Abstract
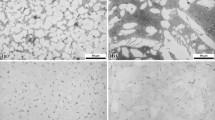
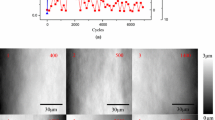
This paper presents an experimental investigation of the tribological behavior of four brass alloys’ synthesis by forging (Mm), free-cutting (Md), gravitational casting (Mc), and casting under pressure (Mi). The experiments were conducted on a pin-on-disk tribometer with a load of 200 N, sliding speed of 2.5 m/s, and a sliding distance of 500 m. The microstructure and the worn surfaces were examined with an optical and scanning electron microscope. The results obtained show that the Mc material has less wear resistance related to the presence of voids and an abrasive wear mechanism and the Md material has a stabilized friction coefficient which is related to the uniform distribution of the various phases in the microstructure and the presence of a thick layer of metal transfer on the counter material.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Mindivan, H. Çimenoğlu, E.S. Kayali, Microstructures and wear properties of brass synchroniser rings. Wear 254, 532–537 (2003)
E. Feyzullahoğlu, A. Zeren, M. Zeren, Tribological behaviour of tin-based materials and brass in oil lubricated conditions. Mater. Des. 29(3), 714–720 (2008)
C.N. Panagopoulos, E.P. Georgiou, K. Simeonidis, Lubricated wear behavior of leaded α + β brass. Tribol. Int. 50, 1–5 (2012)
J.P. Davim, An experimental study of tribological behaviour of brass/steel pair. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 100, 273–277 (2000)
M. Amira, H. Zaidia, A. Djamaia, D. Neciba, D. Eyidib, Influence of the gas environment on the transferred film of the brass (Cu64Zn36)/steel AISI 1045 couple. Wear 267, 433–440 (2009)
M.F. Buchely, J.C. Gutierrez, L.M. Leon, A. Toro, The effect of microstructure on abrasive wear of hardfacing alloys. Wear 259, 52–61 (2005)
K. Elleuch, R. Elleuch, R. Mnif, V. Fridrici, P. Kapsa, Sliding wear transition for the CW614 brass alloy. Tribol. Int. 39, 290–296 (2006)
Mnif, R., Elleuch, K., Elleuch, R., Fridrici, V., Kapsa, P.: Thermal effect on wear behaviour of copper alloys. In: Second International Conference ICAMEM, Hammamet (2004)
T.A. Stolarski, Tribology in Machine Design (Butterworth/Heinemann, Oxford, 2000)
A.B. Aghdam, M.M. Khonsari, On the correlation between wear and entropy in dry sliding contact. Wear 270(11–12), 781–790 (2011)
W.X. Qi, J.P. Tu, F. Liu, Y.Z. Yang, N.Y. Wang, H.M. Lu, X.B. Zhang, S.Y. Guo, M. Liu, Microstructure and tribological behaviour of a peak aged Cu–Cr–Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A343, 89–96 (2003)
A. Williams John, Wear and wear particles—some fundamentals. Tribol. Int. 38, 863–870 (2005)
S. Kalpakjian, S.R. Schmid, Manufacturing Processes for Engineering Materials, 4th edn. (Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, 2003), p. 197
F.A. Sadykov, N.P. Barykin, I.R. Aslanyan, Wear of copper and its alloys with submicrocrystalline structure. Wear 225–229, 649–655 (1999)
J.P. Tu, L. Meng, M.S. Liu, Friction and wear behavior of CuFe3Al powder metallurgical composites in dry sliding. Wear 220, 72–79 (1998)
Acknowledgments
The authors duly acknowledge the support and contribution of the SOPAL Society employees and thank them for their cooperation and assistance in the preparation of samples for laboratory analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouzayeni, N., Kchaou, M., Elleuch, R. et al. Comparative Study of the Tribological Behavior of Brass Alloys Produced by Different Manufacturing Processes. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 13, 584–594 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-013-9713-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-013-9713-2