Abstract
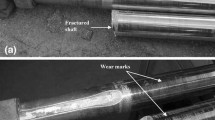
Screw-thread steel bars made of high strength steel fractured after exposure to a constant pre-stress of 650 MPa for more than 10 h. Visual examination, chemical analysis, mechanical tests, metallographic analysis, and fractographic examination were carried out in order to determine the causes of this failure. The fracture surfaces consisted of three regions: the crack source or fracture origin region, steady-state crack growth, and unstable or final fracture region. The crack initiated at the center of the cross section and then propagated to the periphery. The fracture exhibited a brittle appearance, accompanied with secondary cracks, tear ridges, and micropores on the grain boundary. The results revealed that this failure was due to hydrogen embrittlement of the steel.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.Y. Lin, N.H. Burns, Design of Prestressed Concrete Structures (Wiley, New York, 1981)
S. Das, J. Mathur, T. Bhattacharyya, S. Bhattacharyya, Failure analysis of re-bars during bending operations. Case Stud. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2, 51–53 (2014)
X. Li, Y. Wang, P. Zhang, B. Li, X. Song, J. Chen, Effect of pre-strain on hydrogen embrittlement of high strength steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 616, 116–122 (2014)
X.-L. Xu, Z.-W. Yu, H. Yu, Hydrogen embrittlement failure of a galvanized washer. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 14, 197–202 (2014)
J. Ovejero-García, Hydrogen microprint technique in the study of hydrogen in steels. J. Mater. Sci. 20, 2623–2629 (1985)
G. Wang, Y. Yan, J. Li, J. Huang, L. Qiao, A.A. Volinsky, Microstructure effect on hydrogen-induced cracking in TM210 maraging steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 586, 142–148 (2013)
C. Borchers, T. Michler, A. Pundt, Effect of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of stainless steels. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 11–23 (2008)
J. Woodtli, R. Kieselbach, Damage due to hydrogen embrittlement and stress corrosion cracking. Eng. Fail. Anal. 7, 427–450 (2000)
K. Horikawa, N. Ando, H. Kobayashi, W. Urushihara, Visualization of hydrogen gas evolution during deformation and fracture in SCM 440 steel with different tempering conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 534, 495–503 (2012)
Z.Y. Liu, X.G. Li, C.W. Du, L. Lu, Y.R. Zhang, Y.F. Cheng, Effect of inclusions on initiation of stress corrosion cracks in X70 pipeline steel in an acidic soil environment. Corros. Sci. 51, 895–900 (2009)
T.Y. Jin, Z.Y. Liu, Y.F. Cheng, Effect of non-metallic inclusions on hydrogen-induced cracking of API5L X100 steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35, 8014–8021 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhang, J., Zhang, P. et al. Failure Analysis of High Strength Steel Bar Used in a Wind Turbine Foundation. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 15, 295–299 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-9929-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-9929-4