Abstract
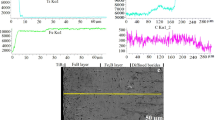
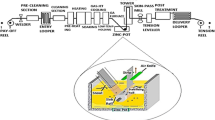
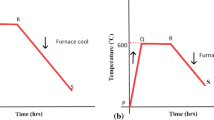
A hot-dip galvanized steel fastener on an electromagnetic product was found to be seriously corroded after 16 years of storage in a room environment. Its surface had become rough and lost its metallic luster, and large amounts of corrosion products had accumulated on the surface, with color ranging from light yellow to red brown. To determine the corrosion mechanism, the manufacturing process and storage information of the fastener were first investigated. Pieces of the corroded fastener were sampled; at the same time, the same kind of steel before and after galvanization was prepared as two control samples. The micromorphology and composition of the surface and corrosion were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray energy-dispersive spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Based on these analyses, as well as the manufacturing process and storage information, the corrosion mechanism was identified to be that zinc plating first reacted with oxygen, water vapor, and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to form Zn(OH)2, ZnCO3, and Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6. Subsequently, the iron under the zinc plating reacted with oxygen and water vapor to form Fe(OH)2, Fe(OH)3 or Fe2O3.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
GB/T 699-1999, Quality carbon structural steels, Chinese Standard
A.A. Shoushtari, K. Ranjbar, S.M. Mousavi, D.A. Yancheshmeh, Study on failure analyses and material characterizations of a damaged booster pump. J. Fail. Anal. Prevent. 13(4), 489–495 (2013)
V.F.C. Lins, R.M.V. Paranhos, E.A. Alvarenga, Behavior of the electrogalvanized and painted carbon steel and low Cu and Cr carbon steel during cyclic and field corrosion tests. J. Mater. Sci. 42(13), 5094–5104 (2007)
H.X. Chen, C.Q. An, J.J. Hao, X.Y. Yu, L. Yuan, G.D. Li, Research on influences of hot-dipped galvanized steel process on corrosion resistance. Surf. Tech. 33(6), 48–49 (2004). (In chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Wang, Y., Zhang, S. et al. Corrosion Failure Analysis of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel in a Room Environment. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 15, 868–872 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-0028-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-015-0028-3