Abstract
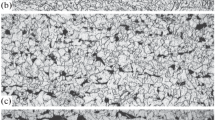
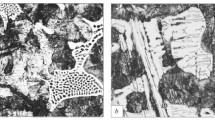
Large motors, such as those that propel ships or generate energy for thermoelectrical plants, for instance, use cylinder heads produced with nodular cast iron. Such components are manufactured by a casting process which must be strictly controlled to prevent the appearance of defects that may spoil the performance of the component in service. When these defects arise, they usually lead to the failure of the cylinder head, mainly causing fluids leakage that can harm or even impede the motor performance. In this study, the microstructure of the material was characterized, with the purpose of investigating the possible causes of the failure, through the use of techniques such as optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Brinell hardness tests were also performed. The results revealed that inadequate casting procedures probably caused the defects and subsequent failure of the cylinder head.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Woodyard, Pounders Marine Diesel, 9th edn. (Elsevier, Burlington, 2009), 896 p
ASM Handbook. Properties and Selection: Irons. Steels and High-Performance Alloys, vol. 1 (ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1990), 6th Printing 2001
R. Elliott, Cast Iron Technology (Butterworth-Heinemann, London, 1988), p. 240
V. Kondic. Metallurgical Principles of Founding (Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd., London, 1968), 286p
P.R. Beeley, Foundry Technology (Butterworths, London, 1972), p. 544
L. Zhang, Inclusion and bubble in steel—a review. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 13(3), 1–8 (2006)
R. Wouters, L. Froyen, Scanning electron microscope fractography in failure analysis of steels. Mater. Charact. 36, 357–364 (1996)
ASM Handbook. Failure Analysis and Prevention, vol. 11 (ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2004), 1164 p
SAE J434 Standard, Automotive Ductile (Nodular) Iron Castings, 2004
ASTM E3, Standard Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens, 2011
ASTM E407, Standard Practice for Microetching Metals and Alloys, 2007
ISO 6506-1 Standard, Metallic Materials—Brinell Hardness Test —Part 1: Test Method, 2005
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Rafael de Abreu Vinhosa for sample preparation, Ricardo Silva Tavares Mello for helpful information about motor mechanics, and CENANO/INT for SEM images. CNPq (Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development) and FAPERJ (Research Funding Agency of Rio de Janeiro) must be acknowledged for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbosa, C., de Cerqueira Abud, I., Barros, T.S. et al. Microstructural Analysis of the Failure of a Cast Iron Cylinder Head of a Thermoelectrical Plant Motor. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 15, 424–429 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-9954-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-9954-3