Abstract
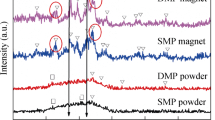
The ferromagnetic MnAl-C powders were prepared by using a one-step solid-state reaction method starting from Mn micro-/nano-particles and Al/C micropowders. The bulk MnAl-C with enhanced coercivity was prepared by high-pressure compaction of these MnAl-C powders. The grain size of the τ-phase was significantly reduced during high-pressure compaction, which may also result in a decomposition of the τ-MnAl. Carbon element stabilizes the τ-phase under both ambient and high pressures. The annealing temperature and time intervals are crucial for the preparation of high purity τ-phase samples. The MnAl-C with smaller particle size were produced from Mn nanoparticles. In comparison with the samples prepared from Mn micropowders, the product prepared from Mn nanoparticles shows lower purity, owing to the surface oxidation of the precursor nanoparticles. After high pressure compaction, the coercivities of the bulk MnAl and MnAl-C were increased from 0.05 T and 0.08 T to 0.39 T and 0.22 T, respectively. The room temperature magnetization of the MnAl-C sample at 4 T reached up to 95 Am2/kg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Zeng, I. Baker, J.B. Cui, and Z.C. Yan, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 308, 214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.05.032.
J.M.D. Coey, Scr. Mater. 67, 524 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.04.036.
J. Cui, M. Kramer, L. Zhou, F. Liu, A. Gabay, G. Hadjipanayis, B. Balasubramanian, and D. Sellmyer, Acta Mater. 158, 118 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.07.049.
G. Hindrichs, Z. Anorg. Chem. 59, 414 (1908). https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19080590136.
H. Kono, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 13, 1444 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.13.1444.
A.J.J. Koch, P. Hokkeling, M.G.V.D. Steeg, and K.J.D.E. Vos, J. Appl. Phys. 31, 75S (1960). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1984610.
R.H. Willens, IEEE Trans. Magn. 16, 5 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.1980.1060667.
J.H. Huang and P.C. Kuo, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 20, 292 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-716X(93)90550-C.
Y. Sakka, M. Nakamura, and K. Hoshimoto, J. Mater. Sci. 24, 4331 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544507.
J. Thielsch, F. Bittner, and T.G. Woodcock, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.11.045.
P.Z. Si, H.D. Qian, C.J. Choi, J.H. Park, and H.L. Ge, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 540 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.11.094.
R. Madugundo, O. Koylu-Alkan, and G.C. Hadjipanayis, AIP Adv. 6, 056009 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4943242.
W. Lu, J.C. Niu, T.L. Wang, K.D. Xia, Z. Xiang, Y.M. Song, H. Zhang, S. Yoshimura, and H. Saito, J. Alloys Compd. 675, 163 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.098.
T. Ohtani, N. Kato, S. Kojima, Y. Sakamoto, I. Konno, M. Tsukahara, and T. Kubo, IEEE Trans. Mag. 13, 1328 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.1977.1059574.
P.Z. Si, E. Brück, Z.D. Zhang, O. Tegus, W.S. Zhang, K.H.J. Buschow, and J.C.P. Klaasse, Mater. Res. Bull. 40, 29 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2004.09.010.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Future Materials Discovery Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2016M3D1A1027835).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, HD., Si, PZ., Park, J. et al. Structure and Magnetic Properties of Nanocrystalline MnAl-C Prepared by Solid-State Reaction and High-Pressure Compaction. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 1395–1399 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-06848-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-06848-2