Abstract
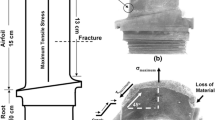
Damage to varying degrees including fracture, cracking, and scraping occurred on inducer blades used in a locomotive turbocharger which had run for 3626 km. The blade fracture was formed by the propagation of axial and radial cracks forming an L-shape. Fractography investigation indicates that the axial fracture mode of the blade was by fatigue. The radial fracture was formed by one instantaneous crack. A strike dent was present on the leading edge of the fractured blade and this dent became the initiation site of fatigue crack. Failure of other blades was subsequent to the original fracture.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Metal Handbook. Fractography and Atlas of Fractographs, 8th edn., vol. 9. American Society for Metals, Metal Park, OH (1974)
Park, M. Hwang, Y.-H., Choi, Y.-S., Kim, T.-G.: Analysis of a J69-T-25 engine turbine blade fracture. Eng. Fail. Anal. 9, 539–601 (2002)
Kushan, M.C., Diltemiz, S.F., Sackesen, I.: Failure analysis of an aircraft propeller. Eng. Fail. Anal. 14(8), 1693–1700 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Zw., Xu, Xl. Failure Investigation on Inducer Blades of Locomotive Turbocharger. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 10, 56–59 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-009-9308-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-009-9308-0