Abstract
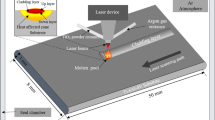
In this study, particle and short fiber-reinforced titanium matrix composite coatings are prepared via laser in situ technique using (0.5 and 50 μm) TiB2 and Ti powder as cladding materials. The microstructure and properties of the composite coatings are studied, and the changing mechanism of the microstructure is discussed. The results reveal that particle agglomeration is prone to appear with using fine TiB2 particles. Decomposition of the particles preferentially occurs with using coarse TiB2 particles. The cracks and pores on the surface of the coating are formed at a lower laser energy density. With the increase in the laser energy density, cracking on the surface of the coating diminishes, but the coating exhibits depression behavior. The depression extent of the coating using fine TiB2 particle as the reinforcement is much less than that of the coating using coarse TiB2 particle. Moreover, the size of the aggregate and the tendency of cracking can be reduced with the increase in Ti addition. Meanwhile, short TiB fiber bundles are formed by the diffusion mechanism of rod aggregate, and randomly oriented TiB short fibers are formed mainly by the dissolution–precipitation mechanism of fine TiB2 particles. Moreover, the growth of short TiB fibers can be in an alternating manner between B27 and Bf structures. The micro-hardness and wear resistance of the coatings are evidently higher than that of the titanium alloy substrate. The wear resistance of the large size TiB2 coating is higher than that of the small size TiB2 coating under the condition of low load.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. Huang, L. Geng, and H.X. Peng, Microstructurally Inhomogeneous Composites: Is a Homogeneous Reinforcement Distribution Optimal, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2015, 71, p 93-168
A.P.I. Popoola, L. Phume, S. Pityana, and V.S. Aigbodion, In-situ Formation of Laser Ti6Al4V-TiB Composite Coatings on Ti6Al4V Alloy for Biomedical Application, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2016, 285, p 161-170
B.J. Choi, I.Y. Kim, Y.Z. Lee, and Y.J. Kim, Microstructure and Friction/Wear Behavior of (TiB + TiC) Particulate-Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composites, Wear, 2014, 318, p 68-77
J. Li, X. Luo, and G.J. Li, Effect of Y2O3 on the Sliding Wear Resistance of TiB/TiC-Reinforced Composite Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding, Wear, 2014, 310, p 72-82
T. Prater, A. Strauss, G. Cook, B. Gibson, and C. Cox, A Comparative Evaluation of the Wear Resistance of Various Tool Materials in Friction Stir Welding of Metal Matrix Composites, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 1807-1813
K.C. Xie, C.H. Jiang, and W.J. Lu, The Influence of Shot Peening on the Surface Properties of (TiB + TiC)/Ti-6Al-4V, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 280, p 981-988
P. Abachi, A. Masoudi, and K. Purazrang, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of SiCP/QE22 Magnesium Alloy Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 435-436, p 653-657
I.Y. Kim, B.J. Choi, Y.J. Kim, and Y.Z. Lee, Friction and Wear Behavior of Titanium Matrix (TiB + TiC) Composites, Wear, 2011, 271, p 1962-1965
R. Dunja, B.D. Narendra, and G. Janez, Laser Coating of Aluminum Alloy EN AW 6082-T651 with TiB2 and TiC: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 282, p 914-922
S. Cygan, L. Jaworska, P. Putyra, W. Ratuszek, J. Cyboron, and P. Klimczyk, Thermal Stability and Coefficient of Friction of the Diamond Composites with the Titanium Compound Bonding Phase, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26, p 2593-2598
L.K. Sylvie, W. Michael, H. Nadia, C. Limei, M. Leo, and B. Frederic, Interfaces and Defects in a Successfully Hot-Rolled Steel-Based Composite Fe-TiB2, Acta Mater., 2015, 98, p 297-305
