Abstract
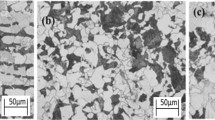
A significant quantity of cold-reducible hot-rolled (HR) coils is produced every year. These are basically low-carbon steels; however, the quality of HR coils with respect to cold reducibility had not been entirely satisfactory. The hardness of HR coil was generally higher (≥65 HRB) than desirable for attaining satisfactory cold reducibility. A systematic study was, therefore, undertaken with the objective to control the hardness to ≤55 HRB by modifying the existing chemistry, finish rolling temperature (FRT), and the coiling temperature (CT). To find the optimum conditions for lower hardness, trial rolling of slabs of cold reducers’ grade of selected chemistry was conducted under varied conditions. An assessment of hardness across the width and of the microstructure was carried out. The evolution of microstructure in the HR band at different locations from the edge of the strip and the genesis for the resulting hardness profile across the width of the HR coil were examined in detail. The influence of grain size on hardness was also analyzed. The paper outlines the role of finish rolling temperature, coiling temperature, chemistry, and grain size in restricting the hardness to values below 55 HRB.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, S., Prasad, S.N., Shukla, S.K., Chaudhuri, S.K., Jha, S.: Control of hardness in HR coils of WTCR grade at Bokaro Steel Plant. Steel India. 25, 28 (2002)
Kang, K.B., Lee, H.B., Lee, J.K., Lee, M.J., Lee, P.J.: Edge masking technology for transverse mechanical properties of hot rolled steel strips, 39th MWSP Conf. Proc., vol. XXXV, ISS, Indianapolis, IN, 679 (1998)
Lee, J.K., Kang, K.B., Lee, K.J., Lee, P.J., Lee, J.D.: Modelling of the microstructure and the mechanical property variation across the transverse direction of hot rolled steels and the effect of edge shielding. ISIJ Int. 38, 752 (1998)
Schickl, A., Yu, D., Killmore, C., Langley, D., Chandra, T.: Prediction of ferrite grain size after warm deformation of low carbon steel. ISIJ Int. 36, 1279 (1996)
Zurek, A.K., Majta, J., Pietrzyk, M.: Modelling of the effects of deformation in the two phase region of C-Mn and microalloyed steels, 39th MWSP Conf. Proc., vol. XXXV, ISS, Indianapolis, IN, 577 (1998)
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the managements of RDCIS and BSL for providing the opportunity to study in details the genesis of hardness in hot-rolled coils of cold reducers’ grade and permission to publish the paper. We are deeply indebted to Sri I.N.P. Gupta and Sri A.P. Singh for providing support of the thermovision camera. We are thankful to Mr. S.K. Shukla for his help toward trials and collection of samples. Our special thanks go to Sri A.K. Singh, HSM, BSL, Bokaro for his active support during the trials. Fruitful technical discussions with Dr. C.D. Singh, Dr. S.K. Sen, and Dr. V. Kumar are acknowledged with pleasure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Prasad, S.N., Deva, A. et al. Genesis of High Hardness in Hot-Rolled Coils of Cold Reducers’ Grade Steels. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 7, 456–463 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-007-9079-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-007-9079-4