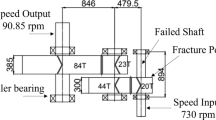
Abstract
This paper presents the experimental process and findings of a forensic investigation of a failed fertilizer plant conveyor belt head roller shaft. A 25-year service life was expected but failure occurred following only 10 years. A gearbox which provided direct power to the roller had been replaced only several weeks earlier. The primary aim for the plant owner was to determine if the gearbox replacement had caused failure of the shaft, or, if the two incidents were unrelated. If incorrect installment of the gearbox had caused failure, liability would fall on the gearbox suppliers in terms of mitigation. However, it was revealed that the shaft had failed due to low-stress rotating bending fatigue, over an extended period of time. A premeditated change of material selection at the manufacturing stage, substituting carbon steel for 304L stainless steel, resulted in reduced corrosion resistance. Fertilizer ingredients tend to pose limited problems in their dry form in terms of corrosion; in the presence of moisture, however, can change the ingredients into aggressive corrosion species. Thus, corrosion allowed multiple fatigue cracks initiated from corrosion pitting under rotating bending load. The cracks then eventually joined together to form a single fatigue crack which propagated through the cross section.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Bhaskaran et al., Cost of corrosion in fertilizer industry—a case study. Mater. Corros. 55(11), 865–871 (2004)
British Standards Institution, BS 2901-2:1990: Filler Rods and Wires For Gas-Shielded Arc Welding. Specification for Stainless Steels (BSI, London, 1990)
ASM Metals Handbook, Failure Analysis and Prevention, vol. 11, 6th edn. (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, 1996), p. 459
Corrosion control of agricultural equipment and buildings. National Corrosion Service. National Physical Laboratory NPL (2014)
J.R. Davis, Corrosion of Weldments, Chapter 2: Corrosion of Carbon Steel and Low-Alloy Steel Weldments (ASM International, Materials Park, 2006)
British Steel, Iron and Steel Specifications, 7th edn. (British Steel Plc, London, 1989)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roffey, P. Corrosion-Initiated Rotating Bending Fatigue Failure of a Fertilizer Conveyor Belt Head Roller. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 15, 190–199 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-9930-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-9930-y