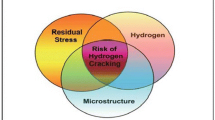
Abstract
Cadmium-plated 0.35C–3.5Ni–1.5Cr–0.5Mo steel threaded fasteners of 1230 MPa properties class are used for aerospace applications. These fasteners were torqued to 13 N·m. Few fasteners parted into two pieces while in use under sustained assembly load for a period of 50 days. The fracture surface of the failed fasteners had two distinct regions when viewed under microscope at higher magnification. Fractography revealed that the larger region consisted of predominantly intergranular features, whereas the smaller region had features of microvoid coalescence. From the metallography evidences it was concluded that the fastener failure was due to hydrogen embrittlement. Electro-deposit of cadmium was identified to be the main source for hydrogen entrapment, which could not be compelled completely by post-plating baking treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter, T.J., Cornish, L.A.: Hydrogen in metals. Eng. Fail. Anal. 8, 113–121 (2001)
ASTM International, B 850-90 (reapproved 2004) standard guide for post-coating treatment of steel for reducing risk of hydrogen embrittlement
Eliaz, N., Shachar, A., Tal, B., Eliezer, D.: Characteristics of hydrogen embrittlement, stress corrosion cracking and tempered martensite embrittlement in high-strength steels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 9, 167–184 (2002)
Troiano, A.R.: The role of hydrogen and other interstitials in the mechanical behaviors of metals, 1959 Edward De Mille Campbell Memorial Lecture, Trans ASM, vol. 52, pp. 54–80 (1960)
Oriani, R.A.: The diffusion and trapping of hydrogen in steel. Acta Metall. 18, 147–157 (1970)
Gerberich, W.W., Marsh, P.G., Hoehn, J.W.: Hydrogen induced cracking mechanism—Are there critical experiments? Hydrogen Effects Mater. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 539–551 (1996)
Olden, V., Thaulow, C., Johnson, R.: Modelling of hydrogen diffusion and hydrogen induced cracking in supermartensitic and duplex stainless steels. Mater. Des. 29, 1934–1948 (2008)
Villalba, E., Atrens, A.: Hydrogen embrittlement and rock bolt stress corrosion cracking. Eng. Fail. Anal. 16, 164–175 (2009)
Wang, M., Akiyama, A., Tsuzaki, K.: Hydrogen degradation of a boron-bearing steel with 1050 and 1300 MPa strength levels. Scr. Mater. 52(5), 403–408 (2005)
Wang, M., Akiyama, E., Tsuzaki, K.: Effect of hydrogen on the fracture behavior of high strength steel during slow strain rate test. Corros. Sci. 49(11), 4081–4097 (2007)
Marcelo, A.L., Tokimatsu, R.C., Ferreira, I.: Hydrogen embrittlement in a AISI 1045 steel component of the sugarcane industry. Eng. Fail. Anal. 16, 468–474 (2009)
Beachem, C.D.: New model for hydrogen-assisted cracking (hydrogen embrittlement). Metall. Trans. 3, 437–451 (1972)
Birnbaun, H.K., Sofronis, P.: Hydrogen enhanced localized plasticity—a mechanism for hydrogen related fracture. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 176, 191–202 (1994)
Lynch, S.P.: Scr. Mater. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.02.031
Woodtli, J., Kieselbach, R.: Damage due to hydrogen embrittlement and stress corrosion cracking. Eng. Fail. Anal. 7, 427–450 (2000)
Jha, A.K., Narayanan, P.R., Sreekumar, K., Mittal, M.C., Ninan, K.N.: Hydrogen embrittlement of 3.5Ni–1.5Cr–0.5Mo steel fastener. Eng. Fail. Anal. 15, 431–439 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. P.P. Sinha, Deputy Director, VSSC (MME), for his technical support during the investigation. They are indebted to Dr. K. Radakrishnanan, Director, VSSC, for permission to publish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, A.K., Sreekumar, K. Hydrogen-Induced Cracking (HIC) of Hardened and Tempered Steel Fastener Used in Space Application. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 9, 420–428 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-009-9277-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-009-9277-3