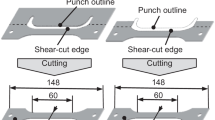
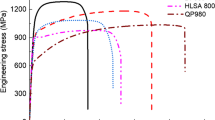
Abstract
The cut-edge condition has an important influence on the formability capacity of high-strength steel (HSS) automotive structures. XF350 and DP600 under examination were observed to display a decreased level of formability in the surface regions because mechanical punched edge hole-flanging capacity is dependent on ductility and the surface quality of the cut-edge produced. Formability was observed to be highly dependent not purely based on the properties of the steel but also the cut-edge properties. Hole expansion capacity (HEC)-forming experiments were performed on flat circular plates with mechanical and laser-cut holes to investigate the fracture and forming limits of HSS. The HEC properties of the cut-edges were determined using mechanical and laser-cutting processes using various cutting process parameters in which certain edge types displayed decreases in edge ductility. It was found that, by altering the processing parameters during the cutting process, the edge quality can be improved, and this has a positive effect on the formability capacity of steel components.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Elongation to failure
- AHSS:
-
Advanced high-strength steel
- HEC:
-
Hole expansion capacity
- HSLA:
-
High-strength low alloy
- HSS:
-
High-strength steel
- R a :
-
Arithmetic mean of departures from the mean line
- R p :
-
Maximum height of profile above the mean line
- R v :
-
Maximum depth of profile below the mean line
- wt:
-
Weight
References
Johnson, W., Mamalis, A.G.: The perforation of circular plates with four-sided pyramidally headed square-section punches. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 20, 849–866 (1978)
Wang, N.M., Wenner, M.L.: An analytical and experimental study of stretch flanging. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 16, 135–143 (1974)
Kumagai, T., Saiki, H.: Deformation analysis of hole flanging with ironing of thick sheet metals. Met. Mater. 4(4), 711–714 (1999)
Cho, Y.R., Chung, J.H., Ku, H.H., Kim, I.B.: Effect of controlled cooling on the formability of TS 590 MPa grade hot-rolled high strength steels. Met. Mater. 5(6), 571–578 (1999)
Chitkara, N.R., Johnson, W.: Hole flanging and piercing of circular plate. Sheet Met. Ind. 51, 635–640 (1974)
Strijbos, G.H., Boesenkool, R.: Hole expansion in hot rolled steels. In: Proceedings of the 19th IDDRG Biennial Congress, Eger, 10–14 June 1996, pp. 459–466
Asnafi, N.: On stretch and shrink flanging of sheet aluminium by fluid forming. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 96, 198–214 (1999)
Cho, Y.R., Chung, J.H., Ku, H.H., Kim, I.B.: A study on the stretch flangeability of hot-rolled high strength steel with ferrite–bainite duplex microstructures. Korean J. Mater. Res. 9(12), 1252–1262 (1999)
S. Keeler, Cutting sheet metal reduces edge formability. The Science of Forming Magazine, March (1999)
Stoughton, T.B.: A general forming limit criterion for sheet metal forming. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 42(1), 1–27 (2000)
Carlsson, B., Larsson, J., Nilsson, T.: Dual phase steels for auto body design forming and welding aspects, pp. 1–14. SSAB Tunnplat AB, Borlange (1984)
Auto Steel Partnership Auto Steel Partnership http://www.asp.org/database/custom/hss_stampingDesignManual.pdf (2000). Accessed 16 May 2010
Sudo, M., Hashimoto, S., Kambe, S.: Niobium bearing ferrite–bainite high strength hot-rolled sheet steel with improved formability. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 23, 303–311 (1983)
Cho, Y.R., Chung, J.H., Ku, H.H., Kim, I.B.: Effect of controlled cooling on the formability of TS 590 MPa grade hot-rolled high strength steels. Met. Mater. Korea 5, 571–578 (1999)
Nagasaka, A., Sugimoto, K., Kobayashi, M., Shirasawa, H.: Effects of second phase morphology on warm stretch-flangeability of TRIPaided dual-phase sheet steels. Tetsu Hagane 84, 218–223 (1998)
Jiang, Z.H., Guan, Z.Z., Lian, J.S.: The relationship between ductility and material parameters for dual-phase steel. J. Mater. Sci. 28(7), 1814–1818 (1993)
Jiang, Z., Lian, J., Chen, J.: Strain-hardening behaviour and its relationship to tensile mechanical properties of dual phase steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 8(12), 1075–1081 (1992)
Sugimoto, K., Sakaguchi, J., Iida, T., Kashima, T.: Stretch-flangeability of a high-strength TRIP type bainitic sheet steel. ISIJ Int. 40, 920–926 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The present research was funded by a grant from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC). The author wishes to acknowledge the support by Swansea University College of Engineering and The Engineering Centre for Manufacturing and Materials during the course of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, D.J. Understanding the Effects of Mechanical and Laser Cut-Edges to Prevent Formability Ruptures During Automotive Manufacturing. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 13, 451–462 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-013-9696-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-013-9696-z