Abstract
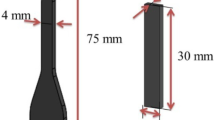
Service lifetime of ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber at room temperature (25 °C) was estimated based on accelerated aging tests. The study followed sealing stress loss on compressed cylinder samples by compression stress relaxation methods. The results showed that the cylinder samples of EPDM can quickly reach the physical relaxation equilibrium by using the over-compression method. The non-Arrhenius behavior occurred at the lowest aging temperature. A significant linear relationship was observed between compression set values and normalized stress decay results, and the relationship was not related to the ambient temperature of aging. It was estimated that the sealing stress loss in view of practical application would occur after around 86.8 years at 25 °C. The estimations at 25 °C based on the non-Arrhenius behavior were in agreement with compression set data from storage aging tests in natural environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Tomohiro, H. Toshio, Y. Yukihiro, K. Tetsuya, and T. Sekiya, Thermal Degradation of Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene Rubber and Ethylene Propylene Diene Terpolymer, Mater. Des., 2012, 42, p 147–155
G.J. Lake, Fatigue and Fracture of Elastomers, Rubber Chem. Technol., 1997, 68, p 435–460
K.T. Gillen, M. Celina, R. Bernstein, and M. Shedd, Lifetime Predictions of EPR Materials Using the Wear-Out Approach, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2006, 91, p 3197–3207
S.W. Chang and S.P. Hyun, Useful Lifetime Prediction of Rubber Component, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2011, 18, p 1645–1651
K.T. Gillen, R. Bernstein, R.L. Clough, and M. Celina, Lifetime Predictions for Semicrystalline Materials: I. Mechanical Properties and Oxygen Consumption Measurements on EPR Materials, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2006, 91, p 2146–2156
K.T. Gillen, M. Celina, and M.R. Keenan, Methods for Predicting more Confident Lifetimes of Seals in Air Environments, Rubber Chem. Technol., 2000, 73, p 265–283
P. Richters, Initiation Process in the Oxidation of Polypropylene, Macromolecules, 1970, 3, p 262–264
F. Gugumus, Effect of Temperature on the Lifetime of Stabilized and Unstabilized PP Films, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1999, 63, p 41–52
P. Gijsman, J. Hennekens, and J. Vincent, The Influence of Temperature and Catalyst Residues on the Degradation of Unstabilized Polypropylene, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1993, 39, p 271–277
J. Wise, K.T. Gillen, and R.L. Clough, An Ultrasensitive Technique for Testing the Arrhenius Extrapolation Assumption for Thermallyaged Elastomers, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1995, 49, p 403–418
K.T. Gillen, M. Celina, R.L. Clough, and J. Wise, Extrapolation of Accelerated Aging Data-Arrhenius or Erroneous, Trends Polym. Sci., 1997, 5, p 250–257
K.T. Gillen and M. Celina, The Wear-Out Approach for Predicting the Remaining Lifetime of Materials, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2001, 71, p 15–30
M. Celina, J. Wise, D.K. Ottesen, K.T. Gillen, and R.L. Clough, Oxidation Profiles of Thermally Aged Neoprene, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2000, 68, p 171–184
M. Celina, K.T. Gillen, A.C. Graham, R.A. Assink, and L.M. Minier, Thermal Degradation Studies of a Polyurethane Propellant Binder, Rubber Chem. Technol., 2000, 73, p 678–693
R. Bernstein and K.T. Gillen, Predicting the Lifetime of Fluorosilicone o-Rings, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2009, 94, p 2107–2113
K.T. Gillen, R. Bernstein, and M.H. Wilson, Predicting and Confirming the Lifetime of o-Rings, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2005, 87, p 257–270
K.T. Gillen, M. Celina, and R. Bernstein, Validation of Improved Methods for Predicting Long-Term Elastomeric Seal Lifetimes from Compression Stress-Relaxation and Oxygen Cconsumption Techniques, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2003, 82, p 25–35
J.R. Cho, K.C. Han, J.S. Kim, S.B. Lee, and O.K. Lim, Fatigue Life Prediction and Optimum Topology Design of EPDM Weather Strip, Finite Elem. Anal. Des., 2012, 60, p 57–63
F. Le Lay, Study on the Lifetime of EPDM Seals in Nuclear-Powered Vessels, Radiat. Phys. Chem., 2013, 84, p 210–217
A. Kommling, M. Jaunich, and D. Wolff, Effects of Heterogeneous Aging in Compressed HNBR and EPDM O-Ring Seals, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2016, 126, p 39–46
T. Cui, Y.J. Chao, and J.W. Van Zee, Stress Relaxation Behavior of EPDM Seals in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Environment, Int. J Hydrog. Energy, 2012, 37, p 13478–13483
ASTM Standard 6147-97, Standard Test Method for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomer—Determination of Force Decay (Stress Relaxation) in Compression
GB/T 7759-1996, Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic—Determination of Compression Set at Ambient Elevated or Low Temperatures
A.V. Tobolsky, Properties and Structure of Polymers, Wiley, New York, 1960
J.D. Ferry, Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 2nd ed., Wiley, New York, 1970
K. Murakami and K. Ono, Chemorheology of Polymers, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1979
J.G. Curro and P. Pincus, A Theoretical Basis for Viscoelastic Relaxation of Elastomers in the Long-Term Limit, Macromolecules, 1983, 16, p 559–562
S. Ronan, T. Alshuth, S. Jerrams, and N. Murphy, Long-Term Stress Relaxation Prediction for Elastomers Using the Time–Temperature Superposition Method, Mater. Des., 2007, 28, p 1513–1523
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation Grant No. ZR2016BQ15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Li, X., Xu, L. et al. Service Lifetime Estimation of EPDM Rubber Based on Accelerated Aging Tests. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 1735–1740 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2519-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2519-8