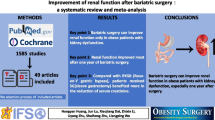
Abstract
Background/Objective
Although promising, data regarding the renal impact and safety of bariatric surgery (BS) are insufficient. We aimed at investigating the benefits and harms of BS for weight loss on kidney function.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies reporting data about the impact of BS (any techniques) on serum/plasma creatinine, creatinine clearance, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), proteinuria, nephrolithiasis, and need for renal replacement therapy (RRT)) was performed. Obese adults (non-chronic kidney disease (CKD), CKD or transplanted patients) that underwent BS for weight loss were included. After searching MEDLINE (inception to August 2017), the Cochrane Library (Issue 10–12, October 2017), and the websiteclinicaltrials.gov (August 2017), data were extracted and summarized using a random-effects model.
Results
The final analysis included 23 cohort studies, comprising 3015 participants. Compared with renal function before treatment, BS significantly decreased serum creatinine level (mean difference (MD), − 0.08 mg dl−1; 95% confidence interval (CI), − 0.10 to − 0.06); p < 0.001) and proteinuria (MD, − 0.04 g 24 h−1; 95% CI, − 0.06 to − 0.02; p < 0.001) in the overall group. GFR significantly improved 6 months or more after BS both in the hyperfiltration and CKD subgroups. Renal function also tended to improve in renal transplant patients. Data on nephrolithiasis and the need for RRT were scarce or not reported.
Conclusions
BS apparently has positive effects on kidney function and tends to normalize GFR across different categories of renal impairment (hyperfiltration and CKD patients).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387(10026):1377–96.
Hill NR, Fatoba ST, Oke JL, et al. Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease—a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0158765.
Hall ME, do Carmo JM, da Silva AA, et al. Obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Int J Nephrol Renov Dis. 2014;7:75–88.
Garland JS. Elevated body mass index as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease: current perspectives. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014;7:347–55.
Navaneethan SD, Yehnert H, Moustarah F, et al. Weight loss interventions in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(10):1565–74.
Afshinnia F, Wilt TJ, Duval S, et al. Weight loss and proteinuria: systematic review of clinical trials and comparative cohorts. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(4):1173–83.
Bolignano D, Zoccali C. Effects of weight loss on renal function in obese CKD patients: a systematic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(Suppl 4):iv82–98.
Piche M, Auclair A, Harvey J, et al. How to choose and use bariatric surgery in 2015. Can J Cardiol. 2015;31(2):153–66.
Duffey BG, Alanee S, Pedro RN, et al. Hyperoxaluria is a long-term consequence of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a 2-year prospective longitudinal study. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;211(1):8–15.
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603–5.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011) 2011.
DerSimonian R, Kacker R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trials. 2007;28(2):105–14.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
Navarro-Diaz M, Serra A, Romero R, et al. Effect of drastic weight loss after bariatric surgery on renal parameters in extremely obese patients: long-term follow-up. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(12 Suppl 3):S213–7.
Serpa-Neto A, Biaco Rossi FM, Dal Moro Amarante R, et al. Effect of weight loss after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, on renal function and blood pressure in morbidly obese patients. J Nephrol. 2009;22(5):637–46.
Friedman AN, Moe S, Fadel WF, et al. Predicting the glomerular filtration rate in bariatric surgery patients. Am J Nephrol. 2014;39(1):8–15.
Saliba J, Kasim NR, Tamboli RA, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass reverses renal glomerular but not tubular abnormalities in excessively obese diabetics. Surgery. 2010;147(2):282–7.
Chagnac A, Weinstein T, Herman M, et al. The effects of weight loss on renal function in patients with severe obesity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(6):1480–6.
Luaces M, Martinez-Martinez E, Medina M, et al. The impact of bariatric surgery on renal and cardiac functions in morbidly obese patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(Suppl 4):iv53–7.
Navaneethan SD, Kelly KR, Sabagh F, et al. Urinary albumin excretion, HMW adiponectin, and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2010;20(3):308–15.
Navaneethan SD, Yehnert H. Bariatric surgery and progression of chronic kidney disease. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2009;5(6):662–5.
Agrawal V, Khan I, Rai B, et al. The effect of weight loss after bariatric surgery on albuminuria. Clin Nephrol. 2008;70(3):194–202.
