Abstract
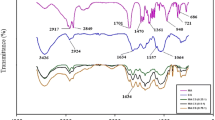
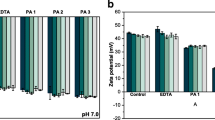
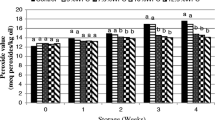
The susceptibility of heart healthy ω-3 fatty acids to lipid oxidation has hindered its incorporation into healthful foods and beverages. In this study, plant-based flaxseed oil rich in ω-3 fatty acids were dispersed into primary, secondary and tertiary emulsion system. A primary emulsion containing sodium caseinate-stabilized cationic droplets was prepared by homogenizing flaxseed oil as oil phase and sodium caseinate solution as the aqueous phase in an ultrasonicator. A secondary emulsion comprising of sodium caseinate–sodium alginate anionic droplets were produced by diluting appropriate primary emulsion with alginate solution. Further, a tertiary emulsion composed of sodium caseinate–sodium alginate–chitosan-coated cationic droplets was produced by diluting secondary emulsion with chitosan solution. The resistance of primary, secondary and tertiary emulsions with the same lipid concentration to destabilization by thermal treatment (30–90 °C for 30 min), sodium chloride addition (≤70 mM NaCl) and oxidative degradation (hydroperoxide concentration and TBARS) was determined. The results showed that secondary emulsions could resist variation in environmental stresses of salt and heat as well as protect the oil phase from decomposition better than primary and tertiary emulsions. Interfacial engineering could be used to design emulsion system with desirable characteristics.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki T, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2005) Influence of environmental stresses on stability of O/W emulsions containing droplets stabilized by multilayered membranes produced by a layer-by-layer electrostatic deposition technique. Food Hydrocoll 19:209–220. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2004.05.006
Berton-Carabin C, Genot C, Gaillard C, Guibert D, Ropers M (2013) Design of interfacial films to control lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 33:99–105. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.02.021
Casanova H, Dickinson E (1998) Influence of protein interfacial composition on salt stability of mixed casein emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 46:72–76. doi:10.1021/jf970600q
Chaprenet J, Berton-Carabin CC, Elias RJ, Coupland JN (2014) Effect of interfacial properties on the reactivity of a lipophilic ingredient in multilayered emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 42:56–65. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.12.009
Corstens MN et al (2017) Destabilization of multilayered interfaces in digestive conditions limits their ability to prevent lipolysis in emulsions. Food Struct 12:54–63. doi:10.1016/j.foostr.2016.07.004
Csaba N, Köping-Höggård M, Alonso MJ (2009) Ionically crosslinked chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles for oligonucleotide and plasmid DNA delivery. Int J Pharm 382:205–214. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.07.028
Dickinson E (2010) Flocculation of protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Coll Surf B 81:130–140. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.06.033
Dickinson E (2011) Mixed biopolymers at interfaces: competitive adsorption and multilayer structures. Food Hydrocoll 25:1966–1983. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.12.001
Dlugogorski BZ, Kennedy EM, Mackie JC (2012) Identification and quantitation of volatile organic compounds from oxidation of linseed oil. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:5645–5652. doi:10.1021/ie202535d
Fang J-L, Vaca CE, Valsta LM, Mutanen M (1996) Determination of DNA adducts of malonaldehyde in humans: effects of dietary fatty acid composition. Carcinogenesis 17:1035–1040. doi:10.1093/carcin/17.5.1035
Fioramonti SA, Martinez MJ, Pilosof AM, Rubiolo AC, Santiago LG (2015) Multilayer emulsions as a strategy for linseed oil microencapsulation: effect of pH and alginate concentration. Food Hydrocoll 43:8–17. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.04.026
Giroux HJ, St-Amant JB, Fustier P, Chapuzet J-M, Britten M (2008) Effect of electroreduction and heat treatments on oxidative degradation of a dairy beverage enriched with polyunsaturated fatty acids. Food Res Int 41:145–153. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2007.10.008
Giroux HJ, Houde J, Britten M (2010) Use of heated milk protein–sugar blends as antioxidant in dairy beverages enriched with linseed oil LWT-food. Sci Technol 43:1373–1378. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2010.05.001
Goyal A, Sharma V, Sihag MK, Tomar SK, Arora S, Sabikhi L, Singh AK (2015) Development and physico-chemical characterization of microencapsulated flaxseed oil powder: a functional ingredient for omega-3 fortification. Powder Technol 286:527–537. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2015.08.050
Gu YS, Decker AE, McClements DJ (2005) Production and characterization of oil-in-water emulsions containing droplets stabilized by multilayer membranes consisting of β-lactoglobulin, ι-carrageenan and gelatin. Langmuir 21:5752–5760. doi:10.1021/la046888c
Gudipati V, Sandra S, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2010) Oxidative stability and in vitro digestibility of fish oil-in-water emulsions containing multilayered membranes. J Agric Food Chem 58:8093–8099. doi:10.1021/jf101348c
Guzey D, McClements DJ (2006) Formation, stability and properties of multilayer emulsions for application in the food industry. Adv Coll Interf Sci 128–130:227–248. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2006.11.021
Guzey D, McClements DJ (2007) Impact of electrostatic interactions on formation and stability of emulsions containing oil droplets coated by β-lactoglobulin–pectin complexes. J Agric Food Chem 55:475–485. doi:10.1021/jf062342f
Güzey D, McClements DJ (2006) Influence of environmental stresses on O/W emulsions stabilized by β-lactoglobulin–pectin and β-lactoglobulin–pectin–chitosan membranes produced by the electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition technique. Food Biophys 1:30–40. doi:10.1007/s11483-005-9002-z
