Abstract
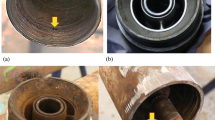
In an onshore oil field, many premature tubing failures were observed in wells operating on sucker rod pump. Failures were in the form of longitudinal crack/vertical slit. During last three to four years, the failure frequency had increased and in one well, new tubing vertically cracked in 8 months only. In the internal surface of the tubing, a longitudinal grooving was observed. The shape of the groove resembled the sucker rod and the crack was along the groove. Observation of grooved region under SEM revealed abrasion features typical of mechanical wear. Small corrosion pits were also observed on some portion of grooved region. As the well was vertical, so chance of contact between tubing and sucker rod was low. But tubing was freely suspended in the well, i.e., there was no tubing anchor which made it vulnerable for the buckling. Analytical studies showed that the failed tubing was in buckling region. On comparison of hardness, it was observed that tubing material was softer than the sucker rod. Buckling of the tubing resulted in rubbing of sucker rod against tubing wall due to which tubing had worn out in the form of groove. Wear-oxidation and oxidation-wear of tubing surface at grooved region and corrosive agents of produced water accelerated this material removal process and when the wall thickness of the tubing at groove region reduced to a point where it was not enough to withstand the hoop stresses, a longitudinal crack formed in the grooved region and tubing failed.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Specification for Casing and Tubing, 5CT, API, Specification (2012)
Standard hardness conversion tables for metals relationship among Brinell hardness, Vickers hardness, Rockwell hardness, Superficial hardness, Knoop hardness, Scleroscope hardness, and Leeb hardness, E140-12b, ASTM International Designation (2013)
A. Lubinski, K.A. Blenkarn, Buckling of tubing in pumping wells, its effects and means for controlling it. SPE 210(672-G), 73–88 (1957)
M.G. Fontana, Corrosion Engineering, 3rd edn. (McGraw Hill Inc., New York, 1986), pp. 105–107
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the ONGC management for providing the necessary infrastructure for carrying out the analysis and its gracious approval for publication of this paper. The views expressed here are of authors not necessarily ONGC management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, J., Kujur, A., Prasad, S.R. et al. Analysis of Frequent Failure of Oil Well Tubings Due to Formation of Longitudinal Slit. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 16, 518–526 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0120-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0120-3