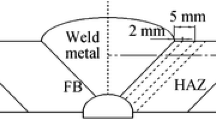
In this study, the microstructural features of 7A52 heat-treatable aluminum alloys welded by variable polarity plasma arc (VPPA) combined with gas metal arc welding (GMAW) (VPPA–GMAW) were investigated and compared with those of 7A52 aluminum alloys welded by GMAW. The grain structures and modification of the precipitates were analyzed by optical microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Complementary to modification of the precipitates, the precipitation evolution in the heat-affected zone and magnesium loss in the fusion zone were measured by differential scanning calorimetry and inductively coupled plasma spectroscopy. In VPPA–GMAW, the weld only needs one pass by depositing on one side of the 10-mm-thick aluminum alloy plates because of the large penetration capability of VPPA and good fluidity of the molten metal in the weld pool. Accordingly, the effect of excessive heat input on the microstructure can be minimized. The results show that the grain growth is not obvious and the magnesium loss is small in the fusion zone of VPPA–GMAW compared with that of GMAW under the condition of equal heat input to the workpiece. Small precipitates inside the grains remain homogeneously distributed, and a large volume fraction of the η′ phase exists. The VPPA–GMAW weld exhibits less tendency to soften; thus, VPPA–GMAW is appropriate for welding thick-plate aluminum alloys with a high production rate.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.D. Liu, Y.B. Yuan, C.B. Li, J.H. You, and X.M. Zhang, Influence of Cooling Rate After Homogenization on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Alloy 7050, Met. Mater. Int., 2012, 18(4), p 679–683
M. Grujicic, J.S. Snipes, R. Galgalikar, S. Ramaswami, and R. Yavari, Improved Gas Metal Arc Welding Multi-Physics Process Model and Its Application to MIL A46100 Armor-Grade Steel Butt-Welds, Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct., 2014, 10(2), p 176–210
M. Grujicic, S. Ramaswami, J.S. Snipes, C.F. Yen, B.A. Cheeseman, and J.S. Montgomery, Multi-Physics Modeling and Simulations of MIL A46100 Armor-Grade Martensitic Steel Gas Metal Arc Welding Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(10), p 2950–2969
M. Grujicic, A. Arakere, S. Ramaswami, J.S. Snipes, R. Yavari, C.F. Yen, B.A. Cheeseman, and J.S. Montgomery, Gas Metal Arc Welding Process Modeling and Prediction of Weld Microstructure in MIL A46100 Armor-Grade Martensitic Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(6), p 1541–1557
M. Grujicic, S. Ramaswami, J.S. Snipes, R. Yavari, A. Arakere, C.F. Yen, and B.A. Cheeseman, Computational Modeling of Microstructure Evolution in AISI1005 Steel During Gas Metal Arc Butt Welding, J. Mater. Eng. Perform, 2013, 22(5), p 1209–1222
V.I. Babushok, F.C. DeLucia, J.L. Gottfried, C.A. Munson, and A.W. Miziolek, Double Pulse Laser Ablation and Plasma: Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Signal Enhancement, Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc., 2006, 61(9), p 999–1014
J.Q. Su, T.W. Nelson, R. Mishra, and M. Mahoney, Microstructural Investigations of Friction Stir Welded 7050-T651 Aluminium, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(3), p 713–729
W.G. Essers and A.C. Liefkens, Plasma-MIG Welding Developed by Philips, Mach. Prod. Eng., 1972, 1(11), p 632–633
K. Ono, Z.J. Liu, T. Era, T. Uezono, T. Ueyama, M. Tanaka, and K. Nakata, Development of a Plasma MIG Welding System for Aluminium, Weld. Int., 2009, 23(11), p 805–809
H. Ton, Physical Properties of the Plasma-MIG Welding Arc, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 1975, 8(8), p 922–933
H. Terasaki and S.W. Simpson, Modelling of the GMAW System in Free Flight and Short Circuiting Transfer, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2005, 10(1), p 120–124
W.G. Essers and R. Walter, Heat Transfer and Penetration Mechanisms with GMA and Plasma-GMA Welding, Weld. J., 1981, 60(2), p 37–42
A.A. Resende, V.A. Ferraresi, A. Scotti, and J.C. Dutra, Influence of Welding Current in Plasma-MIG Weld Process on the Bead Weld Geometry and Wire Fusion Rate, Weld. Int., 2011, 25(12), p 910–916
H.T. Hong, Y.Q. Han, M.H. Du, and J.H. Tong, Investigation on Droplet Momentum in VPPA-GMAW Hybrid Welding of Aluminum Alloys, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016, 86(5–8), p 2301–2308
T. Yang, H.M. Gao, S.H. Zhang, and L. Wu, Interface Behavior of Copper and Steel by Plasma-MIG Hybrid Arc Welding, Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.), 2013, 26(3), p 328–332
S.J. Chen, F. Jiang, J.L. Zhang, N. Huang, and Y.M. Zhang, Principle of Weld Formation in Variable Polarity Keyhole Plasma Arc Transverse Welding of Aluminum Alloy, Trans. China. Weld. Inst., 2013, 34(4), p 1–6
Q.L. Zhang, C.L. Fan, S.B. Lin, and C.L. Yang, Novel Soft Variable Polarity Plasma Arc and Its Influence on Keyhole in Horizontal Welding of Aluminium Alloys, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2014, 19(6), p 493–499
