Abstract
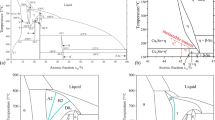
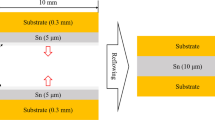
Since manufacturing is transitioning into Pb-free solder development for electronic assembly and packaging, consumer demands for more compact electronics have increased the importance of reliability issues brought about by the increased density of circuitry. Therefore, the role of alloying elements that can be added to common Pb-free solders such as Sn-Cu or Sn-Ag-Cu alloys in enhancing the properties and performance of the solder becomes important. Microstructural analysis along with direct observation in situ synchrotron radiography were used to study the effect of Ni, Zn, Au, In and Sb on the development of phases in Sn-10 wt.%Cu (Sn-10Cu). It was found that adding Ni and Zn to a Sn-10Cu alloy had the greatest impact on the microstructure with the Cu3Sn phase completely absent after these additions were made. Additions of Au and In also resulted in a reduction in the amount of Cu3Sn; however, the effect was not as pronounced. Removing the Cu3Sn phase from Sn-Cu Pb-free solder alloys is a possible approach for the design of more desirable microstructures that translate to better performance in modern electronic packaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Gourlay and B. Arfaei, JOM 71, 131 (2019).
K.N. Reeve, J.R. Holaday, S.M. Choquette, I.E. Anderson, and C.A. Handwerker, J. Phase Equilib. 37, 369 (2016).
M. Fazal, N. Liyana, S. Rubaiee, and A. Anas, Meas. 134, 897 (2019).
S. Cheng, C.-M. Huang, and M. Pecht, Microelec. Rel. 75, 77 (2017).
W.R. Osório, L.C. Peixoto, L.R. Garcia, N. Mangelinck-Noël, and A. Garcia, J. Alloys Compd. 572, 97 (2013).
S. Chen, W. Zhou, and P. Wu, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 3920 (2015).
C.-Y. Yu and J.-G. Duh, Scr. Mater. 65, 783 (2011).
Y. Leong, A. Haseeb, H. Nishikawa, and O. Mokhtari, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 11914 (2019).
B. Chen and G. Li, Thin Solid Films 462, 395 (2004).
N. Wade, K. Wu, J. Kunii, S. Yamada, and K. Miyahara, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1228 (2001).
G. Li, B. Chen, X. Shi, S.C. Wong, and Z. Wang, Thin Solid Films 504, 421 (2006).
J. Kivilahti, Helsinki University of Technology (1996).
L. Xu and J.H. Pang, Thin Solid Films 504, 362 (2006).
M. Amagai, Microelectr. Rel. 48, 1 (2008).
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, and M. Paulasto-Kröckel, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 68, 1 (2010).
C. Yang, F. Song, and S. R. Lee, in 2011 IEEE 61st Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC) (IEEE, 2011).
K. Nogita, Intermetallics 18, 145 (2010).
K. Nogita, C. Gourlay, and T. Nishimura, JOM 61, 45 (2009).
K. Nogita and T. Nishimura, Scr. Mater. 59, 191 (2008).
K. Sweatman and T. Nishimura, IPC Printed Circuits Expo, APEX and the Desidners Summit. Osaka, Japan, 1 (2006).
G. Henshall et al., in Proceedings SMTA International (2008).
Y.-L. Tseng, Y.-C. Chang, and C.-C. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 581 (2015).
S.-W. Chen, Y.-K. Chen, H.-J. Wu, Y.-C. Huang, and C.-M. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 39, 2418 (2010).
C. Du, X. Wang, and S. Tian, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 455 (2018).
C.-H. Wang and S.-W. Chen, J. Mater. Res. 22, 3404 (2007).
Z. Lai, X. Kong, Q. You, and X. Cao, Microelectr. Rel. 68, 69 (2017).
Y.-C. Huang and S.-W. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 40, 62 (2011).
M.N. Bashir, A. Haseeb, A.Z.M.S. Rahman, and M. Fazal, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 1129 (2016).
