nitrogen oxide
- TG:
-
Thermogravimetric
- DTG:
-
Differential thermogravimetric
- LHV:
-
Low heating values
- P0:
-
Diesel
- P10:
-
10% PODE/diesel blends
- P20:
-
20% PODE/diesel blends
- P30:
-
30% PODE/diesel blends
- INTP:
-
Indirect non-thermal plasma
- CN:
-
Cetane number
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- EEPS:
-
Engine exhaust particle sizer spectrometer
- DBD:
-
Dielectric barrier discharge
- D P :
-
Characteristic particle size of PM
- η :
-
The particle filtering efficiency of the DPF
- n :
-
The particle total number concentration
- E a :
-
Apparent activation energy
- m :
-
The mass of reactants at the time of t
- t :
-
The time of the heating process
- A :
-
The pre-exponential factor
- PO 2 :
-
The partial pressure of oxygen
- R :
-
The gas constant
- T :
-
The reaction temperature
- m(C 1):
-
The removal mass of C in CO
- m(C 2):
-
The removal mass of C in CO2
- c1 :
-
The volume fraction of CO
- c2 :
-
The volume fraction of CO2
- M:
-
The molar mass of C
- q a :
-
The flow rate of the active gas
- V m :
-
The gas molar volume
- m(C 12):
-
The sum of m(C1) and m(C2)
- DMC:
-
Dimethyl carbonate
- DME:
-
Dimethyl ether
- DMM:
-
Dimethoxymethane
References
Ahn K (2014) The role of air pollutants in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immun 134(5):993–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.09.025
Alptekin E (2017) Evaluation of ethanol and isopropanol as additives with diesel fuel in a CRDI diesel engine. Fuel 205(C):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.05.076
Bagheri M, Baar R (2018) Simultaneous application of exhaust gas recirculation and non-constant injection rates to reduce NOx and soot emissions in diesel engines. Emiss Control Sci Technol 4:4–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40825-017-0080-4
Bashirnezhad K, Kebriyaee SA, Mehregan M (2016) Experimental analysis of the influence of urea injection upon NOx emissions in internal combustion engines fueled with biodiesels. J Energy Inst 89(1):115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2015.01.005
Burger J, Siegert M, Ströfer E, Hasse H (2010) Poly(oxymethylene) dimethyl ethers as components of tailored diesel fuel: properties, synthesis and purification concepts. Fuel 89(11):3315–3319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2010.05.014
Burtscher H (2005) Physical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: a review. J Aerosol Sci 36(7):896–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2004.12.001
Chaichan MT (2018) Combustion and emission characteristics of E85 and diesel blend in conventional diesel engine operating in PPCI mode. Therm Sci Eng Prog 7:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2018.04.013
Chen L, Stone R (2011) Measurement of enthalpies of vaporization of isooctane and ethanol blends and their effects on PM emissions from a GDI engine. Energy Fuels 25:1254–1259. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef1015796
Chen K, Martirosyan KS, Luss D (2011) Counter-intuitive temperature excursions during regeneration of a diesel particulate filter. AIChE J 57(8):2229–2236. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12427
Chen L, Stone R, Richardson D (2012) Effect of the valve timing and the coolant temperature on particulate emissions from a gasoline direct injection engine fuelled with gasoline and with a gasoline–ethanol blend. Proc IMechE Part D 226:1419–1430. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954407012444966
Chen L, Zhang Z, Gong W, Liang Z (2015) Quantifying the effects of fuel compositions on GDI-derived particle emissions using the optimal mixture design of experiments. Fuel 154:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.03.081
Chen L, Liang Z, Zhang X, Shuai S (2017) Characterizing particulate matter emissions from GDI and PFI vehicles under transient and cold start conditions. Fuel 189:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.055
Devins JC (1956) Mechanism of ozone formation in the silent electric discharge. J Electrochem Soc 103(8):460–466. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2430380
Dong M, Cai YX, Li XH, Jiang F, Han WH (2013) Effects of direct non-thermal plasma on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons emissions in diesel engine. Appl Mech Mater 437(2):1023–1029. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.437.1023
Feng HJ (2016) Effect of PODE3–8/diesel blended fuel on combustion and emissions of diesel engine. Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang Shi
Geng CR (2015) Experimental study on improving combustion and emission performance of compression ignition engine by adding PODE. Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai Shi
Gill SS, Tsolakis A, Herreros JM, York APE (2012) Diesel emissions improvements through the use of biodiesel or oxygenated blending components. Fuel 95:578–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.11.047