Mohan S, Tan J, Gorantla S, et al. Early improvement in albuminuria in non-diabetic patients after roux-en-Y bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2012;22(3):375–80.
Fenske WK, Dubb S, Bueter M, et al. Effect of bariatric surgery-induced weight loss on renal and systemic inflammation and blood pressure: a 12-month prospective study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(4):559–68.
Hou CC, Shyu RS, Lee WJ, et al. Improved renal function 12 months after bariatric surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(2):202–6.
Palomar R, Fernandez-Fresnedo G, Dominguez-Diez A, et al. Effects of weight loss after biliopancreatic diversion on metabolism and cardiovascular profile. Obes Surg. 2005;15(6):794–8.
Getty JL, Hamdallah IN, Shamseddeen HN, et al. Changes in renal function following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a prospective study. Obes Surg. 2012;22(7):1055–9.
Jose B, Ford S, Super P, et al. The effect of biliopancreatic diversion surgery on renal function—a retrospective study. Obes Surg. 2013;23(5):634–7.
Ruiz-Tovar J, Giner L, Sarro-Sobrin F, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy prevents the deterioration of renal function in morbidly obese patients over 40 years. Obes Surg. 2015;25(5):796–9.
Schuster DP, Teodorescu M, Mikami D, et al. Effect of bariatric surgery on normal and abnormal renal function. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7(4):459–64.
Ngoh CL, So JB, Tiong HE, et al. Effect of weight loss after bariatric surgery on kidney function in a multiethnic Asian population. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(3):600–5.
Reid TJ, Saeed S, McCoy S, et al. The effect of bariatric surgery on renal function. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014;10(5):808–13.
Serra A, Granada ML, Romero R, et al. The effect of bariatric surgery on adipocytokines, renal parameters and other cardiovascular risk factors in severe and very severe obesity: 1-year follow-up. Clin Nutr. 2006;25(3):400–8.
Amor A, Jimenez A, Moize V, et al. Weight loss independently predicts urinary albumin excretion normalization in morbidly obese type 2 diabetic patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2013;27(6):2046–51.
Imam TH, Fischer H, Jing B, et al. Estimated GFR before and after bariatric surgery in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;69(3):380–8.
Golomb I, Winkler J, Ben-Yakov A, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as a weight reduction strategy in obese patients after kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2014;14(10):2384–90.
Perrone RD, Madias NE, Levey AS. Serum creatinine as an index of renal function: new insights into old concepts. Clin Chem. 1992;38(10):1933–53.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292(14):1724–37.
Wang C, He B, Piao D, et al. Roux-en-Y Esophagojejunostomy ameliorates renal function through reduction of renal inflammatory and fibrotic markers in diabetic nephropathy. Obes Surg. 2016;26(7):1402–13.
Chan G, Garneau P, Hajjar R. The impact and treatment of obesity in kidney transplant candidates and recipients. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2015;2:26.
MacLaughlin HL, Hall WL, Patel AG, et al. Weight loss, adipokines, and quality of life after sleeve gastrectomy in obese patients with stages 3-4 CKD: a randomized controlled pilot study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64(4):660–3.
Turgeon NA, Perez S, Mondestin M, et al. The impact of renal function on outcomes of bariatric surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23(5):885–94.
Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS) Consortium, Flum DR, Belle SH, et al. Perioperative safety in the longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(5):445–54.
Rao BB, Bhattacharya A, Agrawal V. Renal outcomes of bariatric surgery in obese adults with diabetic kidney disease. J Nephrol. 2014;27(4):361–70.
Nasr SH, D'Agati VD, Said SM, et al. Oxalate nephropathy complicating Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: an underrecognized cause of irreversible renal failure. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3(6):1676–83.
Knight EL, Stampfer MJ, Hankinson SE, et al. The impact of protein intake on renal function decline in women with normal renal function or mild renal insufficiency. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(6):460–7.
Kang JG, Park CY. Anti-obesity drugs: a review about their effects and safety. Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(1):13–25.
Li K, Zou J, Ye Z, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on renal function in obese patients: a systematic review and meta analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0163907.
Funding
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilha, S.C., Nistor, I., Nedelcu, A. et al. The Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Renal Outcomes: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. OBES SURG 28, 3815–3833 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3416-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3416-4