J. Jiang, S. Tsao, T. O’Sullivan, M. Razeghi, and G.J. Brown, Infra. Phys. Technol. 45, 143 (2004).
T. Ventura, C.M. Gourlay, K. Nogita, T. Nishimura, M. Rappaz, and A.K. Dahle, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 32 (2008).
S.U. Mehreen, K. Nogita, S. McDonald, H. Yasuda, and D. StJohn, J. Alloys Compd. 766, 1003 (2018).
J. Chen, Y.-S. Lai, C.-Y. Ren, and D.-J. Huang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 081901 (2008).
T. Laurila, J. Hurtig, V. Vuorinen, and J.K. Kivilahti, Microelectr. Rel. 49, 242 (2009).
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, and J.K. Kivilahti, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 49, 1 (2005).
Y. Wang, Y. Lin, C. Tu, and C. Kao, J. Alloys Compd. 478, 121 (2009).
F. Wang, X. Ma, and Y. Qian, Scr. Mater. 53, 699 (2005).
S.K. Kang, D.-Y. Shih, D. Leonard, D.W. Henderson, T. Gosselin, S.-I. Cho, J. Yu, and W.K. Choi, JOM 56, 34 (2004).
H. Yasuda, T. Nagira, M. Yoshiya, N. Nakatsuka, A. Sugiyama, K. Uesugi, and K. Umetani, ISIJ Int. 51, 402 (2011).
H. Yasuda, T. Nagira, M. Yoshiya, M. Uesugi, N. Nakatsuka, M. Kiire, A. Sugiyama, K. Uesugi, and K. Umetani, in IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng (IOP Publishing, 2012), p. 012084.
C.-H. Lin, S.-W. Chen, and C.-H. Wang, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 907 (2002).
C.-H. Wang and S.-W. Chen, Acta Mater. 54, 247 (2006).
S.-W. Chen and C.-A. Chang, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1071 (2004).
Y.-W. Yen, C.-Y. Lee, M.-H. Kuo, K.-S. Chao, and K.-D. Chen, Int. J. Mater. Res. 100, 672 (2009).
S. U. Mehreen, K. Nogita, S. McDonald, and D. StJohn, in IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng (IOP Publishing, 2019), p. 012009.
D. StJohn, Acta Metall. 38, 631 (1990).
H.W. Kerr and W. Kurz, Int. Mater. Rev. 41, 129 (1996).
W. Zhai and B. Wei, Mater. Lett. 108, 145 (2013).
Z. Xuan, F. Mao, Z. Cao, T. Wang, and L. Zou, J. Alloys Compd. 721, 126 (2017).
B. Gao, E. Guo, X. Meng, S. Nie, H. Liang, Z. Cao, and T. Wang, Mater. Charact. 158, 109969 (2019).
K. Nogita, C. Gourlay, S. McDonald, Y. Wu, J. Read, and Q. Gu, Scr. Mater. 65, 922 (2011).
F. Gao, T. Takemoto, and H. Nishikawa, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 420, 39 (2006).
Y. Wang, C. Chang, and C. Kao, J. Alloys Compd. 478, L1 (2009).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the University of Queensland (UQ)-Nihon Superior (NS) collaboration research project and ARC Linkage Project (LP14010048) and ARC Discovery Project (DP200101949). Real-time observation experiments were performed at SPring-8 BL20XU (2016B1319, 2019A1149 and 2019B1185). The observations in SPring-8 were supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (S) (No. 17H06155), JSPS, Japan. We also acknowledge travel funding (AS/IA191/14935) provided by the International Synchrotron Access Program (ISAP) managed by the Australian Synchrotron, part of ANSTO, and funded by the Australian Government. SEM imaging and EDS mapping were performed at the Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis (CMM), The University of Queensland. Syeda U. Mehreen is financially supported by an Australian Postgraduate Award (APA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (MP4 60042 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (MP4 16062 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehreen, S.U., Nogita, K., McDonald, S.D. et al. Effect of Ni, Zn, Au, Sb and In on the Suppression of the Cu3Sn Phase in Sn-10 wt.%Cu Alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 881–892 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08709-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08709-3