Grundmann J, Müller S, Zahn RJ (2005) Treatment of soot by dielectric barrier discharges and ozone. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 25(5):455–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-005-4992-3
Hao B (2014) Effect of fuel identity on the exhaust particles from diesel engine. Tianjin University, Tianjin
Hong L (2006) Investigation on the performance and emission of oxygenate alternative fueled diesel engines. Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai
Ichikawa Y, Yamada S, Yamada T (1995) Development of wall-flow type diesel particulate filter system with efficient reverse pulse air regeneration. SAE Tech Pap. https://doi.org/10.4271/950735
Jamrozik A, Tutak W, Pyrc M, Gruca M, Kočiško M (2018) Study on co-combustion of diesel fuel with oxygenated alcohols in a compression ignition dual-fuel engine. Fuel 221:329–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.098
Khair KM (2003) A review of diesel particulate filter technologies. SAE Tech Pap. https://doi.org/10.4271/2003-01-2303
Kitagawa J, Hijikata T, Yamada S (1991) Electric heating regeneration of large wall-flow type DPF. SAE Tech Paper. https://doi.org/10.4271/910136
Kittelson DB (1998) Engines and nanoparticles: a review. J Aerosol Sci 29(5):575–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-8502(97)10037-4
Kogelschatz U, Eliasson B, Hirth M (1988) Ozone generation from oxygen and air: discharge physics and reaction mechanisms. Ozone Sci Eng 10(4):366–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919518808552391
Konstandopoulos AG, Skaperdas E, Masoudi M (2002) Microstructural properties of soot deposits in diesel particulate traps. SAE World Congr Exhib 519(1):106–110. https://doi.org/10.4271/2002-01-1015
Lautenschütz L, Oestreich D, Seidenspinner P, Arnold U, Dinjus E, Sauer J (2016) Physico-chemical properties and fuel characteristics of oxymethylene dialkyl ethers. Fuel 173(6):129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.01.060
Li MD (2014) Research on the state characteristics of particles and formation mechanism of precursors formed by oxygenated fuels. Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang
Li XH, Li WJ, Cai YX, Shi YX, Xu H, Gu LB, Pu XY (2016) Comparative analysis on characteristics in non-thermal plasma reactor with oxygen and air. Trans CSAE 32(11):103–108. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.11.015
Li XH, Li WJ, Cai YX, Shi YX, Zheng Y, Xu H, Pu XY, Gu LB (2017) Deposit removal in EGR cooler and effectiveness improvement by non-thermal plasma reactor with different gas sources. Appl Therm Eng 111:694–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.09.055
Liu HY, Wang Z, Wang JX, He X, Zheng YY, Tang Q, Wang JF (2015) Performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE3-4)/diesel blends. Energy 88:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.07.479
Liu JL, Wang H, Li Y, Zheng ZQ, Xue ZZ, Shang HY, Yao MF (2016) Effects of diesel/PODE (polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers) blends on combustion and emission characteristics in a heavy duty diesel engine. Fuel 177:206–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.03.019
Liu H, Ma X, Li B, Chen L, Wang Z, Wang J (2017a) Combustion and emission characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine fueled with biodiesel and PODE/biodiesel fuel blends. Fuel 209:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.07.066
Liu JH, Sun P, Huang H, Meng J, Yao XH (2017b) Experimental investigation on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a common-rail diesel engine fueled with polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers-diesel blends. Appl Energy 202:527–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.05.166
Mei D, Zhao X, Wang S, Yuan Y, Sun P (2013) Thermogravimetric characteristics analysis of particulate matter of emission of divided diesel. Trans CSAE 29(16):50–56. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.16.007
Natarajan M, Frame EA, Naegeli DW, Asmus T, Clark W, Garbak J et al (2001) Oxygenates for advanced petroleum-based diesel fuels: part 1. screening and selection methodology for the oxygenates. Sae Tech Pap. https://doi.org/10.4271/2001-01-3631
Okubo M, Miyashita T, Kuroki T, Miwa S, Yamamoto T (2004) Regeneration of diesel particulate filter using nonthermal plasma without catalyst. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 40(6):1451–1458. https://doi.org/10.1109/ias.2002.1043782
Okubo M, Arita N, Kuroki T, Yamamoto T (2007) Carbon particulate matter incineration in diesel engine emissions using indirect nonthermal plasma processing. Thin Solid Films 515(9):4289–4295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2006.02.071
Okubo M, Arita N, Kuroki T, Yamamoto T (2008) Total diesel emission control system using ozone injection and plasma desorption. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28(2):173–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-008-9121-7
Okubo M, Kuroki T, Kawasaki S, Yamamoto T (2009) Continuous regeneration of ceramic particulate filter in stationary diesel engine by nonthermal-plasma-induced ozone injection. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 45(5):1568–1574. https://doi.org/10.1109/08ias.2008.122
