Abstract
Objective
The aims of this study were to assess the prognostic significance of WHO-based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS) in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) from a single center institute and to compare WPSS with the international prognostic scoring system (IPSS).
Methods
A total of 100 cases with de novo MDS were reviewed and their karyotypes were detected. All of them were followed up and classified according to IPSS and WPSS risk groups. SPSS 13.0 software was applied to deal with all the data. The statistical methods included Kaplan — Meier, Log-rank test and cox regression.
Results
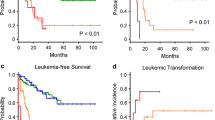
Multivariate cox regression analysis indicated that WHO Classification (P=0.0190), karyotype abnormalities categorized according to IPSS (P=0.0159) and red blood cell (RBC) transfusion (P=0.0009) were the three most important independent factors for predicting overall survival (OS) of MDS. WPSS and IPSS both had great capacity in predicting the OS of MDS at the time of diagnosis (P<0.0001). In time-dependent analysis, WPSS can predict the OS accurately in the following three years after diagnosis (P<0.0001), while IPSS failed to predict the OS 24 months after diagnosis (P=0.1094).
Conclusion
Our single center results proved that WPSS is a dynamic prognostic system which can predict the OS of MDS patients at any time during the course of their disease. This time-dependent prognostic scoring system may replace the IPSS in the near future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cazzola M, Malcovati L. Myelodysplastic syndromes—Coping with ineffective hematopoiesis [J]. N Engl J Med 2005;352:536–538.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes [J]. Blood 1997;89:2079–2088.
Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms [J]. Blood 2002;100: 2292–2302.
Howe RB, Porwit-MacDonald A, Wanat R, et al. The WHO classification of MDS does make a difference [J]. Blood 2004;103:3265–3270.
Breccia M, Carmosino I, Biondo F, et al. Usefulness and prognostic impact on survival of WHO reclassification in FAB low risk myelodyplastic syndromes [J]. Leuk Res 2006;30:178–182.
Malcovati L, Porta MG, Pascutto C, et al. Prognostic factors and life expectancy in myelodysplastic syndromes classified according to WHO criteria: a basis for clinical decision making [J]. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:7594–7603.
Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, et al. Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes [J]. J Clin Oncol 2007;25:3503–3510.
Müller-Berndorff H, Haas PS, Kunzmann R, et al. Comparison of five prognostic scoring systems, the French-American-British (FAB) and World Health Organization (WHO) classifications in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: Results of a single-center analysis [J]. Ann Hematol 2006;85:502–513.
Navarro I, Ruiz MA, Cabello A, et al. Classification and scoring systems in myelodysplastic syndromes: a retrospective analysis of 311 patients [J]. Leuk Res 2006;30:971–977.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes [J]. Br J Haematol 1982;51:189–199.
ISCN. An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. In: Mitelman F, ed. Guidelines for Cancer Cytogenetics [M]. New York: Karger. 1995;1–114.
Haus O, Kotlarek-Haus S, Potoczek S, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes according to FAB and WHO classification. Single center experience [J]. Neoplasma 2006;53:136–143.
Bernasconi P, Klersy C, Boni M, et al. Incidence and prognostic significance of karyotype abnormalities in de novo primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a study on 331 patients from a single institution [J]. Leukemia 2005;19:1424–131.
Haase D, Germing U, Schanz J, et al. New insights into the prognostic impact of the karyotype in MDS and correlation with subtypes: evidence from a core dataset of 2124 patients [J]. Blood 2007;110:4385–4395.
Demirkan F, Alacacioglu I, Piskin O, et al. The clinical, haematological and morphological profile of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: a single institution experience from Turkey [J]. Leuk Lymphoma 2007;48:1372–1378.
Cazzola M, Malcovati L. Myelodysplastic syndromes—coping with ineffective hematopoiesis [J]. N Engl J Med 2005;352:536–538.
Wells DA, Benesch M, Loken MR, et al. Myeloid and monocytic dyspoiesis as determined by flow cytometric scoring in myelodysplastic syndrome correlates with the IPSS and with outcome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Blood 2003;102:394–403.
Pirruccello SJ, Young KH, Aoun P. Myeloblast phenotypic changes in myelodysplasia. CD34 and CD117 expression abnormalities are common [J]. Am J Clin Pathol 2006; 125:884–894.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Zhou, Xf., Zhou, Jf. et al. Analysis of WHO-based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS) of myelody-splastic syndrome and its comparison with international prognostic scoring system (IPSS) in 100 Chinese patients. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 21, 50–55 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-009-0050-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-009-0050-7