H. Zhang, H. Springer, R. Aparicio-Fernandez, and D. Raabe, Improving the Mechanical Properties of Fe-TiB2 High Modulus Steels Through Controlled Solidification Processes, Acta Mater., 2016, 118, p 187-195
M.K. Alam, A. Edrisy, J. Urbanic, and J. Pineault, Microhardness and Stress Analysis of Laser-Cladded AISI, 420 Martensitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26, p 1076-1084
B.C. Zhang, G.J. Bi, S.R. Nai, C.N. Sun, and J. Wei, Microhardness and Microstructure Evolution of TiB2 Reinforced Inconel 625/TiB2 Composite Produced by Selective Laser Melting, Opt. Laser Technol., 2016, 80, p 186-195
X.Z. Zhan, Y. Liu, W.M. Ou, C. Gu, and Y.H. Wei, The Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Multi-Layer Laser-MIG Hybrid Welding for Fe36Ni Invar Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p p4948-p4957
P. Nie, A. Ojooa, and Z.G. Li, Modeling Analysis of Laser Cladding of a Nickel-Based Superalloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 258, p 1048-1059
F.C.R. Hernandez, A.O. Okonkwo, V. Kadekar, T. Metz, and N. Badi, Lasercladding: The Alternative for Field Thermite Welds Life Extension, Mater. Des., 2016, 111, p 165-173
K.Y. Luo, X. Jing, J. Sheng, G.F. Sun, Z. Yan, and J.Z. Lu, Characterization and Analyses on Micro-Hardness, Residual Stress and Microstructure in Lasercladding Coating of 316L Stainless Steel Subjected to Massive LSP Treatment, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 673, p 158-169
B. Liu and S.Y. Dong, Stress Evaluation of Lasercladding Coating with Critically Refracted Longitudinal Wave Based on Cross Correlation Function, Appl. Acoust., 2016, 101, p 98-103
F. Parisa and K. Radovan, An Experimental–Numerical Investigation of Heat Distribution and Stressfield in Single- and Multi-Track Lasercladding by a High-Power Direct Diode Laser, Opt. Laser Technol., 2014, 63, p 154-168
A.S. Rogachev, S.G. Vadchenko, F. Baras, O. Politano, S. Rouvimov, N.V. Sachkova, and A.S. Mukasyan, Structure Evolution and Reactionmechanism in the Ni/Al Reactive Multilayer Nanofoils, Acta Mater., 2014, 66, p 86-96
V.C. Roman and C. Stefano, Calculation of Solubility in Titanium Alloys from First Principles, Acta Mater., 2009, 57, p 5314-5323
K. Kawabata, E. Sato, and K. Kuribayashi, High Temperature Deformation with Diffusional and Plastic Accommodation in Ti/TiB Whisker-Reinforce In situ Composites, Acta Mater., 2003, 51, p 1909-1922
Y.H. Lin, J.H. Yao, Y.P. Lei, H.G. Fu, and L. Wang, Microstructure and Properties of TiB2-TiB Reinforced Titanium Matrix Composite Coating by Laser Cladding, Opt. Laser Eng., 2016, 86, p 216-227
C.J. Zhang, F.T. Kong, L.J. Xu, E.T. Zhao, S.L. Xiao, Y.Y. Chen, N.J. Deng, W. Ge, and G.J. Xu, Temperature Dependence of Tensile Properties and Fracture Behavior of as Rolled TiB/Ti Composite Sheet, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 556, p 962-969
B.J. Kooi, Y.T. Pei, and JThMD Hosson, The Evolution of Microstructure in a Laser Clad TiB-Ti Composite Coating, Acta Mater., 2003, 51, p 831-845
J. Du, A.P. Sanders, V. Jindal, and K.S.R. Chandran, Rapid In situ Formation and Densification of Titanium Boride (TiB) Nano-Ceramic via Transient Liquid Phase in Electric Field Activated Sintering, Scr. Mater., 2016, 123, p 95-99
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful for financial supports from National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFB1103601), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51705464) and Post-Doctor Research Fund of China (No. 2017M610376).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Yao, J., Wang, L. et al. Effects of TiB2 Particle and Short Fiber Sizes on the Microstructure and Properties of TiB2-Reinforced Composite Coatings. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 1876–1889 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3291-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3291-0