Pallavkar S, Kim TH, Dan R, Lin J, Ho T (2009) Active regeneration of diesel particulate filter employing microwave heating. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie800780g
Palma V, Ciambelli P, Meloni E, Sin A (2015) Catalytic DPF microwave assisted active regeneration. Fuel 140:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.09.051
Pirjola L, Rönkkö T, Saukko E, Parviainen H, Malinen A, Alanen J, Saveljeff H (2017) Exhaust emissions of non-road mobile machine: real-world and laboratory studies with diesel and HVO fuels. Fuel 202(15):154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.029
Prashant GK, Lata DB, Joshi PC (2016) Investigations on the effect of methanol blend on the combustion parameters of dual fuel diesel engine. Appl Therm Eng 96:623–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.04.061
Pu XY, Cai YX, Shi YX, Wang J, Gu LB, Tian J, Li WJ (2017a) Diesel particulate filter (DPF) regeneration using non-thermal plasma induced by dielectric barrier discharge. J Energy Inst 91(5):655–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2017.06.004
Pu XY, Cai YX, Shi YX, Wang J, Gu LB, Tian J, Cui YX (2017b) Test on diesel particulate filter regeneration using non-thermal plasma technology aided by exhaust waste heat. Trans CSAE 33(14):70–77. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.14.010
Rajanikanth BS, Srinivasan AD, Ravi V (2005) Discharge plasma treatment for NOx reduction from diesel engine exhaust: a laboratory investigation. IEEE Trans Dielect Electe Insul 12(1):72–80. https://doi.org/10.1109/tdei.2005.1394017
Raza M, Chen L, Leach F, Ding S (2018) A review of particulate number (PN) emissions from gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines and their control techniques. Energies 11:1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061417
Rodríguez-Fernández J, Oliva F, Vázquez RA (2011) Characterization of the diesel soot oxidation process through an optimized thermogravimetric method. Energy Fuel 25(5):2039–2048. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef200194m
Rodríguez-Fernández J, Lapuerta M, Sánchez-Valdepeñas J (2017) Regeneration of diesel particulate filters: effect of renewable fuels. Renew Energy 104:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.11.059
Saliba G, Saleh R, Zhao Y, Presto AA, Lambe AT, Frodin B, Sardar S, Maldonado H, Maddox C, May AA, Drozd GT, Goldstein AH, Russell LM, Hagen FP, Robinson AL (2017) A comparison of gasoline direct injection (GDI) and port fuel injection (PFI) vehicle emissions: emission certification standards, cold start, secondary organic aerosol formation potential, and potential climate impacts. Environ Sci Technol 51:6542–6552. https://doi.org/10.5572/ajae.2016.10.1.051
Shi YX, Cai YX, Li KH, Li XH, Chen YY (2013) Experimental study on the DPF regeneration based on non-thermal plasma technology. Appl Mech Mater 325–326:1347–1351. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.325-326.1347
Shi YX, Cai YX, Li XH, Chen YY, Ding DW, Tang W (2014) Meachanism and method of DPF regeneration by oxygen radical generated by NTP technology. Int J Automot Technol 15(6):871–876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-014-0091-x
Shi YX, Cai YX, Wang J, Pu XY, Gu LB (2016a) Influence of PM size distribution and ingredients on DPF regeneration by non-thermal plasma technology. Plasma Chem Plasma Porcess 37(2):1–14
Shi YX, Cai YX, Li XH, Xu H, Li WJ, Pu XY (2016b) Low temperature diesel particulate filter regeneration by atmospheric air non-thermal plasma injection system. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36(3):783–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-016-9701-x
Singh D, Subramanian KA, Bal R, Singh SP, Badola R (2018) Combustion and emission characteristics of a light duty diesel engine fueled with hydro-processed renewable diesel. Energy 154:498–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.04.139
Song JH, Alam M, Boehman AL (2007) Impact of alternative fuels on soot properties and DPF regeneration. Combust Sci Technol 179(9):1991–2037. https://doi.org/10.1080/00102200701386099
Su CM, Puls RW (1999) Kinetics of trichloroethene reduction by zerovalent iron and tin: pretreatment effect, apparent activation energy, and intermediate products. Environ Sci Technol 33(1):163–168. https://doi.org/10.1021/es980481a
Suhaimi H, Adam A, Mrwan AG, Abdullah Z, Othman MF, Kamaruzzaman MK, Hagos FY (2018) Analysis of combustion characteristics, engine performances and emissions of long-chain alcohol-diesel fuel blends. Fuel 220:682–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.019
Sun WC, Liu G, Guo L, Du JK, Xiao SL, Li GL (2016) Efficiency of DPF on ultrafine particles in a common-rail diesel engine. J Jilin Univ 46(1):133–139. https://doi.org/10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201601020