N.J. Woodward, I.M. Richardson, and A. Thomas, Variable Polarity Plasma Arc Welding of 6.35 mm Aluminium Alloys: Parameter Development and Preliminary Analysis, Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2000, 5(1), p 21–25
Y.Q. Han, P. Zhao, M.H. Du, and Q.H. Yao, Numerical Simulation of Aluminum Alloys Variable Polarity Plasma Arc Welding Temperature Field, China J. Mech. Eng., 2012, 48(24), p 33–37
Y.Q. Han, H.T. Hong, L. Guo, and Q.H. Yao, Vertical Welding of Aluminum Alloy During Variable Polarity Plasma Arc Welding Process with AC-DC Mixing Output Current, Trans. China Weld. Inst., 2013, 34(9), p 59–62
S.C. Wang, F. Lefebvre, J.L. Yan, I. Sinclair, and M.J. Starink, VPPA Welds of Al-2024 Alloys: Analysis and Modeling of Local Microstructure and Strength, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 431(1–2), p 123–136
G.D. Janaki Ram, T.K. Mitra, V. Shankar, and S. Sundaresan, Microstructural Refinement Through Inoculation of Type 7020 Al-Zn-Mg Alloy Welds and Its Effect on Hot Cracking and Tensile Property, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 142(1), p 174–181
L.F. Mondolfo, Structure of the Aluminium: Magnesium, Zinc Alloys, Metall. Rev., 1971, 16(1), p 95–124
C.B. Fuller, M.W. Mahoney, M. Calabrese, and L. Micona, Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Naturally Aged 7050 and 7075 Al Friction Stir Welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(9), p 2233–2240
K. Stiller, P.J. Warren, V. Hansen, J. Angenete, and J. Gjønnes, Investigation of Precipitation in an Al-Zn-Mg Alloy After Two-Step Ageong Treatment at 100° and 150°C, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, 270(1), p 55–63
X.J. Jiang, J. Tafto, B. Noble, B. Holme, and G. Waterloo, Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Electron Diffraction Investigation on Low-Temperature Aging in Al-Zn-Mg Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, 31(2), p 339–348
P.N. Adler and R. Delasi, Calorimetric Studies of 7000 Series Aluminum Alloys: II. Comparison of 7075, 7050 and RX720 Alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1977, 8(7), p 1185–1190
J.L. Petty-Galis and R.D. Goolsby, Calorimetric Evaluation of the Effects of SiC Concentration on Precipitation Processes in SiC Particulate-reinforced 7091 Aluminium, J. Mater. Sci., 1989, 24(4), p 1439–1446
K.V. Jata, K.K. Sankaran, and J.J. Ruschau, Friction-Stir Welding Effects on Microstructure and Fatigue of Aluminum Alloy 7050-T7451, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, 31(9), p 2181–2192
X.F. Lei, D. Ying, Y.Y. Peng, Z.M. Yin, and G.F. Xu, Microstructure and Properties of TIG/FSW Welded Joints of a New Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr Alloy, Met. Mater. Int., 2013, 22(9), p 2723–2729
G.F. Xu, J. Qian, D. Xiao, Y. Deng, L.Y. Lu, and Z.M. Yin, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of TIG and FSW Joints of a New Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr Alloy, Met. Mater. Int., 2016, 25(4), p 1249–1256
X.Z. Li, V. Hansen, J. Gjønnes, and L.R. Wallenberg, HREM Study and Structure Modeling of the η′ Phase, the Hardening Precipitates in Commercial Al-Zn-Mg Alloys, Acta Mater., 1999, 47(9), p 2651–2659
J.K. Park and A.J. Ardell, Microstructures of the Commercial 7075 Al Alloy in the T651 and T7 Tempers, Metall. Trans. A, 1983, 14(10), p 1957–1965
R.N. Shenoy and J.M. Howe, A Differential Scanning Calorimetric Study of a Weldalite Type Alloy, Scr. Metall. Mater., 1995, 33(4), p 651–656
S.C. Wu, X. Yu, R.Z. Zuo, W.H. Zhang, H.L. Xie, and J.Z. Jiang, Porosity, Element Loss, and Strength Model on Softening Behavior of Hybrid Laser Arc Welded Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy with Synchrotron Radiation Analysis, Weld. J., 2013, 92(3), p 64–71
P.K. Ghosh and V. Sharma, Chemical Composition and Microstructure in Pulsed MIG Welded Al-Zn-Mg Alloy, Mater. Trans., 1991, 32(2), p 145–150
A. Deschamps and Y. Brechet, Influence of Predeformation and Ageing of an Al-Zn-Mg Alloy—II. Modeling of precipitation Kinetics and Yield Stress, Acta Mater., 1999, 47(1), p 293–305
R. Labusch, A Statistical Theory of Solid Solution Hardening, Phys. Stat. Sol., 1970, 41(2), p 659–669
J.D. Hunt, Steady State Columnar and Equiaxed Growth of Dendrites and Eutectic, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, 65(1), p 75–83
P. Pan, J.J. Liu, and J. Ma, Influence of Welding Parameters of Pulse TIG on Weld Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Aluminum Alloys, J. Rocket Propuls., 2013, 39(1), p 52–57
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51665044). The authors would also like to acknowledge financial supports from the Science and Technology Key Programs of Inner Mongolia (Grant No. 2016-ZD08), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (Grant No. 2015MS0504), and the Open Project for Key Basic Research of Inner Mongolia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, H., Han, Y., Yao, Q. et al. Microstructural Investigation of VPPA–GMAW Welded 7A52 Aluminum Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 5571–5580 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3450-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3450-3