Abstract
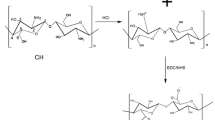
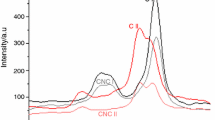
Films made of xylan (X) and quaternized chitosan (QC) were prepared and the interactions of the polysaccharides on interfaces were discussed. According to elemental analysis, the X film contained also cellulose (31%) which could not be separated from the water suspension. The QC sample was soluble in water due to the presence of quaternized glucosamine units (4%) despite the presence of equal amounts of chitosan (CS, 48%) and chitin (CT, 48%). According to mechanical tests on QC/X = 1/3 composite film, the modulus and tensile strength values were the best from all mixtures measured, but still not better than on the film from X. We assume this is due to the sorption of xylan onto the surface of insoluble cellulose fibrils in the X film. Cyclic voltammetry indicates that the incorporation of X into the QC film decreases the overall positive charge provided by the QC. The X composite with net negative charge is indeed a barrier against the diffusion of ferricyanide anions. Based on TG/DTG/DTA analysis, the onset temperatures (OT) are decreasing with increasing X content in the blended films. X and QC films exhibited the highest OT values in comparison with the blended samples. The lowest OT temperature was observed at QC/X = 1/3. We think it is due to the thermocatalytic effect of the 4-O-methyl-d-glucuronate in X and the QC quaternary groups on the thermolysis–thermo-oxidation mechanism. According to AFM, the QC/X = 1/3 film exhibited the largest roughness values on both sides of the films, likely due to having the highest density of electrostatic interactions. XRD profiles of the films indicate some crystalline residues of cellulose in the xylan component as well as some chitin in the QC component. We assume that the properties are the result of the combination of the electrostatic interactions of carboxyl and quaternary groups of the soluble components of X and QC bonded to the surface of insoluble cellulose fibrils by hydrogen bonds. This probably results in both synergistic and antagonistic effects expressed by the improved or diminished values of determined properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capron I, Rojas OJ, Bordes R (2017) Behavior of nanocelluloses at interfaces. Curr Opinion Colloid Interface Sci 29:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2017.04.001
Ferreira AS, Nunes C, Castro A, Ferreira P, Coimbra MA (2014) Influence of grape pomace extract incorporation on chitosan films properties. Carbohydr Polym 113:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.07.32
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Ge-Gu C, Xian-Ming Q, Ying G, Feng P, Chun-Li Y, Run-Cang S (2016) high strength hemicellulose-based nanocomposite film for food packing applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:1985–1993. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5g01252
Grondahl M, Eriksson L, Gatenholm P (2004) Material properties of plasticized hardwood xylans for potential application as oxygen barrier films. Biomacromol 5:1528–1535. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm049925n
Luo Y, Pan X, Ling Y, Wang X, Sun R (2014) Facile fabrication of chitosan active film with xylan via direct immersion. Cellulose 21:1873–1883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0156-4
Mocchiutti P, Schnell CN, Rossi GD, Peresin MS, Zanutti MA, Galván MV (2016) Cationic and anionic polyelectrolyte complexes of xylan and chitosan. Interaction with lignocellulosic surfaces. Carbohydr Polym 150:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.111
Muzzarelli RAA, Boudrant J, Meyer D, Manno N, DeMarchis M, Paoletti MG (2012) Current view of fungal chitin/chitosan, human chitinases, food preservation, glucans, pectins and inulin: a tribute to Henri Braconnot, precursor of the carbohydrate polymers science, on the chitin bicentennial. Carbohydr Polym 87:995–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.09.063
Nunes C, Maricato E, Cunha A, Rocha MA, Rocha MAM, Santos S, Ferreira P, Silva MA, Rodrigues A, Amado O, Coimbra J, Silva D, Moreira A, Mendo S, Lopes da Silva J, Pereira E, Rocha SA, Coimbra MA (2016) Chitosan-genipin film, a sustainable methodology for wine preservation. Green Chem 18:5331–5341. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6GC01621A
Šimkovic I (2013) Unexplored possibilities of all-polysaccharide composites. Carbohydr Polym 95:697–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.040
Šimkovic I, Jakab E (2001) Thermogravimetry/mass spectrometry study of weakly basic starch-based ion exchanger. Carbohydr Polym 45:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(00)00230-7
Šimkovic I, Varhegyi G, Antal MJ Jr, Ebringerová A, Székely T, Szabo P (1988) Thermogravimetric/mass spectrometric characterization of (4-O-methyl-D-glucurono)-D-xylan. J Appl Polym Sci 36:721–728. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1988.070360320
Šimkovic I, Tracz A, Kelnar I, Uhliariková I, Mendichi R (2014a) Quaternized and sulfated xylan derivative films. Carbohydr Polym 99:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.075
Šimkovic I, Kelnar I, Uhliariková I, Mendichi R, Mandalika A, Elder T (2014b) Carboxymethylated-, hydroxypropylsulfonated- and quaternized xylan derivative films. Carbohydr Polym 110:464–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.055
Šimkovic I, Kelnar I, Mendichi R, Bertok T, Filip J (2017) Composite films prepared from agricultural by-products. Carbohydr Polym 156:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.09.014
Sun Q, Mandalika A, Elder T, Nair SS, Meng X, Huang F, Ragauskas AJ (2014) Nanocomposite film prepared by depositing xylan on cellulose nanowhiskers matrix. Green Chem 16:3458–3462. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4GC00793J
Zangmeister RA, Park JJ, Rubloff GW, Tarlov MJ (2006) Electrochemical study of chitosan films deposited from solution at reducing potentials. Electrochim Acta 51:5324–5333
Zhang Y, Xue C, Xue Y, Gao R, Zhang X (2005) Determination of degree of deacetylation of chitin and chitosan by X-ray powder difraction. Carbohydr Res 340:1914–1917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2005.05.005
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge funding from State programs #2003SP200280203 and 2003SP200280301; Slovak Granting Agency VEGA (Project Nos. 2/7030/7, 2/0087/11, 2/0007/13 and 2/0100/14). We thank Eva Hadzimová for performing the TG/DTG/DTA experiments. This contribution is also the result of the project implementation: Centre of Excellence for White-Green Biotechnology, ITMS 26220120054, supported by the Research & Development Operational Program funded by the ERDF. P.K. thanks Qatar University for QUUG-CAM-2017-1 grant funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Adam Tracz passed away on December 23, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šimkovic, I., Kelnar, I., Mendichi, R. et al. Interfaces study of all-polysaccharide composite films. Chem. Pap. 72, 711–718 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0329-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0329-y