Tan PQ, Hu ZY, Lou DM, Wan G, Li ZJ (2008) Effects of diesel particulate filter structural parameters on filtration performance of different size particles. Chin J Mech Eng 44(2):175–181. https://doi.org/10.3901/jme.2008.02.175
Tan YS, Botero ML, Sheng Y, Dreyer JAH, Xu R, Yang W, Kraft M (2018) Sooting characteristics of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether blends with diesel in a diffusion flame. Fuel 224:499–506
Tao F, Reitz RD, Foster DE, Liu Y (2009) Nine-step phenomenological diesel soot model validated over a wide range of engine conditions. Int J Therm Sci 48(6):1223–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2008.08.014
Tunér M (2015) Combustion of alternative vehicle fuels in internal combustion engines. The Swedish Energy Agency, Frösön
Wang JX, Wu FJ, Xiao JH, Shuai SJ (2009) Oxygenated blend design and its effects on reducing diesel particulate emissions. Fuel 88(10):2037–2045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.02.045
Wang P, Cai YX, Wang J, Zheng R, Yan Y (2010) Carbon particles reduction in diesel engine with non-thermal plasma technology. Int Conf Elec Control Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/icece.2010.840
Wang J, Sun P, Mei D, Guo L (2011) Particulate matter emission and its pyrolysis kinetic analysis of ethanol-diesel engine. Trans CSAE 27(2):110–113. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2011.z2.022
Wang D, Liu ZC, Liu JW, Zhang JR (2012) Investigation of particle emission characteristics from a diesel engine with a diesel particulate filter for alternative fuels. Int J Automot Technol 13(7):1023–1032. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-012-0105-5
Wang Y, Raj A, Chung SH (2013) A PAH growth mechanism and synergistic effect on PAH formation in counterflow diffusion flames. Combust Flame 160(9):1667–1676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.03.013
Xia D, Chen GX, Liao ZJ, Wang HM, Wang XC, Du PF (2015) Recearch status and development tendency of ashless diesel additives. Energy Conserv Tech 33(2):155–158. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-6339.2015.02.014
Xie M, Ma ZJ, Wang QH, Liu JC, Liu SH (2017) Investigation of engine combustion and emission performance fuelled with neat PODE and PODE/diesel blend. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ 51(3):32–37. https://doi.org/10.7652/xjtuxb201703006
Xu X, Gao X, Zhang Y, Yang D, Wang X (2002) Infrared heating regeneration method for diesel exhaust participate filter. Chin Intern Combust Engine Eng 23(1):60–62. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-0925.2002.01.016
Yamada H, Inomata S, Tanimoto H (2017) Mechanisms of increased particle and VOC emissions during DPF active regeneration and practical emissions considering regeneration. Environ Sci Technol 51(5):2914–2923. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05866
Yang H, Li X, Wang Y, Mu M, Li X, Kou G (2016) Experimental investigation into the oxidation reactivity and nanostructure of particulate matter from diesel engine fuelled with diesel/polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers blends. Sci Rep 6:37611. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37611
Yoon S, Quiros DC, Dwyer HA, Collins JF, Burnitzki M, Chernich D et al (2015) Characteristics of particle number and mass emissions during heavy-duty diesel truck parked active DPF regeneration in an ambient air dilution tunnel. Atmos Environ 122:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.09.032
Zhang W (2010) Study on the microstructure, surface functional groups and oxidation reactivity of diesel in-cylinder particles. Tianjin University, Tianjin
Zhang ZH, Balasubramanian R (2015) Effects of oxygenated fuel blends on carbonaceous particulate composition and particle size distributions from a stationary diesel engine. Fuel 141:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.10.023
Zhang WG, Wei XD, Lin D, Zhu YJ (2016) Experimental study on the influence of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE) on ultrafine particle emission of a compression ignition engine. J. Autom Saf Energ 7(3):329–336. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2016.03.012
Zhang M, Hong W, Xie F, Su Y, Han L, Wu B (2018) Experimental investigation of impacts of injection timing and pressure on combustion and particulate matter emission in a spray-guided gdi engine. Int J Automot Technol 19(3):393–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-018-0038-8
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51676089), the Key University Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (No. 16KJA470002), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and the Science Research Project of Xuzhou Institute of Technology (No. XKY2016223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Cai, Y., Pu, X. et al. Effect of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers on particle properties and diesel particulate filter regeneration. Chem. Pap. 73, 455–468 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0593-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0593-5