Abstract
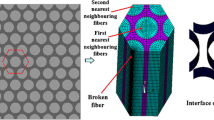
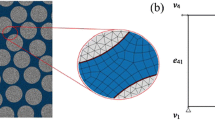
This paper studies the micromechanical progressive failure properties of glass fiber/phenolic resin composites by finite element analysis and experiments. First, a set of theoretical methods on the failure criteria and damage evolution of fiber, matrix, and interface are introduced, which include Monte Carlo simulation on random fiber fracture, damage evolution and stiffness degradation of matrix based on thermodynamic theory, an exponential cohesive model for interface debonding, and a strain localization-based Mori–Tanaka homogenization method. Second, the proposed model is implemented using ANSYS PARAMETRIC DESIGN LANGUAGE (ANSYS-APDL) that uses the restart numerical technique. In order to predict the tensile strength of the composites, the numerical convergence issue is solved by introducing viscous effect into the stiffness equations. Finally, numerical results in terms of the damage evolution behaviors and tensile strengths of composite microstructures are validated by tensile experiments and acoustic emission tests on unidirectional glass fiber/phenolic composites.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Dharmawan, G. Simpson, I. Herszberg, S. John, Mixed mode fracture toughness of GFRP composites. Compos. Struct. 75, 328–338 (2006)
P.F. Liu, J.K. Chu, S.J. Hou, J.Y. Zheng, Micromechanical damage modeling and multiscale progressive failure analysis of composite pressure vessel. Comput. Mater. Sci. 60, 137–148 (2012)
P.F. Liu, J.Y. Zheng, Progressive failure analysis of carbon fiber/epoxy composite laminates using continuum damage mechanics. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 485(1–2), 711–717 (2008)
P.F. Liu, Z.P. Gu, Y.H. Yang, X.Q. Peng, A nonlocal finite element model for progressive failure analysis of composite laminates. Compos. Part B Eng. 86, 178–196 (2016)
P.F. Liu, J.K. Chu, Y.L. Liu, J.Y. Zheng, A study on the failure mechanisms of carbon fiber/epoxy composite laminates using acoustic emission. Mater. Des. 37, 228–235 (2012)
P.F. Liu, J. Yang, B. Wang, Z.F. Zhou, J.Y. Zheng, A study on the intralaminar damage and interlaminar delamination of carbon fiber composite laminates under three-point bending using acoustic emission. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 15(1), 101–121 (2015)
X.K. Li, P.F. Liu, Delamination analysis of carbon fiber composites under dynamic loads using acoustic emission. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 16, 142–153 (2016)
L.P. Canal, J. Segurado, J. LLorca, Failure surface of epoxy-modified fiber-reinforced composites under transverse tension and out-of-plane shear. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46(11-12), 2265–2274 (2009)
E. Totry, C. González, J. LLorca, Influence of the loading path on the strength of fiber-reinforced composites subjected to transverse compression and shear. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45(6), 1663–1675 (2008)
T.J. Vaughan, C.T. McCarthy, Micromechanical modelling of the transverse damage behaviour in fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71(3), 388–396 (2011)
J. Andersonsa, R. Joffeb, M. Hojoc, S. Ochiaic, Glass fibre strength distribution determined by common experimental methods. Compos. Sci. Technol. 62, 131–145 (2002)
S.K. Ha, K.K. Jin, Y. Huang, Micro-mechanics of failure MMF for continuous fiber reinforced composites. J. Compos. Mater. 42, 1873–1895 (2008)
X.P. Xu, A. Needleman, Numerical simulations of fast crack growth in brittle solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 42(9), 1397–1434 (1994)
J.D. Eshelby, The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion and related problems. Proc. R. Soc. A 241, 376–396 (1957)
R. Hill, A self-consistent mechanics of composite materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 13, 213–222 (1965)
T. Mori, K. Tanaka, Average stress in the matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions. Acta Metall. 21, 571–574 (1973)
Acknowledgments
Dr. P.F. Liu would sincerely like to thank the support by the National Key Fundamental Research and Development Project of China (No. 2015CB057603), the National Natural Science Funding of China (No. 51375435), and Aerospace Science and Technology Innovation Funding (No. GFJG-112108-E81504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P.F., Li, X.K. & Pang, J.C. Finite Element Analysis of Micromechanical Progressive Failure Properties of Glass Fiber/Phenolic Resin Composites by Monte Carlo Simulation. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 16, 1108–1120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0192-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0192-0