Abstract
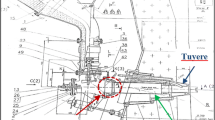
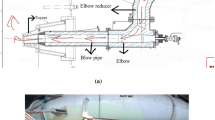
Bulging of a blow pipe of a blast furnace in service has been investigated. The blow pipe connects the bustle main to the furnace tuyeres. Hot blast at a temperature of 1,225 °C flows through the blow pipes to the tuyeres. The investigation consisted of visual inspection, chemical analysis, characterization of microstructures by optical and scanning electron microscopes, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), hardness measurement, and mechanical testing (tensile and impact tests). Visual inspection revealed that the refractory lining at the inner portion of the blow pipe cracked during service. The blow pipe bulged just above the location where the refractory lining cracked. The chemical composition of blow pipe was found to be as per specification P265 GH (EN-10028) which is a non-resulfurized carbon steel. Microstructural examination and EDS analysis showed voids formation, scale formation, grain boundary oxidation, decarburization, and grain coarsening at the inner surface of the blow pipe shell indicating overheating of the component. Formation of voids at the grain boundaries as revealed by the microstructure suggests initiation of creep. The hardness measurements and mechanical tests showed lowering of hardness and strength of the component at the bulged out portion. Analyses of the results suggest that due to the cracking of the refractory lining at the inner portion of the blow pipe, the component was exposed to high temperatures and ultimately bulged out due to creep.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
IS 228: Part 20: Methods for Chemical Analysis of Steels—Part 20: Determination of Carbon and Sulphur by Infra Red Absorption Method. Bureau of Indian Standard, New Delhi (2003)
ASM International: Worldwide Guide to Equivalent Irons and Steels, 4th edn, pp. 4–166. ASM International, Materials Park
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM E8M-03
Indian Standard Method for Charpy Impact Test (V-Notch) on Metallic Material. IS 1757-1988
Al-Hajer, K.F.: The grain coarsening and subsequent transformation of austenite in the HSLA steel during high temperature thermomechanical processing. Ph.D thesis, University of Pittsburgh (2005).http://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/6884/1/KFHPDF3.pdf
ASME Handbook, vol. 4, p. 651
ASM Metals Handbook, vol. 11, p. 506
Chen, J., Young, B., Uy, B.: Behavior of high strength structural steel at elevated temperatures. J. Struct. Eng. 132, 1948-1954 (2006)
Ng, G.P., Norlia, B.: Failure analysis of power utility boiler tubes. In: CEPSI Conference, Taipei (2010)
French, D.N.: Creep and Creep Failures. David N. French, Inc., Northborough, MA (1991). http://www.nationalboard.org/Index.aspx?pageID=181
Lonsdale, D., Flewitt, P.E.J.: Damage accumulation and microstructural changes occurring during the creep of a 21/4%Cr1%Mo steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 39, 217–229 (1979)
Ashby, M.F., Dyson, B.F.: Creep damage mechanics and micromechanisms. In: Valluri, S.R., et al. (eds.) Advances in Fracture Research, vol. 1, p. 3. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1984)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, P., Mukhopadhyay, G. & Bhattacharyya, S. Investigation on Bulging of Blow Pipe in a Blast Furnace. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 13, 257–263 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-013-9666-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-013-9666-5