Hu M, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2003) Lipid oxidation in corn oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by casein, whey protein isolate, and soy protein isolate. J Agric Food Chem 51:1696–1700. doi:10.1021/jf020952j
Jo Y-J, Chun J-Y, Kwon Y-J, Min S-G, Choi M-J (2015) Formulation development of multilayered fish oil emulsion by using electrostatic deposition of charged biopolymers. Int J Food Eng 11:31–39. doi:10.1515/ijfe-2014-0177
Julio LM, Ixtaina VY, Fernández MA, Sánchez RMT, Wagner JR, Nolasco SM, Tomás MC (2015) Chia seed oil-in-water emulsions as potential delivery systems of ω-3 fatty acids. J Food Eng 162:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.04.005
Kartal C, Unal MK, Otles S (2016) Flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by multilayer membranes: oxidative stability and the effects of pH. J Dispers Sci Technol. doi:10.1080/01932691.2016.1141294
Katsuda MS, McClements DJ, Miglioranza LH, Decker EA (2008) Physical and oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with β-lactoglobulin and pectin. J Agric Food Chem 56:5926–5931. doi:10.1021/jf800574s
Laye C, McClements DJ, Weiss J (2008) Formation of biopolymer-coated liposomes by electrostatic deposition of chitosan. J Food Sci 73:N7–N15. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00747.x
Leong T, Wooster T, Kentish S, Ashokkumar M (2009) Minimising oil droplet size using ultrasonic emulsification. Ultrason Sonochem 16:721–727. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.02.008
Liu Y, Qiu S, Li J, Chen H, Tatsumi E, Yadav M, Yin L (2015) Peroxidase-mediated conjugation of corn fiber gum and bovine serum albumin to improve emulsifying properties. Carbohydr Polym 118:70–78. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.059
Liu F, Wang D, Sun C, McClements DJ, Gao Y (2016) Utilization of interfacial engineering to improve physicochemical stability of β-carotene emulsions: Multilayer coatings formed using protein and protein–polyphenol conjugates. Food Chem 205:129–139. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.155
Mao Y, Dubot M, Xiao H, McClements DJ (2013) Interfacial engineering using mixed protein systems: Emulsion-based delivery systems for encapsulation and stabilization of β-carotene. J Agric Food Chem 61:5163–5169. doi:10.1021/jf401350t
McClements DJ (2010) Emulsion design to improve the delivery of functional lipophilic components. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 1:241–269. doi:10.1146/annurev.food.080708.100722
Noshad M, Mohebbi M, Shahidi F, Koocheki A (2015) Freeze–thaw stability of emulsions with soy protein isolate through interfacial engineering. Int J Refrig 58:253–260. doi:10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2015.05.007
Noshad M, Mohebbi M, Koocheki A, Shahidi F (2016) Influence of interfacial engineering on stability of emulsions stabilized with soy protein isolate. J Dispers Sci Technol 37:56–65. doi:10.1080/01932691.2015.1027907
Ogawa S, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2004) Production and characterization of O/W emulsions containing droplets stabilized by lecithin–chitosan–pectin mutilayered membranes. J Agric Food Chem 52:3595–3600. doi:10.1021/jf034436k
Qiu C, Zhao M, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2015) Influence of protein type on oxidation and digestibility of fish oil-in-water emulsions: gliadin, caseinate, and whey protein. Food Chem 175:249–257. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.112
Rabetafika HN, Van Remoortel V, Danthine S, Paquot M, Blecker C (2011) Flaxseed proteins: food uses and health benefits. Int J Food Sci Technol 46:221–228. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02477.x
Riediger ND, Othman R, Fitz E, Pierce GN, Suh M, Moghadasian MH (2008) Low n-6: n-3 fatty acid ratio, with fish-or flaxseed oil, in a high fat diet improves plasma lipids and beneficially alters tissue fatty acid composition in mice. Eur J Nutr 47:153–160. doi:10.1007/s00394-008-0709-8
Scheffler SL, Wang X, Huang L, San-Martin Gonzalez F, Yao Y (2009) Phytoglycogen octenyl succinate, an amphiphilic carbohydrate nanoparticle, and ε-polylysine to improve lipid oxidative stability of emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 58:660–667. doi:10.1021/jf903170b
Shim YY, Gui B, Wang Y, Reaney MJT (2015) Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) oil processing and selected products. Trends Food Sci Technol 43:162–177. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2015.03.001
Siddiqui RA, Shaikh SR, Sech LA, Yount HR, Stillwell W, Zaloga GP (2004) Omega 3-fatty acids: health benefits and cellular mechanisms of action. Mini Rev Med Chem 4:859–871. doi:10.2174/1389557043403431
Taherian AR, Britten M, Sabik H, Fustier P (2011) Ability of whey protein isolate and/or fish gelatin to inhibit physical separation and lipid oxidation in fish oil-in-water beverage emulsion. Food Hydrocoll 25:868–878. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.08.007
Tokle T, Mao Y, McClements DJ (2013) Potential biological fate of emulsion-based delivery systems: lipid particles nanolaminated with lactoferrin and β-lactoglobulin coatings. Pharm Res 30:3200–3213. doi:10.1007/s11095-013-1003-x
Yang Y, Cui SW, Gong J, Guo Q, Wang Q, Hua Y (2015) A soy protein-polysaccharides Maillard reaction product enhanced the physical stability of oil-in-water emulsions containing citral. Food Hydrocoll 48:155–164. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.02.004
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the technical support extended by Mr. Susanta Pradhan for confocal laser scanning microscopy imaging.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivapratha, S., Sarkar, P. Oxidative stability and effect of stress factors on flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by sodium caseinate–sodium alginate–chitosan interfacial membrane. Chem. Pap. 72, 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0252-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0252-2